Question
Bob is an existing bank customer. When the loan to Bob was originally made in 2016, the bank required Bob to increase the YE 2016
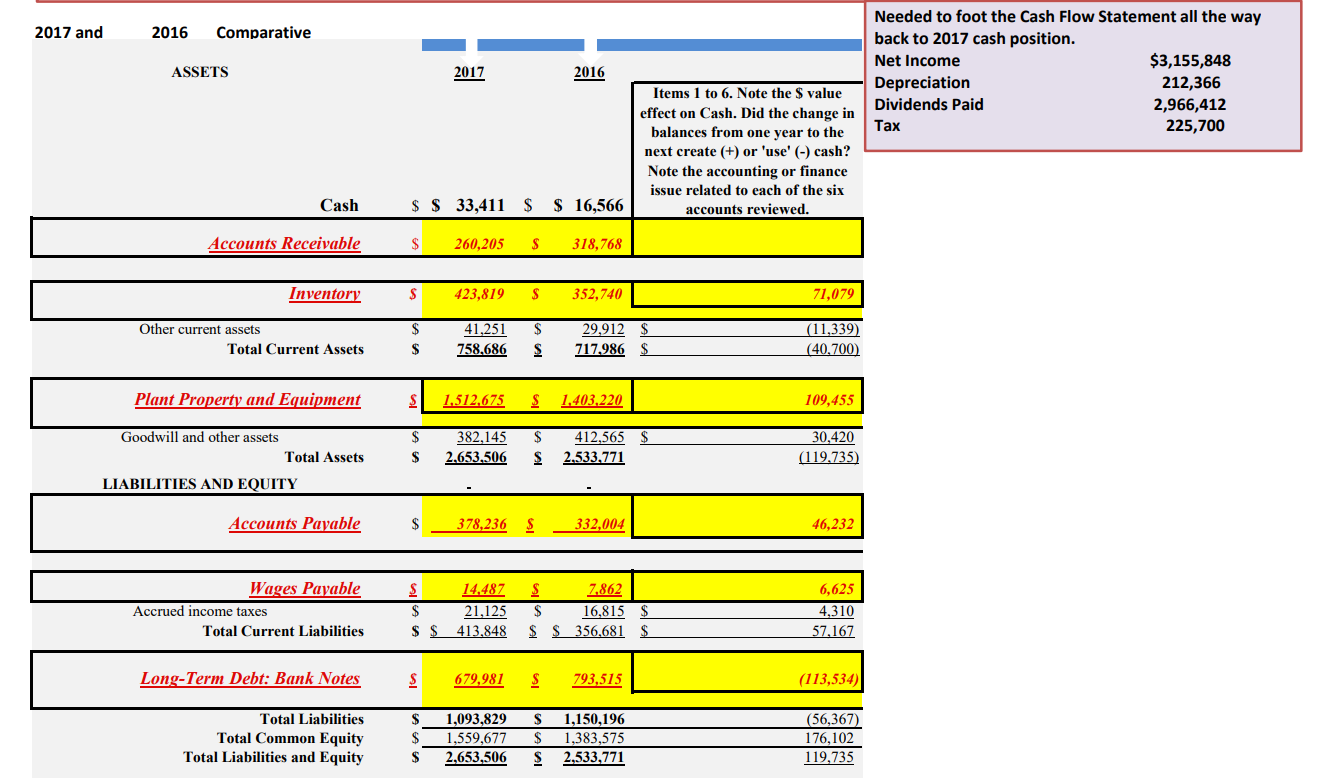
Bob is an existing bank customer. When the loan to Bob was originally made in 2016, the bank required Bob to increase the YE 2016 cash balance to at least $70,000 to qualify for the interest rate that the bank used for the original loan. This cash balance was required for the bank to make its target yield on the loan created. The Cash Flow Statement and Balance Sheet show an actual YE 2017 cash balance of less than $34,000.
Please prepare Common Sized Financial Statements for the 2 years shown. Answer two questions below
What could be managements motivation for not complying with the loans CC&Rs?
Where was the major portion of the companys working capital used?
During the original loan, the bank included, as part of the loan documentation, a document called Covenants, Conditions & Restrictions (CC&Rs), which the company had to comply with to maintain its credit facility with the bank. The major conditions of this included: 1. The company will maintain at least $70,000 in their DDA (noninterest bearing checking) at all times as compensating balances against their loan. 2. The company will maintain a current ratio of at least 2:1. 3. The company will maintain a quick ratio of at least 1.5:1. 4. The company will not increase officer salaries by more than 5% while the loan is outstanding. 5. The company will not pay bonuses to officers without the banks explicit approval.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


