Specialty Products produces items that are of interest to a more upscale market. Their products include scented soaps, shampoos, and balms. In response to
![[Yes] Our materials supplier, which was our only materials supplier, had a temporary outage that lasted through June and at t](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2021/04/60816d9574e01_1619094928216.jpg)
![[Yes] December The plant started back up in early December and the maintenance performed in November appears to have resolved](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2021/04/60816d95aa546_1619094928440.jpg)
![May The input error from April reversed. [No Effect] [No Effect] Our materials supplier, which was our only materials supplie](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2021/04/60816d95b9c1a_1619094928610.jpg)
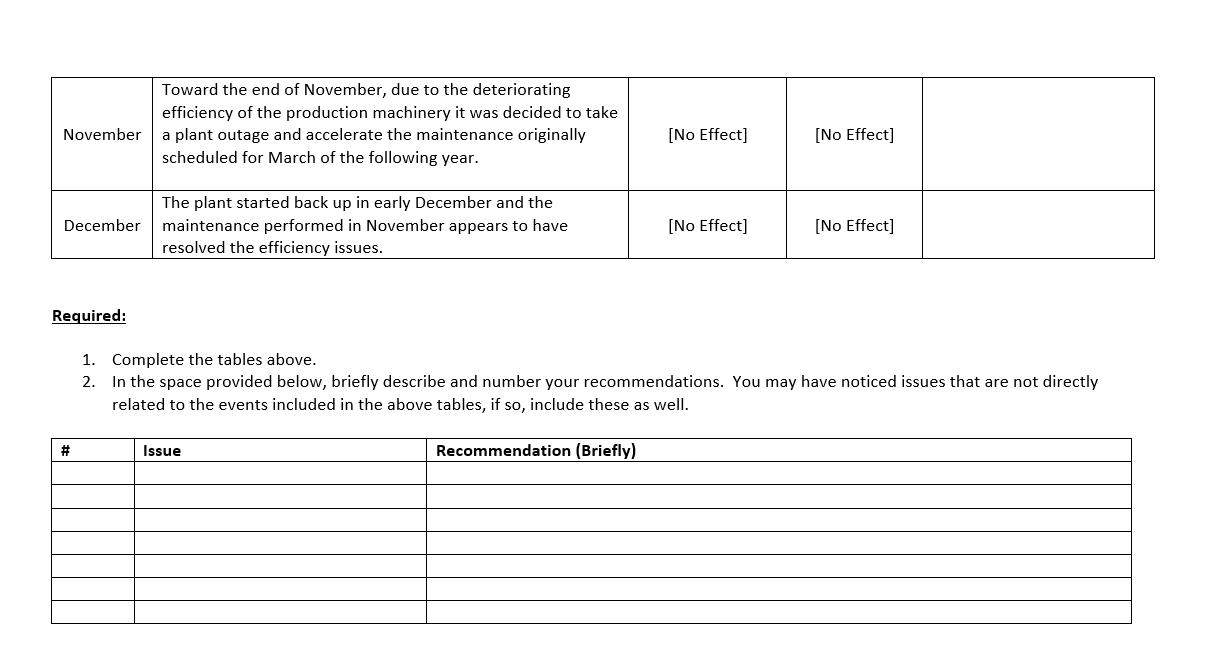
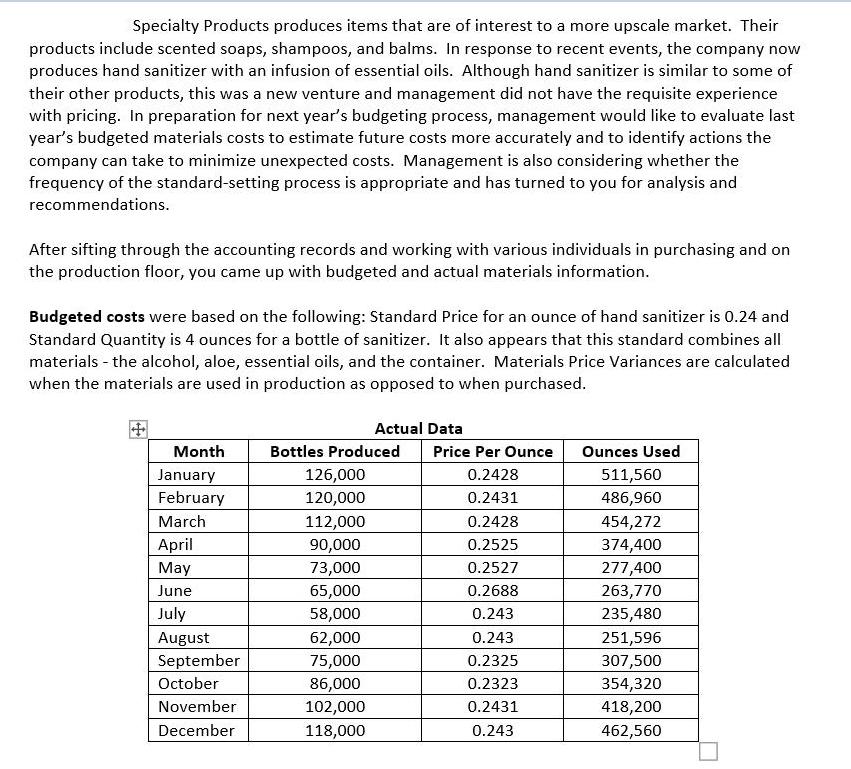
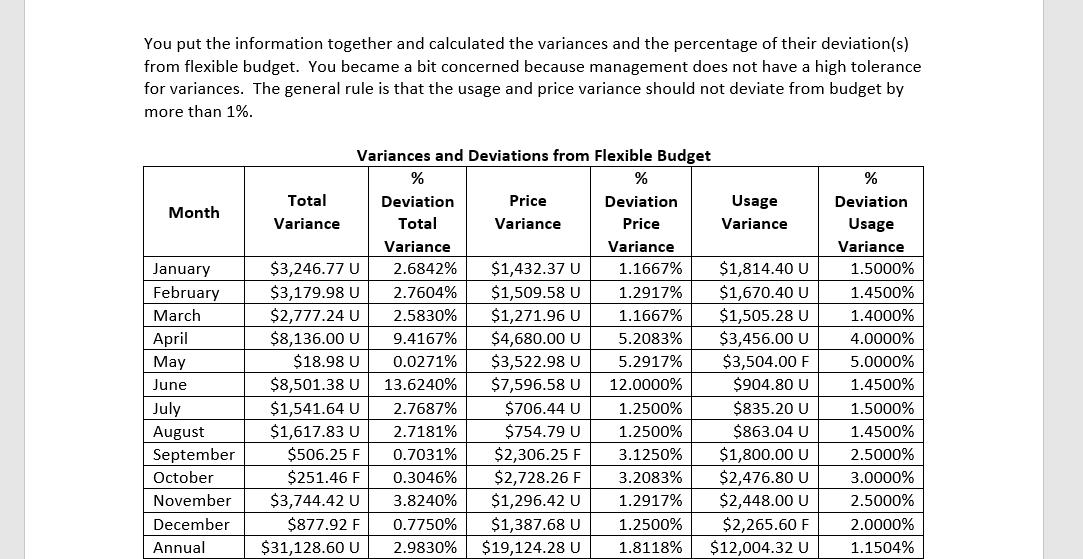
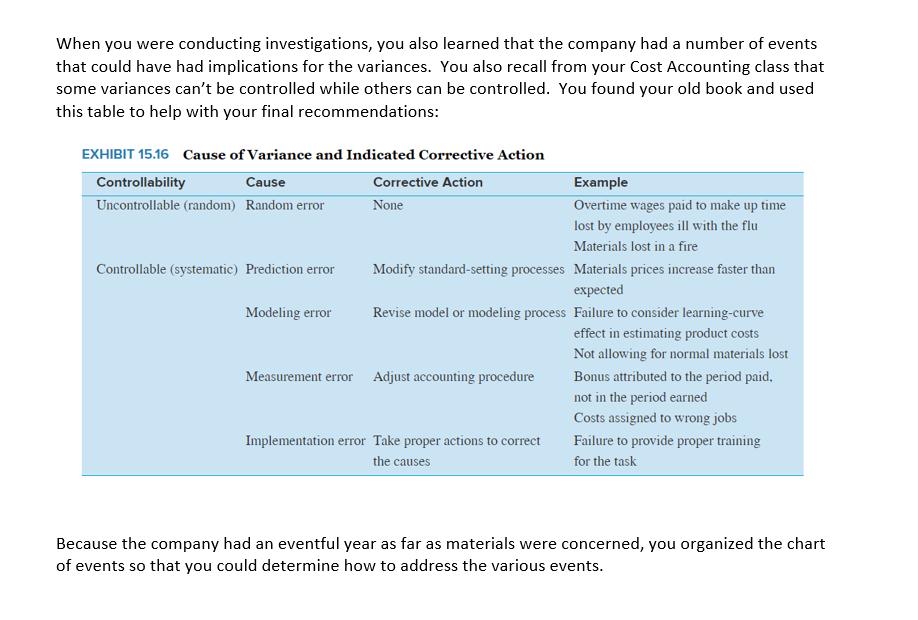
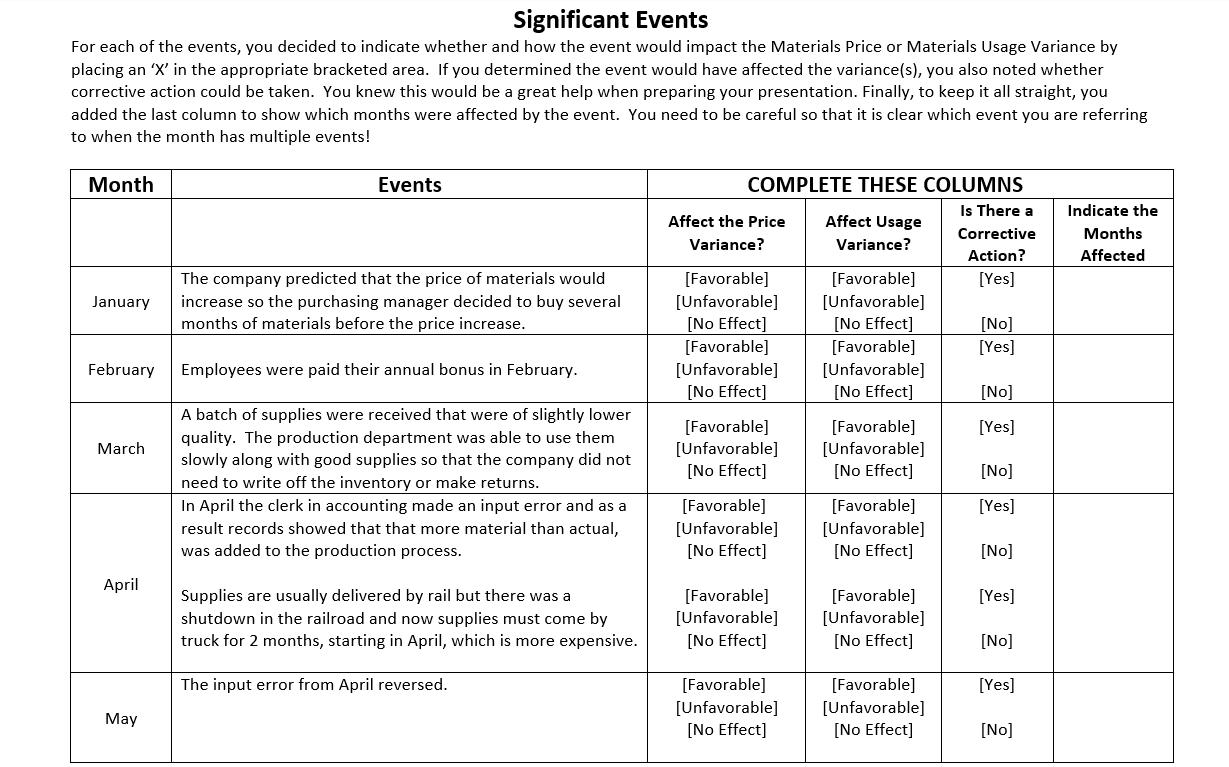
Specialty Products produces items that are of interest to a more upscale market. Their products include scented soaps, shampoos, and balms. In response to recent events, the company now produces hand sanitizer with an infusion of essential oils. Although hand sanitizer is similar to some of their other products, this was a new venture and management did not have the requisite experience with pricing. In preparation for next year's budgeting process, management would like to evaluate last year's budgeted materials costs to estimate future costs more accurately and to identify actions the company can take to minimize unexpected costs. Management is also considering whether the frequency of the standard-setting process is appropriate and has turned to you for analysis and recommendations. After sifting through the accounting records and working with various individuals in purchasing and on the production floor, you came up with budgeted and actual materials information. Budgeted costs were based on the following: Standard Price for an ounce of hand sanitizer is 0.24 and Standard Quantity is 4 ounces for a bottle of sanitizer. It also appears that this standard combines all materials - the alcohol, aloe, essential oils, and the container. Materials Price Variances are calculated when the materials are used in production as opposed to when purchased. Month January February March April May June July August September October November December Actual Data Bottles Produced 126,000 120,000 112,000 90,000 73,000 65,000 58,000 62,000 75,000 86,000 102,000 118,000 Price Per Ounce 0.2428 