

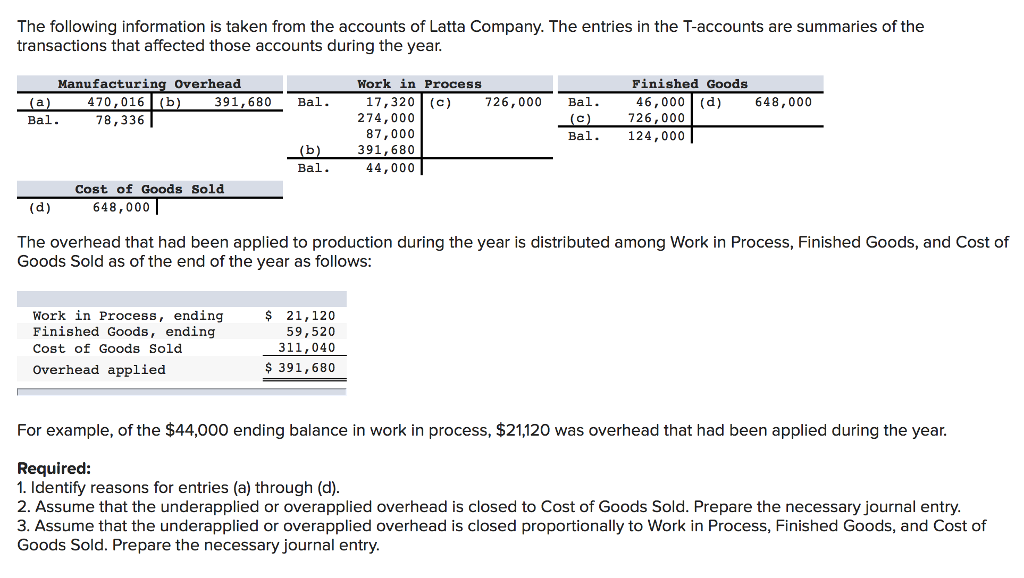
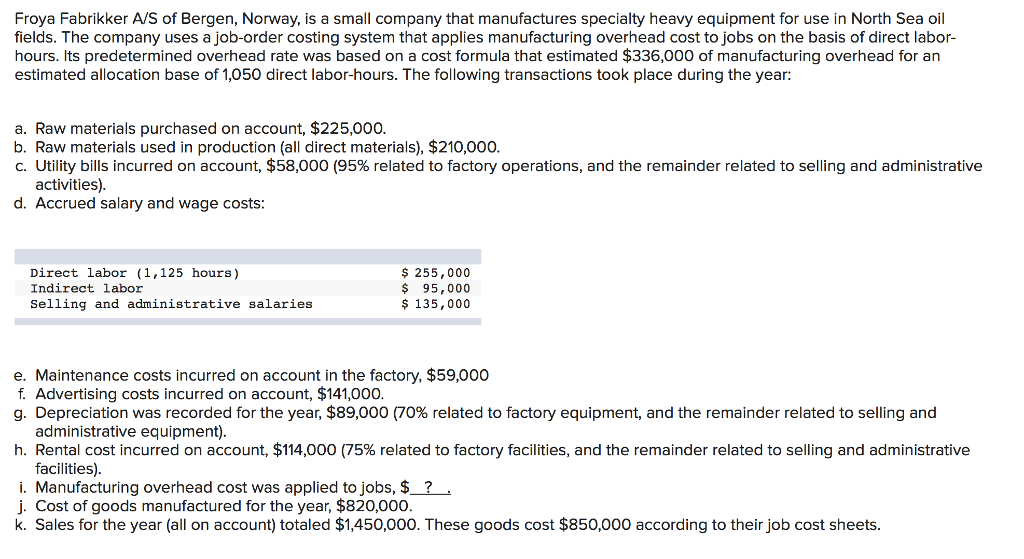
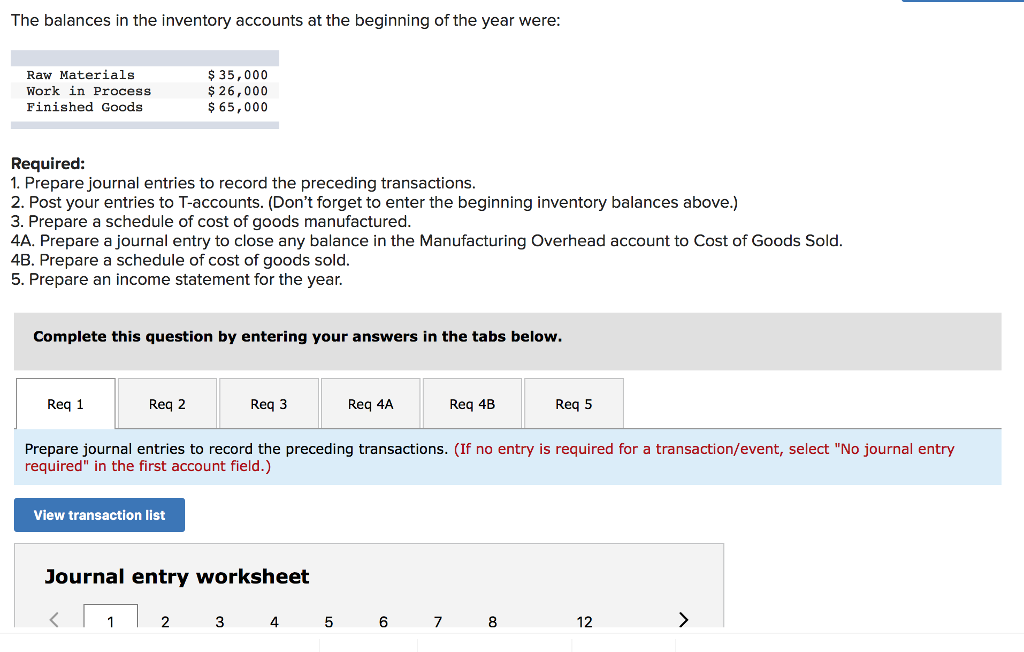
Bunnell Corporation is a manufacturer that uses job-order costing. On January 1, the company's inventory balances were as follows: Raw materials$50,500 Work in process 25,000 Finished goods38,100 The company applies overhead cost to jobs on the basis of direct labor-hours. For the current year, the company's predetermined overhead rate of $11.75 per direct labor-hour was based on a cost formula that estimated $470,000 of total manufacturing overhead for an estimated activity level of 40,000 direct labor-hours. The following transactions were recorded for the year: a. Raw materials were purchased on account, $592,000. b. Raw materials use in production, $557,000. All of of the raw materials were used as direct materials. c. The following costs were accrued for employee services: direct labor, $420,000; indirect labor, $150,000; selling and administrative salaries, $295,000. d. Incurred various selling and administrative expenses (e.g., advertising, sales travel costs, and finished goods warehousing), $381,000. e. Incurred various manufacturing overhead costs (e.g., depreciation, insurance, and utilities), $320,000. f. Manufacturing overhead cost was applied to production. The company actually worked 41,000 direct labor-hours on all jobs during the year. g. Jobs costing $1,399,450 to manufacture according to their job cost sheets were completed during the year. h. Jobs were sold on account to customers during the year for a total of $2,925,000. The jobs cost $1,409,450 to manufacture according to their job cost sheets. 13. Assuming that the company closes its underapplied or overapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold, what is the adjusted cost of goods sold for the year? Adjusted cost of goods sold The following information is taken from the accounts of Latta Company. The entries in the T-accounts are summaries of the transactions that affected those accounts during the year Manufacturing Overhead Work in Process Finished Goods 46,000 (d) 726,000 470,016 (b 391,680 Bal. 17,320 (c) 726,000 Bal 648,000 274,000 87,000 391,680 44,000 Bal. 78,336 Bal. 124,000 Bal. Cost of Goods Sold 648,000 The overhead that had been applied to production during the year is distributed among Work in Process, Finished Goods, and Cost of Goods Sold as of the end of the year as follows: Work in Process, ending Finished Goods, ending Cost of Goods Sold $21,120 59,520 311,040 $ 391,680 Overhead applied For example, of the $44,000 ending balance in work in process, $21,120 was overhead that had been applied during the year. Required: 1. Identify reasons for entries (a) through (d) 2. Assume that the underapplied or overapplied overhead is closed to Cost of Goods Sold. Prepare the necessary journal entry. 