Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Blake plans to sell 1,500 stuffed mascots next month. How much operating income can Blake expect to earn next month if he realizes his planned
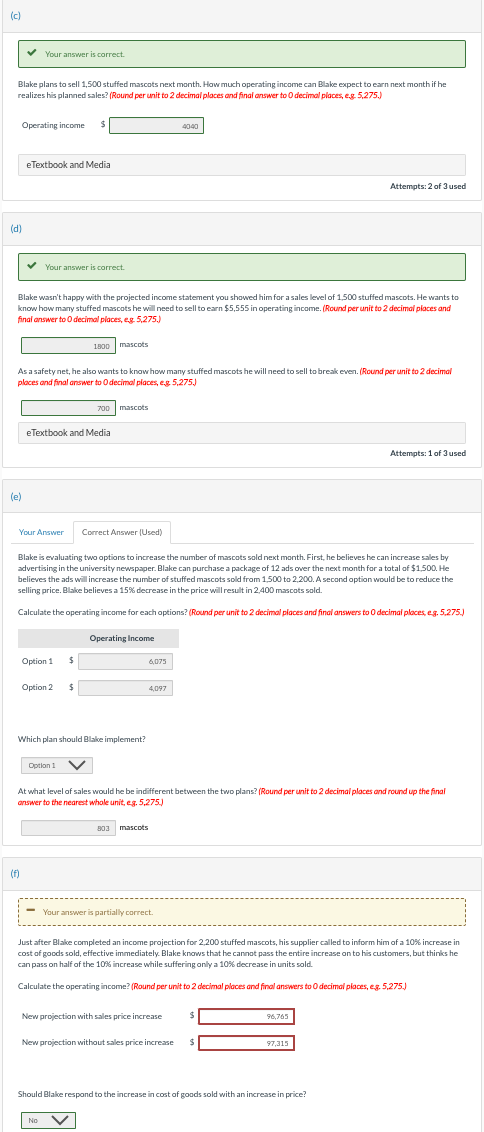 Blake plans to sell 1,500 stuffed mascots next month. How much operating income can Blake expect to earn next month if he realizes his planned sales? (Round per unit to 2 decimal places and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275.) Operating income $ Attempts: 2 of 3 used (d) Your answer is correct. Blake wasn't happy with the projected income statement you showed him for a sales level of 1,500 stuffed mascots. He wants to know haw many stuffed mascots he will need to sell to earn \$5,555 in operating income. (Round per unit to 2 decimal places and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275.) mascots As a safetynet, he also wants to know how many stuffed mascots he will need to sell to break even. (Round per unit to 2 decimal places and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275.) mascots eTextbook and Media Attempts: 1 of 3 used (e) Blake is evaluating two options to increase the number of mascots sold next month. First, he believes he can increase sales by advertising in the university newspaper. Blake can purchase a package of 12 ads over the next month for a total of $1,500. He believes the ads will increase the number of stuffed mascots sold from 1,500 to 2,200. A second aption would be to reduce the selling price. Blabe believes a 15% decrease in the price will result in 2,400 mascots sold. Calculate the operating income for each options? (Round per unit to 2 decimal places and final answers to 0 decimal places, eg. 5,275.) Which plan should Blake implement? At what level of sales would he be indifferent between the two plans? (Round per unit to 2 decimal places and round up the final answer to the nearest whale unit, eg. 5,275. mascots (f) Just after Blabe completed an income projection for 2,200 stuffed mascots, his supplier called to inform him of a 10% increase in cost of goods sold, effective immediately. Blake knows that he cannot pass the entire increase on to his customers, but thirks he can pass on half of the 10% increase while suffering only a 10% decrease in units sold. Calculate the operating income? (Round per unit to 2 decimal ploces and final answers to 0 decimal places, es, 5,275.) New projection with sales price increase $ New projection without sales price increase $ Should Blake respond to the increase in cost of goods sold with an increase in price? Blake plans to sell 1,500 stuffed mascots next month. How much operating income can Blake expect to earn next month if he realizes his planned sales? (Round per unit to 2 decimal places and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275.) Operating income $ Attempts: 2 of 3 used (d) Your answer is correct. Blake wasn't happy with the projected income statement you showed him for a sales level of 1,500 stuffed mascots. He wants to know haw many stuffed mascots he will need to sell to earn \$5,555 in operating income. (Round per unit to 2 decimal places and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275.) mascots As a safetynet, he also wants to know how many stuffed mascots he will need to sell to break even. (Round per unit to 2 decimal places and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275.) mascots eTextbook and Media Attempts: 1 of 3 used (e) Blake is evaluating two options to increase the number of mascots sold next month. First, he believes he can increase sales by advertising in the university newspaper. Blake can purchase a package of 12 ads over the next month for a total of $1,500. He believes the ads will increase the number of stuffed mascots sold from 1,500 to 2,200. A second aption would be to reduce the selling price. Blabe believes a 15% decrease in the price will result in 2,400 mascots sold. Calculate the operating income for each options? (Round per unit to 2 decimal places and final answers to 0 decimal places, eg. 5,275.) Which plan should Blake implement? At what level of sales would he be indifferent between the two plans? (Round per unit to 2 decimal places and round up the final answer to the nearest whale unit, eg. 5,275. mascots (f) Just after Blabe completed an income projection for 2,200 stuffed mascots, his supplier called to inform him of a 10% increase in cost of goods sold, effective immediately. Blake knows that he cannot pass the entire increase on to his customers, but thirks he can pass on half of the 10% increase while suffering only a 10% decrease in units sold. Calculate the operating income? (Round per unit to 2 decimal ploces and final answers to 0 decimal places, es, 5,275.) New projection with sales price increase $ New projection without sales price increase $ Should Blake respond to the increase in cost of goods sold with an increase in price