0.2431 0.2428 0.2525 0.2527 0.2688 0.243 0.243 0.2325 0.2323 0.2431 0.243 Ounces Used 511,560 486,960 454,272 374,400 277,400 263,770 235,480 251,596 307,500 354,320 418,200 462,560 You put the information together and calculated the variances and the percentage of their deviation(s) from flexible budget. You became a bit concerned because management does not have a high tolerance for variances. The general rule is that the usage and price variance should not deviate from budget by more than 1%. Month January February March April May June July August September October November December Annual Total Variance Variances and Deviations from Flexible Budget % Deviation Price Variance 1.1667% 1.2917% 1.1667% 5.2083% 5.2917% 12.0000% 1.2500% 1.2500% 3.1250% 3.2083% 1.2917% 1.2500% 1.8118% % Deviation Total Variance 2.6842% $3,246.77 U $3,179.98 U 2.7604% $2,777.24 U 2.5830% $8,136.00 U 9.4167% $18.98 U 0.0271% $8,501.38 U 13.6240% $1,541.64 U 2.7687% $1,617.83 U 2.7181% $506.25 F 0.7031% $251.46 F 0.3046% $3,744.42 U 3.8240% $877.92 F 0.7750% $31,128.60 U 2.9830% Price Variance $1,432.37 U $1,509.58 U $1,271.96 U $4,680.00 U $3,522.98 U $7,596.58 U $706.44 U $754.79 U $2,306.25 F $2,728.26 F $1,296.42 U $1,387.68 U $19,124.28 U Usage Variance $1,814.40 U $1,670.40 U $1,505.28 U $3,456.00 U $3,504.00 F $904.80 U $835.20 U $863.04 U $1,800.00 U $2,476.80 U $2,448.00 U $2,265.60 F $12,004.32 U % Deviation Usage Variance 1.5000% 1.4500% 1.4000% 4.0000% 5.0000% 1.4500% 1.5000% 1.4500% 2.5000% 3.0000% 2.5000% 2.0000% 1.1504% When you were conducting investigations, you also learned that the company had a number of events that could have had implications for the variances. You also recall from your Cost Accounting class that some variances can't be controlled while others can be controlled. You found your old book and used this table to help with your final recommendations: EXHIBIT 15.16 Cause of Variance and Indicated Corrective Action Corrective Action None Controllability Cause Uncontrollable (random) Random error Controllable (systematic) Prediction error Modeling error Measurement error Modify standard-setting processes Materials prices increase faster than expected Revise model or modeling process Failure to consider learning-curve effect in estimating product costs Not allowing for normal materials lost Bonus attributed to the period paid, not in the period earned Costs assigned to wrong jobs Failure to provide proper training for the task Adjust accounting procedure Example Overtime wages paid to make up time lost by employees ill with the flu Materials lost in a fire Implementation