
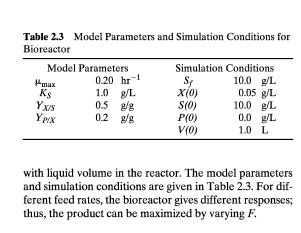

Biological reactions that involve microorganisms and enzyme catalysts are pervasive and play a crucial role in the natural world. Without such bioreactions, plant and animal life as we know it simply could not exist. Bioreactions also provide the basis for production of a wide variety of pharmaceuticals and healthcare and food products. Other important industrial processes that involve bioreactions include fermentation and wastewater treatment. Chemical engineers are heavily involved with biochemical and biomedical processes. In this section we present a dynamic model for a representative process, a bioreactor operated in a semi-batch mode. Additional biochemical and biomedical applications appear in other chapters. In general, bioreactions are characterized by the conversion of feed material (or substrate) into products and cell mass (or biomass). The reactions are typically catalyzed by enzymes (Bailey and Ollis, 1986; Fogler, 1999). When the objective is to produce cells, a small amount of cells (inoculum) is added to initiate subsequent cell growth. A broad class of bioreactions can be represented in simplified form as substrateceilsmorecells+products(2-90) The stoichiometry of bioreactions can be very complex and depends on many factors that include the environmental conditions in the vicinity of the cells. For simplicity we consider the class of bioreactions where the substrate contains a single limiting nutrient and only one product results. The following yield coefficients are based on the reaction stoichiometry: YXISYPIS=massofsubstrateconsumedtoformnewcellsmassofnewcellsformed=massofsubstrateconsumedtoformproductmassofproductformed Many important bioreactors are operated in a semicontinuous manner that is referred to as fed-batch operation, which is illustrated in Figure 2.13. A feed stream containing substrate is introduced to the fed-batch reactor continually. The mass flow rate is denoted by F and the substrate mass concentration by Sf Because there is no exit stream, the volume V of the bioreactor contents increases during the batch. The advantage of fed-batch operation is that it allows the substrate Table 2.3 Model Parameters and Simulation Conditions for Bioreactor with liquid volume in the reactor. The model parameters and simulation conditions are given in Table 2.3. For different feed rates, the bioreactor gives different responses; thus, the product can be maximized by varying F. Problem 2. Dynamics of a Fed-Batch Bioreactor. (50 points) Knumberendinginanevennumber. Refer to Section 2.4.9 given in the course text on pages 31-33. This example refers to the results given in Figure 2.14 that were produced by solving the model eqs. 2-98 to 2-101 using a numerical integration method with the model parameters and two sets of initial conditions listed in Table 2.3 on page 33. The assignment is to write a Matlab code (and not a Polymath code) that reproduces the results shown in the above-referenced figures. There are two cases shown, namely, those at F=0.05L/hr and another set at F=0.02L/hr. The methodology is similar to what was done in one of the early lab exercises where we created a MATLAB code to numerically solve ODE's. If needed, refer to this exercise and follow a similar procedure. Your solution package should consist of the following. (a) A summary of the model assumptions and starting ODE model equations and the various initial conditions that were used to generate each of the results. Do not derive the equations, but use them directly as given. Show that the units for the various parameters that are given are consistent. (b) A table that shows the actual variable that appears in the model equations and the corresponding computer-based variable. For example, the model variable rP may be written as rP while the model variable Sf may be written in your code Ssubf. (c) Listing of the Matlab codes that were used to generate the sub-plots shown in Figure 2.14 (d) A copy of the figures that are formatted like those shown in Figure 2.14










