Question
Below I have copied the prompt. The question I have is in the image, how do you get the numbers for Net Working Capital. For
Below I have copied the prompt. The question I have is in the image, how do you get the numbers for Net Working Capital. For example in the image the Net Working Capital is -4835000 for year 2013. I need an explanation on how to get that number so that I can do the same for the remaining years.
Question: 1) Which project do you think is more risky? How do you think you should incorporate differences in risk into your analysis?
Question: 2) Based on the calculated payback period, net present value (NPV), and internal rate of return (IRR) for each project, which project looks better for New Balance sharehold-ers? Why?
Question: 3) Should Rodriguez be more or less critical of cash flow forecasts for Persistence than of cash flow forecasts for Sneaker 2013? Why?
Question: 4) What is your final recommendation to Rodriguez? Please explain your answer.
Project 1, Sneaker 2013:
1. The life of the Sneaker 2013 project was expected to be six years. Assume the analysis took place at the end of 2012.
2. The suggested retail price of the shoe was $190. Gross margins for high-end athletic footwear averaged about 40% at the retail level, meaning each pair sold would net New Balance $115.
3. The global athletic footwear market in 2011 totaled approximately $74.5 billion and was expected to grow at a CAGR of 1.8% from 2011 to 2018, reaching $84.4 billion by 2018.3 Based on market research and analysis of other recent athlete endorsements, the New Balance marketing division estimated the following sales volumes for Sneaker 2013: The 2016 number assumed Kirani James participated in the 2016 games in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, and won at least one medal.4
4. For the first two years, the introduction of Sneaker 2013 would reduce sales of existing New Balance shoes as follows: Lost sales: 2013: $35 million 2014: $15 million Assume the lost revenue had the same margins as Sneaker 2013.
5. In order to produce the shoe, the firm needed to build a factory in Vietnam. This required an immediate outlay of $150 million, to be depreciated on a 39-year MACRS5 basis. Depreciation percentages for the first six years respectively were: 2.6%, 5%, 4.7%, 4.5%, 4.3%, and 4.0%. The firms analysts estimated the building would be sold for $102 million at project termination. This salvage value has not been taken into consideration when computing annual depreciation charges.6
6. The company must immediately purchase equipment costing $15 million. Freight and installation of the equipment would cost $5 million. The cost of equipment and freight/installation was to be depreciated on a five-year MACRS basis. Depreciation percentages for the six years respectively were: 20%, 32%, 19%, 12%, 11%, and 6%. It was believed the equipment could be sold for $3 million upon project termination.
7. In order to manufacture Sneaker 2013, two of the firms working capital accounts were expected to increase immediately. Approximately $15 million of inventory would be needed quickly to fill the supply chain, and accounts payable were expected to increase by $5 million. By the end of 2013, the accounts receivable balance would be 8% of project revenue; the inventory balance would be 25% of the projects variable costs; and accounts payable would be 20% of the projects variable costs. All working capital would be recovered at the end of the project by the end of the sixth year.
8. Variable costs were expected to be 55% of revenue.
9. Selling, general, and administrative expenses were expected to be $7 million per year.
10. Kirani James would be paid $2 million per year for his endorsement of Sneaker 2013, with an additional $1 million Olympic bonus in 2016.
11. Other advertising and promotion costs were estimated as follows:
12. New Balance had already spent $2 million in research and development on Sneaker 2013.
13. The Sneaker 2013 project was to be financed using a combination of equity and debt. The interest costs on the debt were expected to be approximately $1.2 million per year. The New Balance discount rate for new projects such as this was 11%.
14. New Balances effective tax rate was 40%.
Project 2, Persistence:
1. The life of the Persistence project would be only three years, given the steep technological learning curve for this new product line.
2. The wholesale price of Persistence (net to New Balance) would be $90.00.
3. The hiking segment of the athletic shoe market was projected to reach $350 million during 2013, and it was growing at a rate of 15% per year. New Balances market share projections for Persistence were: 2013, 15%; 2014, 18%; and 2015, 20%.
4. The firm would be able to use an idle section of one of its factories to produce the hiking shoe. A cost accountant estimated that, according to the square footage in the factory, this sections overhead allocation would amount to $1.8 million per year. The firm would still incur these costs if the product were not undertaken. In addition, this section would remain idle for the life of the project if the Persistence project were not undertaken.
5. The firm must purchase manufacturing equipment costing $8 million. The equipment fell into the five-year MACRS depreciation category. Depreciation percentages for the first three years respectively were: 20%, 32%, and 19%. The cash outlay would be at Time 0, and depreciation would start in 2013. Analysts estimated the equipment could be sold for book value at the end of the projects life.
6. Inventory and accounts receivable would increase by $25 million at Time 0 and would be recovered at the end of the project (2015). The accounts payable balance was projected to increase by $10 million at Time 0 and would also be recovered at the end of the project.
7. Because the firm had not yet entered the hiking shoe market, introduction of this product was not expected to impact sales of the firms other shoe lines.
8. Variable costs of producing the shoe were expected to be 38% of the shoe's sales.
9. General and administrative expenses for Persistence would be 12% of revenue in 2013. This would drop to 10% in 2014 and 8% in 2015.
10. The product would not have a celebrity endorser. Advertising and promotion costs would initially be $3 million in 2013, then $2 million in both 2014 and 2015.
11. The company's federal plus state marginal tax rate was 40%.
12. In order to begin immediate production of Persistence, the design technology and the manufacturing specifications for a new hiking shoe would be purchased from an outside source for $50 million. This outlay was to take place immediately and be expensed immediately for tax purposes.
13. Annual interest costs on the debt for this project would be $600,000. In addition, Rodriguez estimated the cost of capital for the hiking shoe would be 14%.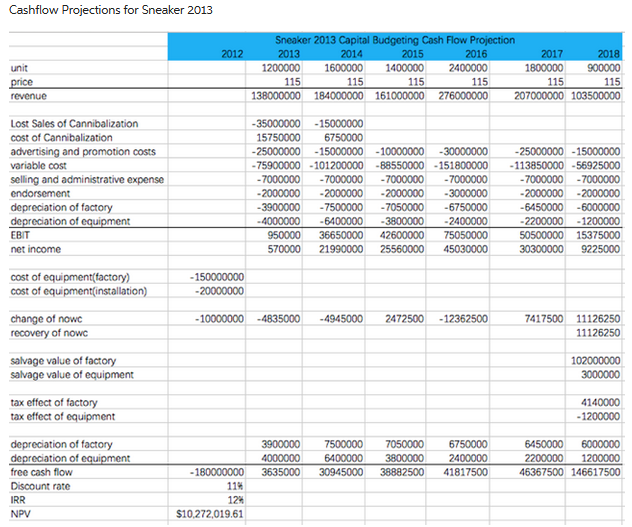
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