error Take proper actions to correct the causes Because the company had an eventful year as far as materials were concerned, you organized the chart of events so that you could determine how to address the various events. Significant Events For each of the events, you decided to indicate whether and how the event would impact the Materials Price or Materials Usage Variance by placing an 'X' in the appropriate bracketed area. If you determined the event would have affected the variance(s), you also noted whether corrective action could be taken. You knew this would be a great help when preparing your presentation. Finally, to keep it all straight, you added the last column to show which months were affected by the event. You need to be careful so that it clear which event you are referring to when the month has multiple events! Month January February March April May Events The company predicted that the price of materials would increase so the purchasing manager decided to buy several months of materials before the price increase. Employees were paid their annual bonus in February. A batch of supplies were received that were of slightly lower quality. The production department was able to use them slowly along with good supplies so that the any did not need to write off the inventory or make returns. In April the clerk in accounting made an input error and as a result records showed that that more material than actual, was added to the production process. Supplies are usually delivered by rail but there was a shutdown in the railroad and now supplies must come by truck for 2 months, starting in April, which is more expensive. The input error from April reversed. COMPLETE THESE COLUMNS Is There a Corrective Action? [Yes] Affect the Price Variance? [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] Affect Usage Variance? [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [NO] [Yes] [NO] [Yes] [NO] [Yes] [NO] [Yes] [NO] [Yes] [NO] Indicate the Months Affected June July August September October November Our materials supplier, which was our only materials supplier, had a temporary outage that lasted through June and at the last minute we had to find a temporary (emergency) supplier. Since it was last minute, the supplier charged premium pricing and had to expedite shipping. A major equipment purchase was planned for June but was delayed until August. Many of our employees took vacation to enjoy summer activities. Our supplier informed purchasing that they were going to halt production for maintenance and requested that our company take a two-month supply of materials now. Union