Question
b) Suppose that the risk-free rate is 10% p.a. with continuous compounding and that the dividend yield on a stock index is 4% per annum.
b) Suppose that the risk-free rate is 10% p.a. with continuous compounding and that the dividend yield on a stock index is 4% per annum. The index is standing at 400, and the futures price for a contract deliverable in 4 months is 405. Identify the arbitrage opportunity and clearly demonstrate how an investor can profit from this situation.
d) In option valuation, explain the principle of risk-neutral valuation.
e) A three-month European put option on a non-dividend paying stock has the following features: strike price of 50 when the current price is 50, risk free rate is 10% per annum, and the volatility is 30% per annum. Write down the Black-Scholes option pricing formula, derive d1 and d2 and calculate the price of the put given that N(-d1) = 0.4045 and N(-d2) = 0.4634
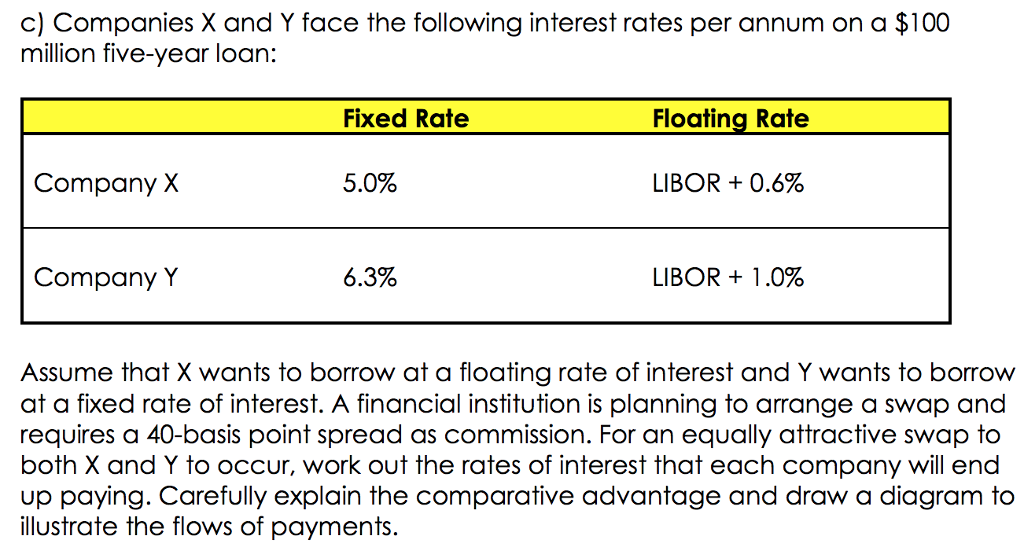
c) Companies X and Y face the following interest rates per annum on a $100 million five-year loar: Fixed Rate Floating Rate Company X 50% LIBOR + 0.6% Company Y 63% LIBOR + 1.0% Assume that X wants to borrow at a floating rate of interest and Y wants to borrow at a fixed rate of interest. A financial institution is planning to arrange a swap and requires a 40-basis point spread as commission. For an equally attractive swap to both X and Y to occur, work out the rates of interest that each company will end up paying. Carefully explain the comparative advantage and draw a diagram to illustrate the flows of payments
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