Blake plans to sell 1,500 stuffed mascots next month. How much operating income can Blake expect to earn next month if he realizes his planned sales? (Round per unit to 2 decimal places and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275.) Operating income $ Attempts: 2 of 3 used (d) Your answer is correct. Blake wasn't happy with the projected income statement you showed him for a sales level of 1,500 stuffed mascots. He wants to know haw many stuffed mascots he will need to sell to earn \$5,555 in operating income. (Round per unit to 2 decimal places and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275.) mascots As a safetynet, he also wants to know how many stuffed mascots he will need to sell to break even. (Round per unit to 2 decimal places and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275.) mascots eTextbook and Media Attempts: 1 of 3 used (e) Blake is evaluating two options to increase the number of mascots sold next month. First, he believes he can increase sales by advertising in the university newspaper. Blake can purchase a package of 12 ads over the next month for a total of $1,500. He believes the ads will increase the number of stuffed mascots sold from 1,500 to 2,200. A second aption would be to reduce the selling price. Blabe believes a 15% decrease in the price will result in 2,400 mascots sold. Calculate the operating income for each options? (Round per unit to 2 decimal places and final answers to 0 decimal places, eg. 5,275.) Which plan should Blake implement? At what level of sales would he be indifferent between the two plans? (Round per unit to 2 decimal places and round up the final answer to the nearest whale unit, eg. 5,275. mascots (f) Just after Blabe completed an income projection for 2,200 stuffed mascots, his supplier called to inform him of a 10% increase in cost of goods sold, effective immediately. Blake knows that he cannot pass the entire increase on to his customers, but thirks he can pass on half of the 10% increase while suffering only a 10% decrease in units sold. Calculate the operating income? (Round per unit to 2 decimal ploces and final answers to 0 decimal places, es, 5,275.) New projection with sales price increase $ New projection without sales price increase $ Should Blake respond to the increase in cost of goods sold with an increase in price? Blake plans to sell 1,500 stuffed mascots next month. How much operating income can Blake expect to earn next month if he realizes his planned sales? (Round per unit to 2 decimal places and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275.) Operating income $ Attempts: 2 of 3 used (d) Your answer is correct. Blake wasn't happy with the projected income statement you showed him for a sales level of 1,500 stuffed mascots. He wants to know haw many stuffed mascots he will need to sell to earn \$5,555 in operating income. (Round per unit to 2 decimal places and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275.) mascots As a safetynet, he also wants to know how many stuffed mascots he will need to sell to break even. (Round per unit to 2 decimal places and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275.) mascots eTextbook and Media Attempts: 1 of 3 used (e) Blake is evaluating two options to increase the number of mascots sold next month. First, he believes he can increase sales by advertising in the university newspaper. Blake can purchase a package of 12 ads over the next month for a total of $1,500. He believes the ads will increase the number of stuffed mascots sold from 1,500 to 2,200. A second aption would be to reduce the selling price. Blabe believes a 15% decrease in the price will result in 2,400 mascots sold. Calculate the operating income for each options? (Round per unit to 2 decimal places and final answers to 0 decimal places, eg. 5,275.) Which plan should Blake implement? At what level of sales would he be indifferent between the two plans? (Round per unit to 2 decimal places and round up the final answer to the nearest whale unit, eg. 5,275. mascots (f) Just after Blabe completed an income projection for 2,200 stuffed mascots, his supplier called to inform him of a 10% increase in cost of goods sold, effective immediately. Blake knows that he cannot pass the entire increase on to his customers, but thirks he can pass on half of the 10% increase while suffering only a 10% decrease in units sold. Calculate the operating income? (Round per unit to 2 decimal ploces and final answers to 0 decimal places, es, 5,275.) New projection with sales price increase $ New projection without sales price increase $ Should Blake respond to the increase in cost of goods sold with an increase in price Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