negotiations were in full swing and the production manager noted that employees seemed a bit disgruntled. He also noticed that they were taking more 'personal' breaks and seemed less conscientious about the quality of their work. The production manager also said that it seemed like there was more waste. Material purchase price for the containers is based on a contract tied to the price of oil. Oil prices declined during the months of September and October. OPEC is meeting this month to negotiate supply levels of oil for the following year. Toward the end of November, due to the deteriorating efficiency of the production machinery it was decided to take a plant outage and accelerate the maintenance originally scheduled for March of the following year. [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [Yes] [NO] [Yes] [NO] [Yes] [NO] [Yes] [NO] [Yes] [NO] [Yes] [NO] [Yes] [NO] [Yes] [NO] December January February March The plant started back up in early December and the maintenance performed in November appears to have resolved the efficiency issues. April To make sure you weren't missing anything, you also kept track of your reasoning for determining that the event would not have affected either the materials price or usage variance. You created another table as you were completing the process to make sure your thoughts were in order. You have all of the events listed in the Events column but decided to fill in the [No Effect] box when the event would not have affected the price or the usage variance. You provided another column to keep track of your logic when you determined that the event would not have affected the respective variance(s). Month Events The company predicted that the price of materials would increase so the purchasing manager decided to buy several months of materials before the price increase. Employees were paid their annual bonus in February A batch of supplies were received that were of slightly lower quality. The production department was able to use them slowly along with good supplies so that the company did not need to write off the inventory or make returns. In April the clerk in accounting made an input error and as a result records showed that that more material than actual, was added to the production process. [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] Supplies are usually delivered by rail but there was a shutdown in the railroad and now supplies must come by truck for 2 months, starting in April, which is more expensive. Affect the Price Variance? [No Effect] COMPLETE THESE COLUMNS [No Effect] [No Effect] [Favorable] [Unfavorable] [No