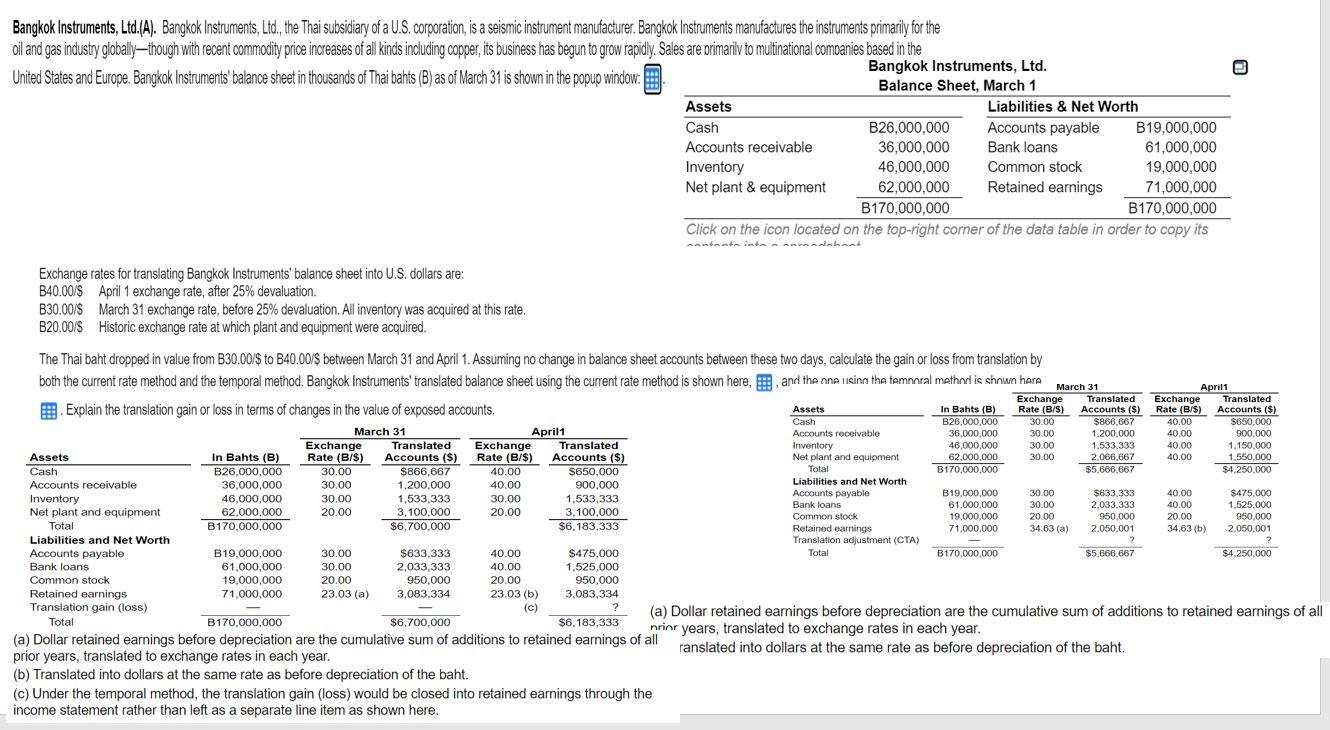
Bangkok Instruments, Ltd.(A). Bangkok Instruments, Ltd., the Thai subsidiary of a U.S. corporation, is a seismic instrument manufacturer. Bangkok Instruments manufactures the instruments primarily for the oil and gas industry globallythough with recent commodity price increases of all kinds including copper, its business has begun to grow rapidly. Sales are primarily to multinational companies based in the Bangkok Instruments, Ltd. United States and Europe. Bangkok Instruments' balance sheet in thousands of Thai bahts (B) as of March 31 is shown in the popup window. Balance Sheet, March 1 Assets Liabilities & Net Worth Cash B26,000,000 Accounts payable B19,000,000 Accounts receivable 36,000,000 Bank loans 61,000,000 Inventory 46,000,000 Common stock 19,000,000 Net plant & equipment 62,000,000 Retained earnings 71,000,000 B170,000,000 B170,000,000 Click on the icon located on the top-right corner of the data table in order to copy its entante intendebant 30.00 Exchange rates for translating Bangkok Instruments' balance sheet into U.S. dollars are: B40.00/$ April 1 exchange rate, after 25% devaluation. B30.00$ March 31 exchange rate, before 25% devaluation. All inventory was acquired at this rate. B20.00/Historic exchange rate at which plant and equipment were acquired. The Thai baht dropped in value from B30.00/$ to B40.00/$ between March 31 and April 1. Assuming no change in balance sheet accounts between these two days, calculate the gain or loss from translation by both the current rate method and the temporal method. Bangkok Instruments' translated balance sheet using the current rate method is shown here, and the one lising the temporal method is shown here March 31 April1 Exchange Translated Exchange Translated 5. Explain the translation gain or loss in terms of changes in the value of exposed accounts. Assets In Bahts (B) Rate (B/s) Accounts ($) Rate (B/s) Accounts ($) Cash B26,000,000 30.00 $866,667 40.00 $650,000 March 31 April1 Accounts receivable 36,000,000 1.200.000 40.00 900,000 Exchange Translated Exchange Translated Inventory 46,000,000 30.00 1,533,333 40.00 1.150.000 Assets In Bahts (B) Rate (B/S) Accounts ($) BIS) Rate (B/S) Accounts ($) Net plant and equipment 62,000,000 30.00 2,066,667 40.00 1.550,000 Cash B26,000,000 30.00 $866,667 40.00 $650,000 Total B170,000,000 $5,666,667 $4.250.000 Accounts receivable 36,000,000 30.00 1,200,000 40.00 900,000 Liabilities and Net Worth 30.00 30.00 Accounts payable $633,333 Inventory $475,000 46,000,000 1,533.333 B19,000,000 30.00 40.00 1,533,333 Bank loans 61.000.000 30.00 40.00 2,033,333 1,525.000 Net plant and equipment 62.000.000 20.00 3,100,000 20.00 3.100.000 Common stock 19,000,000 20.00 950.000 20.00 950.000 Total B170,000,000 $6,700,000 $6.183,333 Retained earnings 71,000,000 34.63 (a) 2,050 001 34.63 (b) 2.050.001 Liabilities and Net Worth Translation adjustment (CTA) ? Accounts payable B19,000,000 30.00 $633,333 40.00 $475,000 Total B170,000,000 $5,666,667 $4,250.000 Bank loans 61,000,000 30.00 2,033,333 40.00 1,525,000 Common stock 19,000,000 20.00 950.000 20.00 950,000 Retained earnings 71,000,000 23.03 (a) 3,083,334 23.03 (b) 3,083,334 Translation gain (loss) (c) c ? (a) Dollar retained earnings before depreciation are the cumulative sum of additions to retained earnings of all Total B170,000,000 $6,700,000 $6.183,333 nrior years, translated to exchange rates in each year. (a) Dollar retained earnings before depreciation are the cumulative sum of additions to retained earnings of all ranslated into dollars at the same rate as before depreciation of the baht. prior years, translated to exchange rates in each year. (b) Translated into dollars at the same rate as before depreciation of the baht. (c) Under the temporal method, the translation gain (loss) would be closed into retained earnings through the income statement rather than left as a separate line item as shown here. ? Bangkok Instruments, Ltd.