Question
C++ Code Help Edit the following codes or code to get the desired output: First Code: #include #include #include #define TOTAL_THREADS 2 int count; int
C++ Code Help
Edit the following codes or code to get the desired output:
First Code:
#include
#include
#include
#define TOTAL_THREADS 2
int count;
int turn; // Shared variable, indicates
// whose turn it is to execute
bool interested[TOTAL_THREADS]; // Shared variable, indicates
// processes interested in executing
// The thread_id will be either 0 or 1
void enter_region(int thread_id)
{
int other; // ID of the other thread
other = 1 - thread_id; // The oposite of thread_id
// TODO: Add the code to indicate the
// thread's interest in executing.
// TODO: Indicate the thread's turn to execute next
// TODO: Busy wait until it is the thread's turn to execute
}
void leave_region(int thread_id)
{
// TODO: Add the code to set the flag
// indicating that the thread has
// exited the critical region.
}
void* myFunction(void* arg)
{
int thread_id = *((int*) arg);
for(unsigned int i = 0; i
// TODO:
// Make sure that the thread waits for its turn
// before it enters the critical region.
//
// HINT: You need one function call
// Beginning of the critical region
count++;
std::cout
// Random wait - This code is just to ensure that the threads
// show data sharing problems
int max = rand() % 100000;
for (int x = 0; x
// End of random wait code
// End of the critical region
// TODO:
// Make sure that the other thread gets a turn
//
// HINT: You need one function call
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
// HINT: It is not necessary to make any changes in main()
int main()
{
int rc[TOTAL_THREADS];
pthread_t ids[TOTAL_THREADS];
int args[TOTAL_THREADS];
count = 0;
for(unsigned int i = 0; i
args[i] = i;
rc[i] = pthread_create(&ids[i], NULL, myFunction, (void*) &args[i]);
}
for(unsigned int i = 0; i
pthread_join(ids[i], NULL);
}
std::cout
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
Second Code:
#include
#include
#include
#define TOTAL_THREADS 4
int count;
pthread_mutex_t the_mutex; // phread mutex variable
void* myFunction(void* arg)
{
int actual_arg = *((int*) arg);
for(unsigned int i = 0; i
// TODO:
// Use a Pthread mutex to control
// access to the critical region
// Beginning of the critical region
count++;
std::cout
// Random wait - This code is just to ensure that the threads
// show data sharing problems
int max = rand() % 100000;
for (int x = 0; x
// End of random wait code
// End of the critical region
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main()
{
int rc[TOTAL_THREADS];
pthread_t ids[TOTAL_THREADS];
int args[TOTAL_THREADS];
// TODO: Initialize the pthread mutex here
count = 0;
for(unsigned int i = 0; i
args[i] = i;
rc[i] = pthread_create(&ids[i], NULL, myFunction, (void*) &args[i]);
}
for(unsigned int i = 0; i
pthread_join(ids[i], NULL);
}
std::cout
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
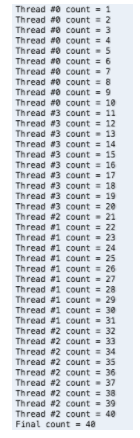
Order of threads does not have to be exact but final count must be 40
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


