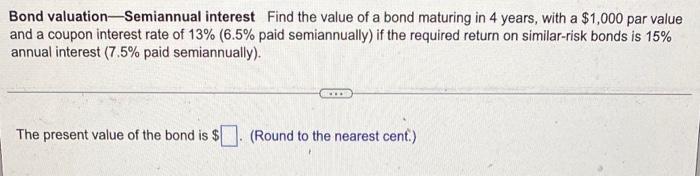
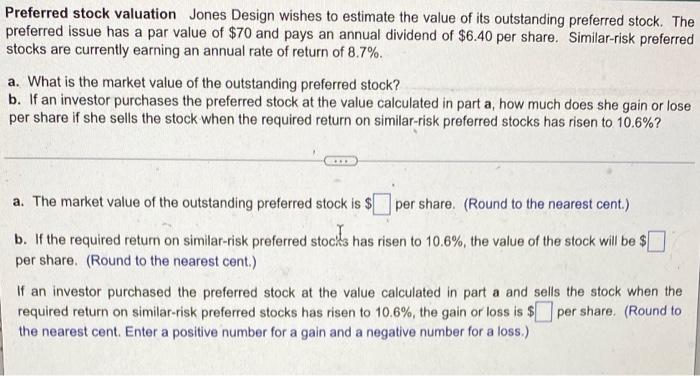
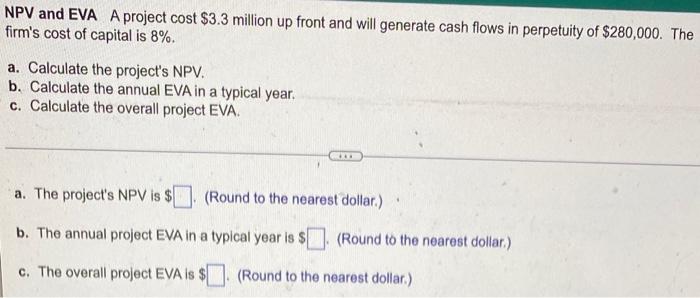
Bond valuation-Semiannual interest Find the value of a bond maturing in 4 years, with a $1,000 par value and a coupon interest rate of 13% (6.5% paid semiannually) if the required return on similar-risk bonds is 15% annual interest (7.5% paid semiannually). The present value of the bond is $. (Round to the nearest cent.) Yield to maturity The relationship between a bond's yield to maturity and coupon interest rate can be used to predict its pricing level. For the bond listed below, state whether the price of the bond will be at a premium to par, at par, or at a discount to par. Coupon interest rate Yield to maturity 6% 10% What is the price of the bond in relation to its par value? (Select the best answer below.) O A. The bond sells at a discount to par. OB. The bond sells at par. O C. The bond sells at a premium to par. Preferred stock valuation Jones Design wishes to estimate the value of its outstanding preferred stock. The preferred issue has a par value of $70 and pays an annual dividend of $6.40 per share. Similar-risk preferred stocks are currently earning an annual rate of return of 8.7%. a. What is the market value of the outstanding preferred stock? b. If an investor purchases the preferred stock at the value calculated in part a, how much does she gain or lose per share if she sells the stock when the required return on similar-risk preferred stocks has risen to 10.6%? a. The market value of the outstanding preferred stock is $ per share. (Round to the nearest cent.) b. If the required return on similar-risk preferred stocks has risen to 10.6%, the value of the stock will be $ [] per share. (Round to the nearest cent.) If an investor purchased the preferred stock at the value calculated in part a and sells the stock when the required return on similar-risk preferred stocks has risen to 10.6%, the gain or loss is $ per share. (Round to the nearest cent. Enter a positive number for a gain and a negative number for a loss.) NPV and EVA A project cost $3.3 million up front and will generate cash flows in perpetuity of $280,000. The firm's cost of capital is 8%. a. Calculate the project's NPV. b. Calculate the annual EVA in a typical year. c. Calculate the overall project EVA. a. The project's NPV is $. (Round to the nearest dollar.) b. The annual project EVA in a typical year is $ (Round to the nearest dollar) c. The overall project EVA is $ (Round to the nearest dollar)