Question
(b) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (3+c)u +(4+uu tru =0 (2+x)ux +(5+ y)uy + 3xu = 0 (6+x)ux +(2+ y)uy + (5 + x)u =
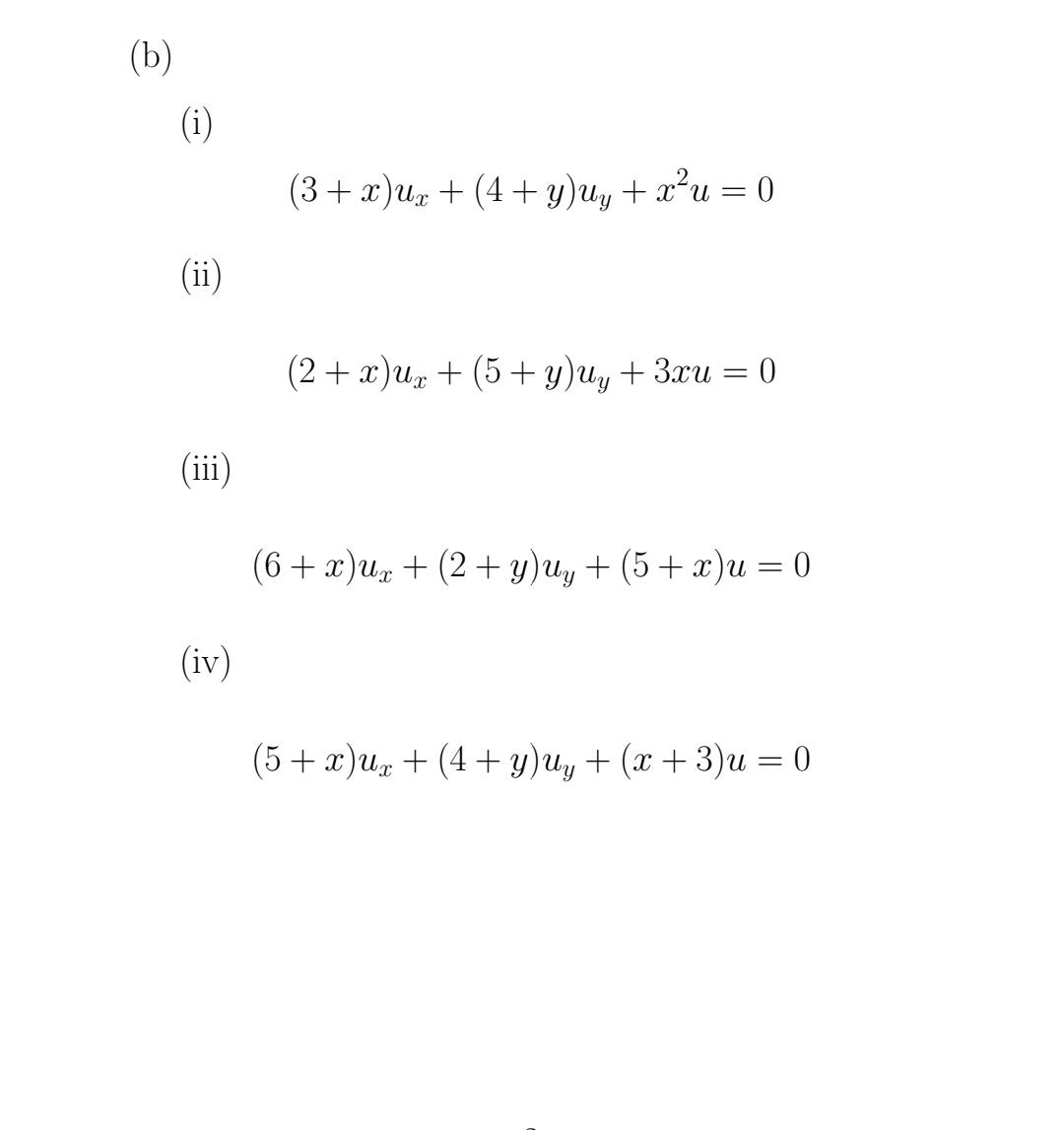
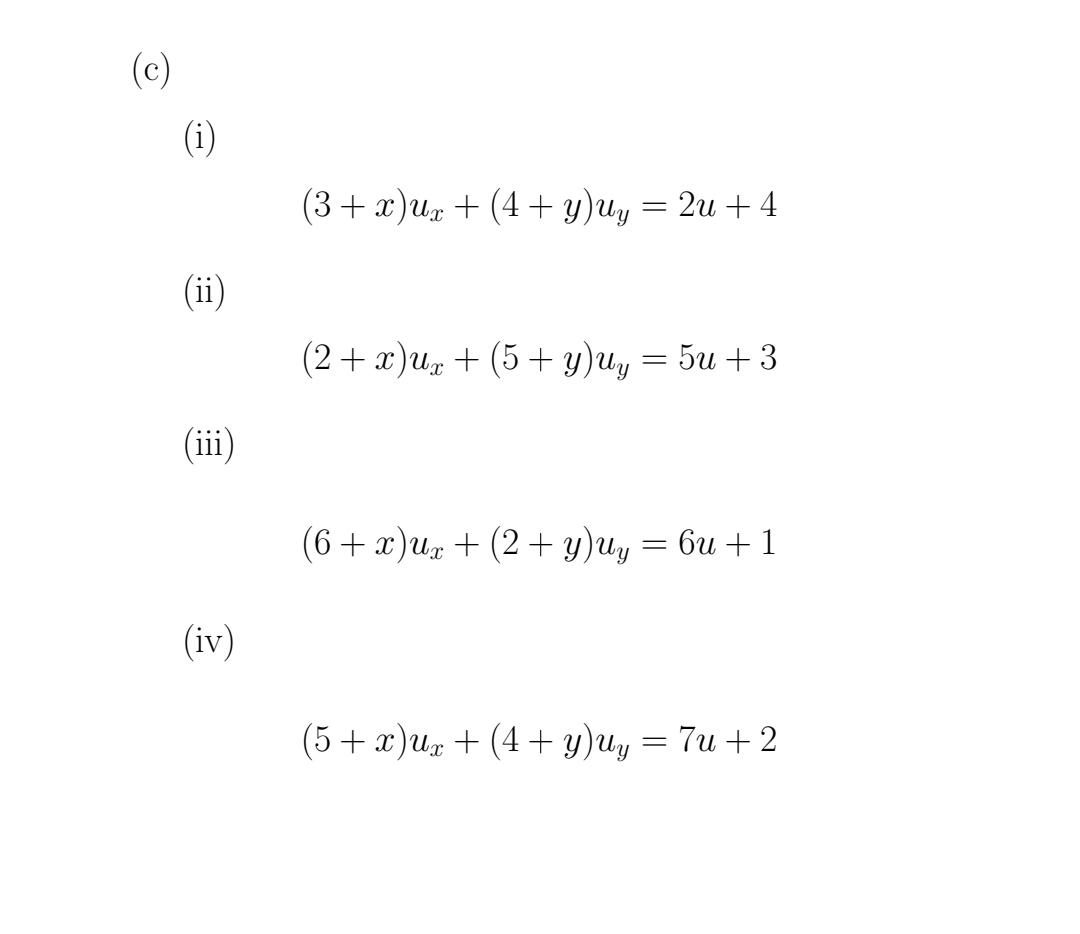
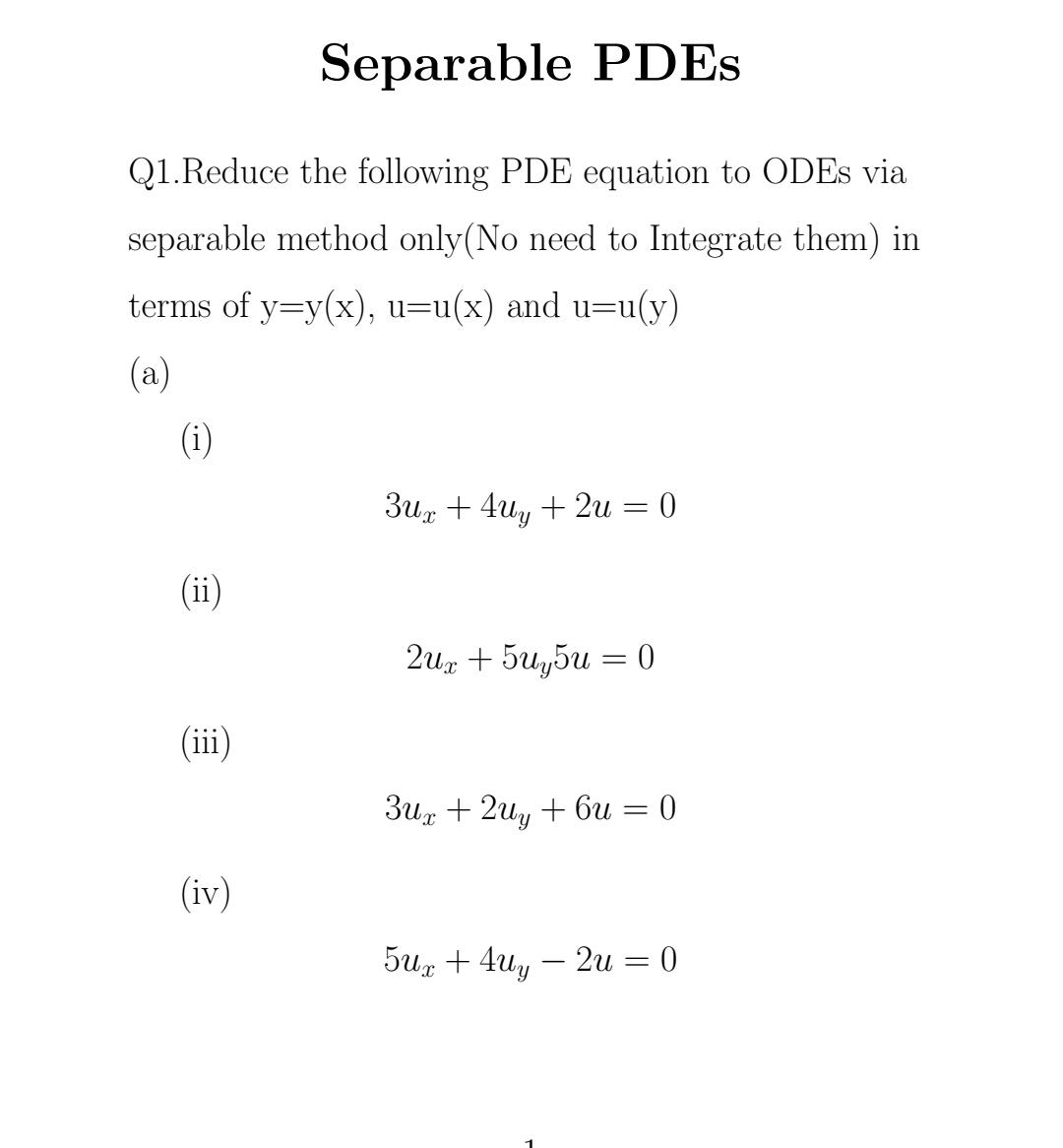
(b) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (3+c)u +(4+uu tru =0 (2+x)ux +(5+ y)uy + 3xu = 0 (6+x)ux +(2+ y)uy + (5 + x)u = 0 (5+x)ux +(4+ y)uy + (x+3)u = 0 (c) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (3+x)+(4+y) uy = = 2u +4 (2+x)ux + (5+ y)uy = 5u +3 (6+x)ux +(2+ y)uy = 6u + 1 (5+x)ux +(4+ y)uy = 7u + 2 Separable PDES Q1.Reduce the following PDE equation to ODEs via separable method only (No need to Integrate them) in terms of y=y(x), u=u(x) and u=u(y) (a) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) 3ux + 4y +2u = 0 2ux + 5uy5u = 0 3ux+2uy +6u = 0 5ux + 4uy - 2u = 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
To classify the given secondorder partial differential equations we need to analyze their characteri...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get StartedRecommended Textbook for
Discrete and Combinatorial Mathematics An Applied Introduction
Authors: Ralph P. Grimaldi
5th edition
201726343, 978-0201726343
Students also viewed these Physics questions
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
View Answer in SolutionInn App



