Question
b Hey Chegg, the image above is Table 21-3 for a case problem that I need your help with. Case Problem National Petrochemicals National Petrochemicals
b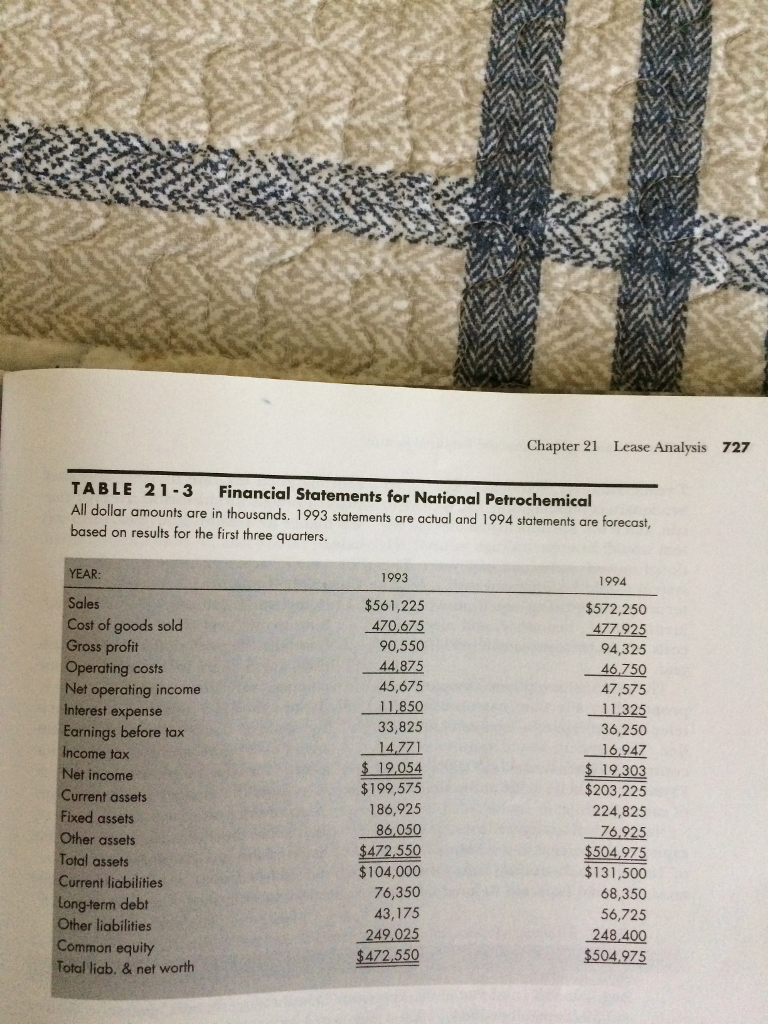
Hey Chegg, the image above is Table 21-3 for a case problem that I need your help with.
Case Problem
National Petrochemicals
National Petrochemicals was a producer of various chemicals, primarily based on petroleum. Security analysts had been critical of National for several reasons. First and foremost, return on equity was low and declining. National had a profit margin on sales similar to the rest of the industry, but National had a lower total asset turnover ratio and used less financial leverage than the industry. While asset turnover and profit margin had improved slightly in the past year, operating costs had increased faster than sales and total asset turnover had declined. None of these trends seemed healthy. National's operating results for 1993 and 1994 are shown in Table 21-3. For comparison, average ratios for a sample of six similar companies were as follows:
| Ratio | 1993 Competitor Averages |
| Sales/Total Assets | 1.3 |
| Net Income/Sales | 4.00% |
| Net Income/Total Assets | 5.20% |
| Debt/Total Assets | 50.53% |
| Return on Equity | 11.34% |
Profitability problems were on the mind of the controller, Irene Watson, when she began to analyze two proposals for a new telephone system for the company's headquarters. There was no question about the need for a new system, but the choices available would affect the company's financial position differently. The impact of a communication system was small compared to something like a new factory. But Watson knew that performance would be improved by doing a lot of small things right, not by one or two dramatic actions. She was, therefore, determined to make a communication system decision that would move the company in the right direction. One system consisted of a central telephone switch located on National's premises. This switch would cost $4,832,000, including installation. A parts inventory would cost $223,680 and would have no salvage value. Maintenance was estimated at $343,267 a year. The system would be placed in service for tax purposes on December 31, 1994, and would have a depreciation life of 7 years. However, National's lease on its headquarters building only had 5 years to run, and it was not anticipated that the system would have any salvage value if National moved at the end of 5 years. The system would be financed with a 5-year term loan requiring equal annual payments. Space, insurance, and electricity costs would be approximately $110,000 a year. The regional telephone company had proposed an alternate system, using the telephone company's local switching office. That system would require service contract payments of $1,800,000 a year. Payments would be made at the beginning of each month. National had weighted average cost of capital of 13 percent and a borrowing rate of 10 percent. Including state and local taxes, National expected to have a 40% marginal tax rate in 1994 and later years although the historical average rate was higher for reasons not relevant to this case.
Questions:
1. Assume the 1995 financial statement is the same as the pro forma 1994 statement, except for tax rates, and the impact of the new telephone system.
a. Show the financial statement impacts of the purchase
b. Show the financial statement impacts of the service contract.
2. Should National purchase the equipment or enter into a service contract?
Please answer both questions. Do not leave any questions unanswered. Please show your work and explain thoroughly for each question if necessary. The more detailed your work is or explanation is, it will really help me to understand where I went wrong. It is important for me. Thanks in advance.
Chapter 21 Lease Analysis 727 TABLE 21-3 Financial Statements for National Petrochemical All dollar amounts are in thousands. 1993 statements are actual and 1994 statements are forecast based on results for the first three quarters 993 1994 Sales $561,225 $572,250 Cost of goods sold 470,675 477925 Gross profit 90,550 94,325 44,875 Operating costs 46.750 45,675 Net operating income 47,575 850 nterest expense 325 33,825 36,250 Earnings before tax 4,771 6,947 ncome tax 9,054 9,303 Net income $199,575 $203,225 Current assets 186,925 224,825 Fixed assets 6,050 76,925 her assets 472,550 504,975 Total assets $104,000 $131,500 Current liabilities 76,350 68,350 Long-term debt 43,175 56,725 Other liabilities 248,400 49,025 Common equity $504975 472.550 Total liab. & net worth
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