(A). Bangkok Instruments, Ltd., the Thai subsidiary of a U.S. corporation, is a seismic instrument manufacturer. Bangkok Instruments manufactures the instruments primarily for the oil and gas industry globallythough with recent commodity price increases of all kinds including copper, its business has begun to grow rapidly. Sales are primarily to multinational companies based in the Bangkok Instruments, Ltd. United States and Europe. Bangkok Instruments' balance sheet in thousands of Thai bahts (B) as of March 31 is shown in the popup window. Balance Sheet, March 1 Assets Liabilities & Net Worth Cash B26,000,000 Accounts payable B19,000,000 Accounts receivable 36,000,000 Bank loans 61,000,000 Inventory 46,000,000 Common stock 19,000,000 Net plant & equipment 62,000,000 Retained earnings 71,000,000 B170,000,000 B170,000,000 Click on the icon located on the top-right corner of the data table in order to copy its entante intendebant 30.00 Exchange rates for translating Bangkok Instruments' balance sheet into U.S. dollars are: B40.00/$ April 1 exchange rate, after 25% devaluation. B30.00$ March 31 exchange rate, before 25% devaluation. All inventory was acquired at this rate. B20.00/Historic exchange rate at which plant and equipment were acquired. The Thai baht dropped in value from B30.00/$ to B40.00/$ between March 31 and April 1. Assuming no change in balance sheet accounts between these two days, calculate the gain or loss from translation by both the current rate method and the temporal method. Bangkok Instruments' translated balance sheet using the current rate method is shown here, and the one lising the temporal method is shown here March 31 April1 Exchange Translated Exchange Translated 5. Explain the translation gain or loss in terms of changes in the value of exposed accounts. Assets In Bahts (B) Rate (B/s) Accounts ($) Rate (B/s) Accounts ($) Cash B26,000,000 30.00 $866,667 40.00 $650,000 March 31 April1 Accounts receivable 36,000,000 1.200.000 40.00 900,000 Exchange Translated Exchange Translated Inventory 46,000,000 30.00 1,533,333 40.00 1.150.000 Assets In Bahts (B) Rate (B/S) Accounts ($) BIS) Rate (B/S) Accounts ($) Net plant and equipment 62,000,000 30.00 2,066,667 40.00 1.550,000 Cash B26,000,000 30.00 $866,667 40.00 $650,000 Total B170,000,000 $5,666,667 $4.250.000 Accounts receivable 36,000,000 30.00 1,200,000 40.00 900,000 Liabilities and Net Worth 30.00 30.00 Accounts payable $633,333 Inventory $475,000 46,000,000 1,533.333 B19,000,000 30.00 40.00 1,533,333 Bank loans 61.000.000 30.00 40.00 2,033,333 1,525.000 Net plant and equipment 62.000.000 20.00 3,100,000 20.00 3.100.000 Common stock 19,000,000 20.00 950.000 20.00 950.000 Total B170,000,000 $6,700,000 $6.183,333 Retained earnings 71,000,000 34.63 (a) 2,050 001 34.63 (b) 2.050.001 Liabilities and Net Worth Translation adjustment (CTA) ? Accounts payable B19,000,000 30.00 $633,333 40.00 $475,000 Total B170,000,000 $5,666,667 $4,250.000 Bank loans 61,000,000 30.00 2,033,333 40.00 1,525,000 Common stock 19,000,000 20.00 950.000 20.00 950,000 Retained earnings 71,000,000 23.03 (a) 3,083,334 23.03 (b) 3,083,334 Translation gain (loss) (c) c ? (a) Dollar retained earnings before depreciation are the cumulative sum of additions to retained earnings of all Total B170,000,000 $6,700,000 $6.183,333 nrior years, translated to exchange rates in each year. (a) Dollar retained earnings before depreciation are the cumulative sum of additions to retained earnings of all ranslated into dollars at the same rate as before depreciation of the baht. prior years, translated to exchange rates in each year. (b) Translated into dollars at the same rate as before depreciation of the baht. (c) Under the temporal method, the translation gain (loss) would be closed into retained earnings through the income statement rather than left as a separate line item as shown here







