c) Exercise 3: What is the Net Present Value for Project 1? See circle on printed exercise. If NPV is negative, place a minus sign in front of your answer.
d) Exercise 3: What is the Net Present Value for Project 2? See circle on printed exercise. If NPV is negative, place a minus sign in front of your answer.
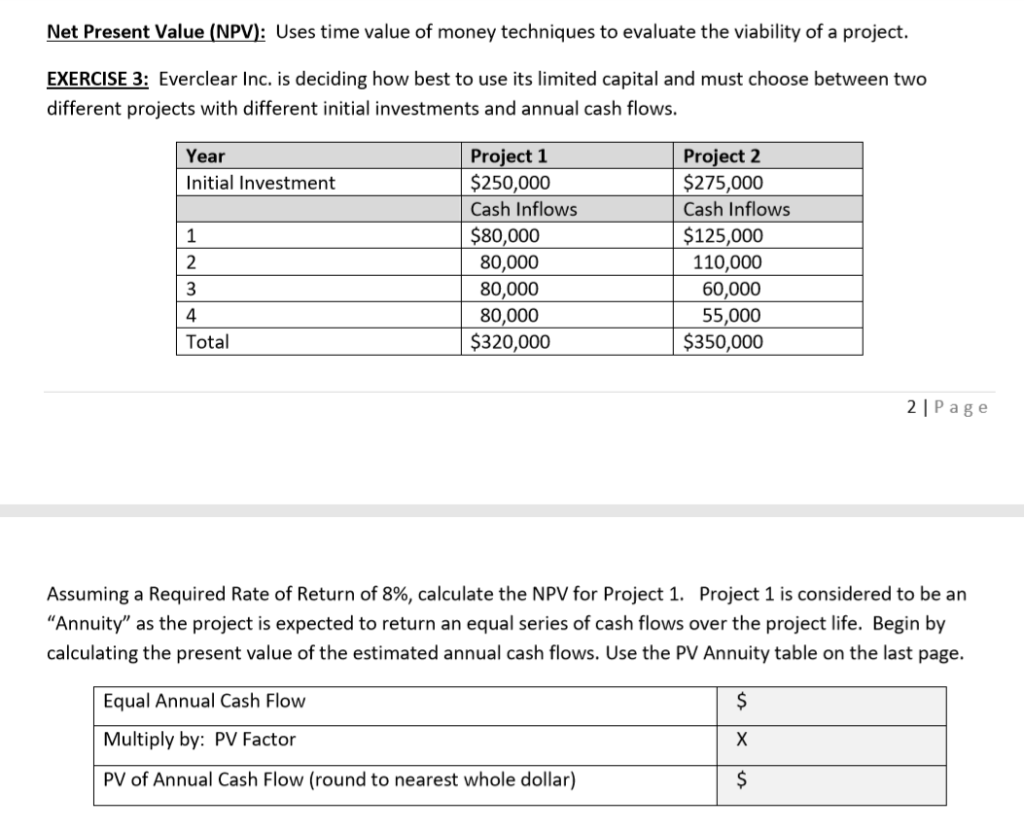
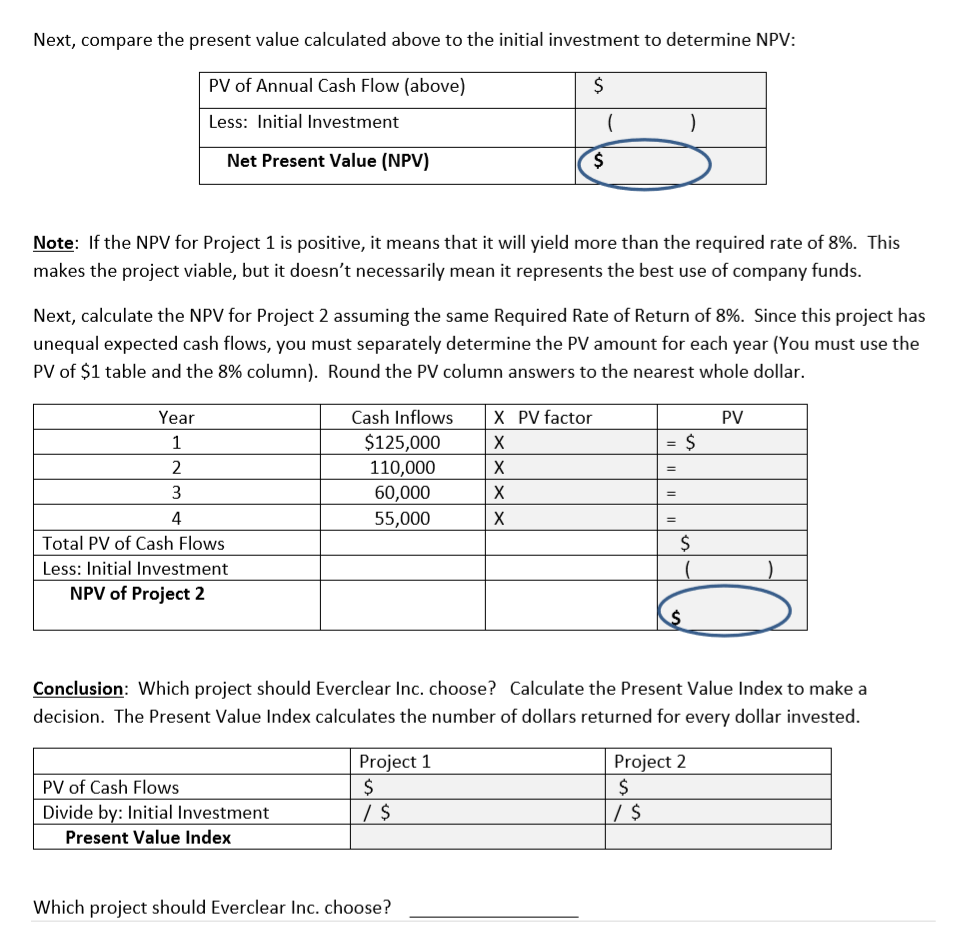
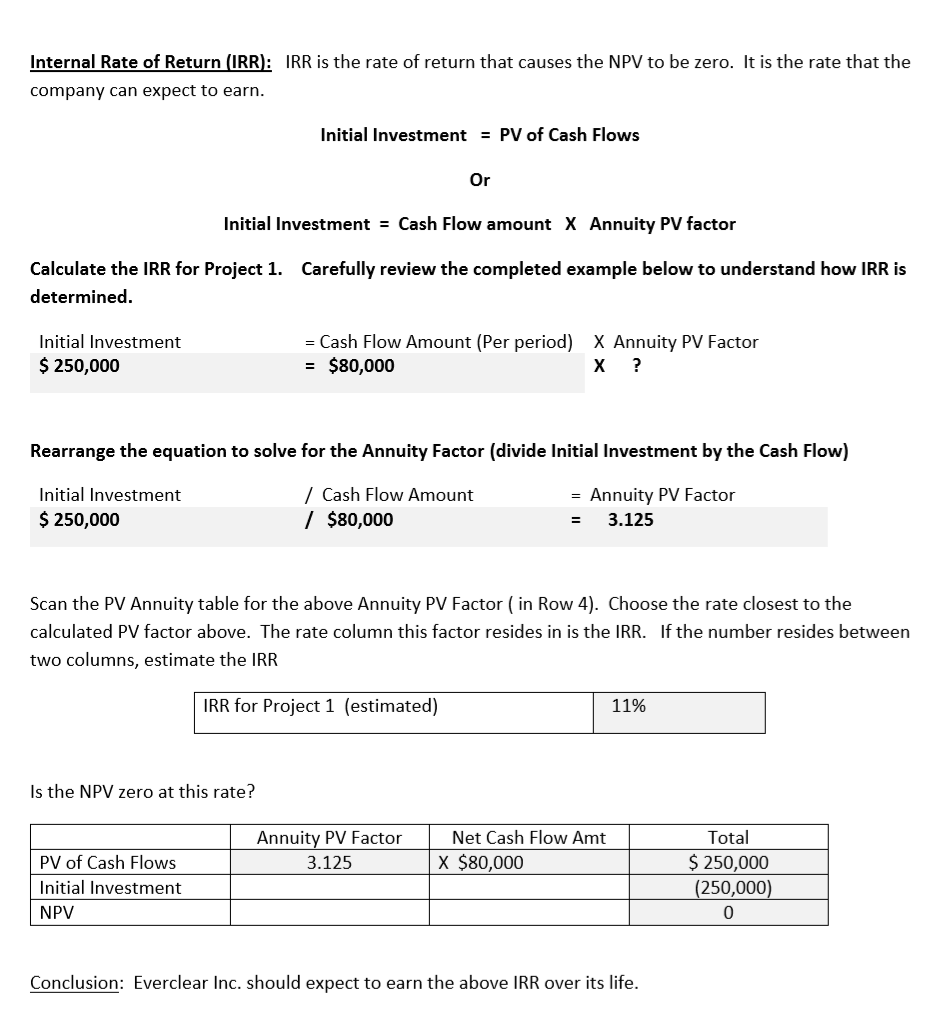
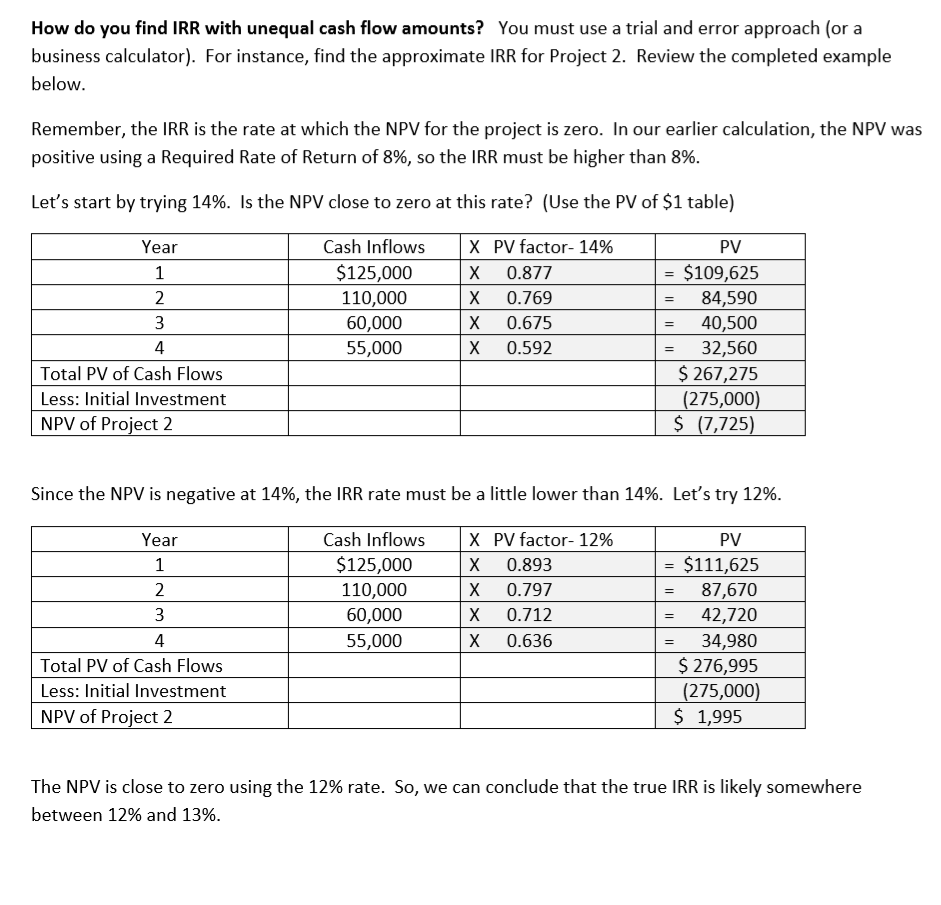
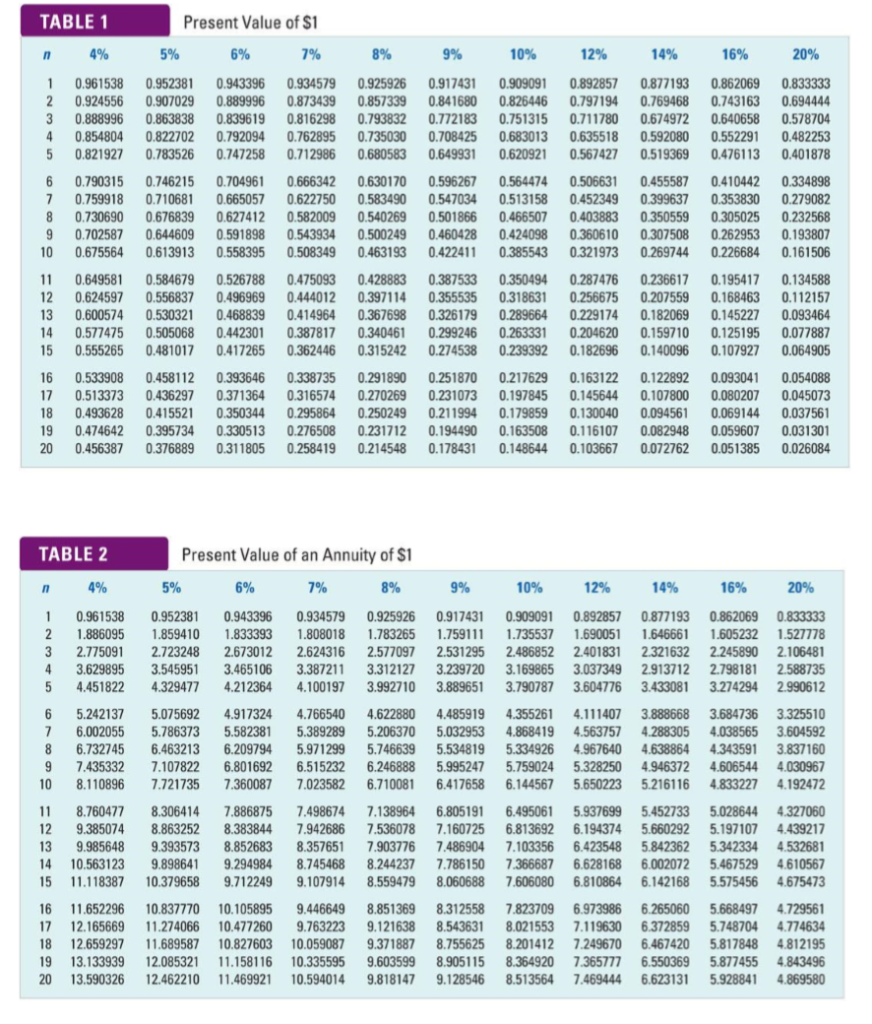
Net Present Value (NPV): Uses time value of money techniques to evaluate the viability of a project EXERCISE 3: Everclear Inc. is deciding how best to use its limited capital and must choose between two different projects with different initial investments and annual cash flows. Project 1 $250,000 Year Project 2 $275,000 Initial Investment Cash Inflows Cash Inflows $125,000 110,000 60,000 55,000 $350,000 $80,000 1 2 80,000 80,000 4 80,000 Total $320,000 2 | Page