3. Assume that the underapplied or overapplied overhead is closed proportionally to Work in Process, Finished Goods, and Cost of Goods Sold. Prepare the necessary journal entry Froya Fabrikker A/S of Bergen, Norway, is a small company that manufactures specialty heavy equipment for use in North Sea oil fields. The company uses a job-order costing system that applies manufacturing overhead cost to jobs on the basis of direct labor- hours. Its predetermined overhead rate was based on a cost formula that estimated $336,000 of manufacturing overhead for an estimated allocation base of 1,050 direct labor-hours. The following transactions took place during the year: a. Raw materials purchased on account, $225,000. b. Raw materials used in production (all direct materials), $210,000 C. Utility bills incurred on account, $58,000 (95% related to factory operations, and the remainder related to selling and administrative activities) d. Accrued salary and wage costs Direct labor (1,125 hours) Indirect labor Selling and administrative salaries $ 255,000 $ 95,000 $ 135,000 e. Maintenance costs incurred on account in the factory, $59,000 f. Advertising costs incurred on account, $141,000. g. Depreciation was recorded for the year, $89,000 (70% related to factory equipment, and the remainder related to selling and administrative equipment) h. Rental cost incurred on account, $114,000 (75% related to factory facilities, and the remainder related to selling and administrative facilities). i. Manufacturing overhead cost was applied to jobs, $?_ j. Cost of goods manufactured for the year, $820,000 k. Sales for the year (all on account) totaled $1,450,000. These goods cost $850,000 according to their job cost sheets The balances in the inventory accounts at the beginning of the year were: Raw Materials Work in Process Finished Goods $35,000 $26,000 $ 65,000 Required: 1. Prepare journal entries to record the preceding transactions 2. Post your entries to T-accounts. (Don't forget to enter the beginning inventory balances above.) 3. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured 4A. Prepare a journal entry to close any balance in the Manufacturing Overhead account to Cost of Goods Sold 4B. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods sold . Prepare an income statement for the year Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req 1 Req 2 Req 3 Req 4A Req 4B Req 5 Prepare journal entries to record the preceding transactions. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) View transaction list Journal entry worksheet 4 6 7 12











