Bomb Calorimetry Lab for Thermodynamics, Answer all question and all calculations


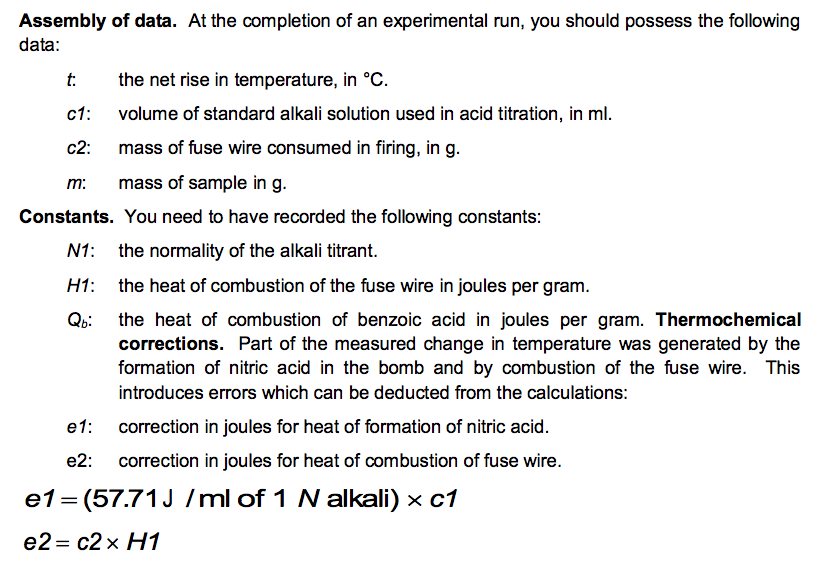


No. 3415 10 Pellets BENZOIC ACID CAS Reg. No. 65-85-0 ONE GRAM C.H.COOH PELLETS STANDARDIZED FOR BOMB CALORIMETRY Heat of Combustion 11373 Btu/lb 6318 IT. calg 26.454 MJ/kg Parr Instrument Company Moline, IL U.S.A. 61265 www.parrinst.com/support/downloads/sds 123015 10 FUSE WIRE FOR Pary OXYGEN BOMB REORDER FROM YOUR PARR DEALER OR FROM PARR INSTRUMENT CO. MOLINE. !!.. U.S.A. AT U LUMOUSTON II UU 11 1400 cal./9.. OR 2. 10cm I 10 15 20 11111 !1!1 5 CORRECTION IN CALORIES FOR RESIDUAL FUSE WIRE Sample ID: Unknown C 0.9906 0.0063 Sample ID: Benzoic acid Mass of sample (in grams to 0.9856 four decimal places) Mass of wire consumed in 0.0107 firing: (in grams to four decimals places) Net rise in temperature C 2.6083 Titre volume of 0.079N 6.90 Na,Co, in mL to two decimal places 3.4079 10.48 Unknown C: M.W.=144.2 g/mol An= -3/2 Assembly of data. At the completion of an experimental run, you should possess the following data: m: t: the net rise in temperature, in C. c1: volume of standard alkali solution used in acid titration, in ml. c2: mass of fuse wire consumed in firing, in g. mass of sample in g. Constants. You need to have recorded the following constants: N1: the normality of the alkali titrant. H1: the heat of combustion of the fuse wire in joules per gram. Qb: the heat of combustion of benzoic acid in joules per gram. Thermochemical corrections. Part of the measured change in temperature was generated by the formation of nitric acid in the bomb and by combustion of the fuse wire. This introduces errors which can be deducted from the calculations: e1: correction in joules for heat of formation of nitric acid. e2: correction in joules for heat of combustion of fuse wire. e1=(57.71J /ml of 1 N alkali) x c1 e2= c2 x H1 Energy equivalent of the calorimeter, W, determined from the benzoic acid standardization. Calculate this in joules per degree Celsius, using the following formula. mQ, + e1+e2 W t Gross heat of combustion, Q, for the test sample. Calculate this in joules per gram, using the following formula: tW -e1-e2 Q m AU and AH. Multiply Q by the molecular weight of the compound being analysed. Multiply this result by -1 to calculate AU (this is necessary to follow the modern thermodynamic sign convention. Calculate AHusing Equations 1.5 and 1.6. Discussion Questions 1. Why must the water in the bucket be weighed, when this weight of water appears nowhere in the calculation (or does it?) 2. The titration is carried out to correct for the formation of Nitric acid during the combustion reaction. What is the source of Nitrogen in the bomb and why does it react? 3.How important are the corrections, e1 and e2, to the accuracy of the overall measurement? 4.Discuss all valid sources of error in your report