Assuming a Required Rate of Return of 8%, calculate the NPV for Project 1. Project 1 is considered to be an "Annuity" as the project is expected to return an equal series of cash flows over the project life. Begin by calculating the present value of the estimated annual cash flows. Use the PV Annuity table on the last page. Equal Annual Cash Flow Multiply by: PV Factor X PV of Annual Cash Flow (round to nearest whole dollar) Next, compare the present value calculated above to the initial investment to determine NPV: PV of Annual Cash Flow (above) S Less: Initial Investment Net Present Value (NPV) $ Note: If the NPV for Project 1 is positive, it means that it will yield more than the required rate of 8%. This makes the project viable, but it doesn't necessarily mean it represents the best use of company funds. Next, calculate the NPV for Project 2 assuming the same Required Rate of Return of 8%. Since this project has unequal expected cash flows, you must separately determine the PV amount for each year (You must use the PV of $1 table and the 8% column). Round the PV column answers to the nearest whole dollar. Year Cash Inflows X PV factor PV $125,000 = S 1 X X 2 110,000 = 3 60,000 X 4 55,000 X $ Total PV of Cash Flows Less: Initial Investment ( NPV of Project 2 Conclusion: Which project should Everclear Inc. choose? Calculate the Present Value Index to make a decision. The Present Value Index calculates the number of dollars returned for every dollar invested Project 2 $ / S Project 1 $ / $ PV of Cash Flows Divide by: Initial Investment Present Value Index Which project should Everclear Inc. choose? Internal Rate of Return (IRR): IRR is the rate of return that causes the NPV to be zero. It is the rate that the company can expect to earn. Initial Investment = PV of Cash Flows Or Initial Investment = Cash Flow amount X Annuity PV factor Calculate the IRR for Project 1. determined Carefully review the completed example below to understand