Question: Below is the given code of implementation: #include #include #include #include using namespace std; class List; class Iterator; class Node { public: /* Constructs a

Below is the given code of implementation:
#include#include #include #include
using namespace std; class List; class Iterator; class Node { public: /* Constructs a node with a given data value. @param s the data to store in this node */ Node(string s); /* Destructor */ ~Node() {} private: string data; Node* previous; Node* next; friend class List; friend class Iterator; }; class List { public: /** Constructs an empty list. */ List(); /* Destructor. Deletes Nodes that are dynamically allocated */ ~List(); /** Appends an element to the list. @param data the value to append */ void push_back(string data); /** Inserts an element into the list. @param iter the position before which to insert @param s the value to append */ void insert(Iterator iter, string s); /** Removes an element from the list. @param iter the position to remove @return an iterator pointing to the element after the erased element */ Iterator erase(Iterator iter); /** Gets the beginning position of the list. @return an iterator pointing to the beginning of the list */ Iterator begin(); /** Gets the past-the-end position of the list. @return an iterator pointing past the end of the list */ Iterator end(); bool empty(); private: Node* first; Node* last; friend class Iterator; }; class Iterator { public: /** Constructs an iterator that does not point into any list. */ Iterator(); /* Copy constructor */ Iterator(const Iterator & pos); /** Looks up the value at a position. @return the value of the node to which the iterator points */ string get() const; /** Advances the iterator to the next node. */ void next(); /** Moves the iterator to the previous node. */ void previous(); /** Compares two iterators. @param b the iterator to compare with this iterator @return true if this iterator and b are equal */ bool equals(Iterator b) const; /* Overloaded Operators */ bool operator==(const Iterator& b) const; bool operator!=(const Iterator& b) const; Iterator operator++(int unused); //postfix Iterator& operator++(); //prefix Iterator operator--(int unused); //postfix Iterator& operator--(); //prefix string operator*() const; private: Node* position; List* container; friend class List; }; Node::Node(string s) { data = s; previous = NULL; next = NULL; } List::List() { first = NULL; last = NULL; } List::~List() { if (!empty()) // if the list is nonempty { Node* node = this->first; while (node->next != NULL) { node = node->next; // jump to the next one delete node->previous; // deleting the memory for previous } if (node->next == NULL) // reaching the last node { delete node; } } } bool List::empty() { return (last == NULL); } void List::push_back(string data) { Node* new_node = new Node(data); if (last == NULL) // List is empty { first = new_node; last = new_node; } else { new_node->previous = last; last->next = new_node; last = new_node; } } void List::insert(Iterator iter, string s) { if (iter.position == NULL) { push_back(s); return; } Node* after = iter.position; Node* before = after->previous; Node* new_node = new Node(s); new_node->previous = before; new_node->next = after; after->previous = new_node; if (before == NULL) // Insert at beginning first = new_node; else before->next = new_node; } Iterator List::erase(Iterator iter) { assert(iter.position != NULL); Node* remove = iter.position; Node* before = remove->previous; Node* after = remove->next; if (remove == first) first = after; else before->next = after; if (remove == last) last = before; else after->previous = before; delete remove; Iterator r; r.position = after; r.container = this; return r; } Iterator List::begin() { Iterator iter; iter.position = first; iter.container = this; return iter; } Iterator List::end() { Iterator iter; iter.position = NULL; iter.container = this; return iter; } Iterator::Iterator() { position = NULL; container = NULL; } Iterator::Iterator(const Iterator & pos) { (*this) = pos; } string Iterator::get() const { assert(position != NULL); return position->data; } void Iterator::next() { assert(position != NULL); position = position->next; } void Iterator::previous() { assert(position != container->first); if (position == NULL) position = container->last; else position = position->previous; } bool Iterator::equals(Iterator b) const { return position == b.position; } bool Iterator::operator==(const Iterator& b) const { return position == b.position; } bool Iterator::operator!=(const Iterator& b) const { return position != b.position; } Iterator & Iterator::operator++() // prefix { assert(position != NULL); position = position->next; return *this; } Iterator Iterator::operator++(int unused) // postfix { assert(position != NULL); Iterator clone(*this); position = position->next; return clone; } Iterator & Iterator::operator--() //prefix { assert(position != container->first); if (position == NULL) position = container->last; else position = position->previous; return *this; } Iterator Iterator::operator--(int unused) { assert(position != container->first); Iterator clone(*this); if (position == NULL) position = container->last; else position = position->previous; return clone; } string Iterator::operator*() const { assert(position != NULL); return position->data; }
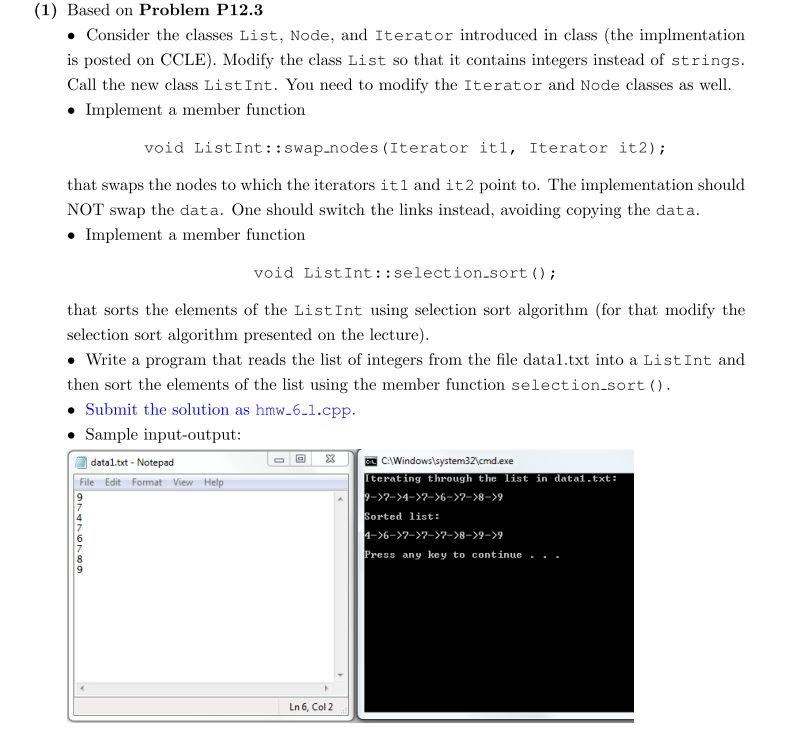
Exercise P12.3. Write a function sort that sorts the elements of a linked list (without copying them into a vector)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