Effect] [No Effect] [No Effect] Affect Usage Variance? [No Effect] [No Effect] [No Effect] [Yes] [No Effect] [NO] [No Effect] If you marked the 'No Effect' area, please explain why there is no effect May June July August September October The input error from April reversed. Our materials supplier, which was our only materials supplier, had a temporary outage that lasted through June and at the last minute we had to find a temporary (emergency) supplier. Since it was last minute, the supplier charged premium pricing and had to expedite shipping. A major equipment purchase was planned for June but was delayed until August. Many of our employees took vacation to enjoy summer activities. Our supplier informed purchasing that they were going to halt production for maintenance and requested that our company take a two-month supply of materials now. Union negotiations were in full swing and the production manager noted that employees seemed a bit disgruntled. He also noticed that they were taking more 'personal' breaks and seemed less conscientious about the quality of their work. The production manager also said that it seemed like there was more waste. Material purchase price for the containers is based on a contract tied to the price of oil. Oil prices declined during the months of September and October. OPEC is meeting this month to negotiate supply levels of oil for the following year. [No Effect] [No Effect] [No Effect] [No Effect] [No Effect] [No Effect] [No Effect] [No Effect] [No Effect] [No Effect] [No Effect] [No Effect] [No Effect] [No Effect] [No Effect] [No Effect] November December Required: # Toward the end of November, due to the deteriorating efficiency of the production machinery it was decided to take a plant outage and accelerate the maintenance originally scheduled for March of the following year. The plant started back up in early December and the maintenance performed in November appears to have resolved the efficiency issues. [No Effect] Issue [No Effect] [No Effect] [No Effect] 1. Complete the tables above. 2. In the space provided below, briefly describe and number your recommendations. You may have noticed issues that are not directly related to the events included in the above tables, if so, include these as well. Recommendation (Briefly)
Step by Step Solution
3.52 Rating (159 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Complete the tables above Month Price Variance Usage Variance Corrective Action Months Affected January Unfavorable Favorable Yes NA February Unfavorable Unfavorable No ...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