how IRR is Initial Investment = Cash Flow Amount (Per period) $80,000 X Annuity PV Factor ? $ 250,000 Rearrange the equation to solve for the Annuity Factor (divide Initial Investment by the Cash Flow) Initial Investment /Cash Flow Amount Annuity PV Factor = / $80,000 $250,000 3.125 - Scan the PV Annuity table for the above Annuity PV Factor ( in Row 4). Choose the rate closest to the calculated PV factor above. The rate column this factor resides in is the IRR. If the number resides between two columns, estimate the IRR IRR for Project 1 (estimated) 11% Is the NPV zero at this rate? Net Cash Flow Amt Total Annuity PV Factor $ 250,000 (250,000) PV of Cash Flows X $80,000 3.125 Initial Investment NPV 0 Conclusion: Everclear Inc. should expect to earn the above IRR over its life. How do you find IRR with unequal cash flow amounts? You must use a trial and error approach (or a business calculator). For instance, find the approximate IRR for Project 2. Review the completed example below Remember, the IRR is the rate at which the NPV for the project is zero. In our earlier calculation, the NPV was positive using a Required Rate of Return of 8%, so the IRR must be higher than 8%. Let's start by trying 14%. Is the NPV close to zero at this rate? (Use the PV of $1 table) PV Cash Inflows X PV factor- 14% Year $125,000 $109,625 84,590 40,500 1 X 0.877 2 110,000 0.769 60,000 55,000 3 X 0.675 0.592 4 X 32,560 = $267,275 (275,000) $ (7,725) Total PV of Cash Flows Less: Initial Investment NPV of Project 2 Since the NPV is negative at 14%, the IRR rate must be a little lower than 14%. Let's try 12%. Cash Inflows X PV factor- 12% Year PV $125,000 $111,625 87,670 42,720 1 X 0.893 2 110,000 X 0.797 3 60,000 0.712 0.636 4 55,000 X 34,980 $276,995 (275,000) $ 1,995 Total PV of Cash Flows Less: Initial Investment NPV of Project 2 The NPV is close to zero using the 12% rate. So, we can conclude that the true IRR is likely somewhere between 12% and 13% TABLE 1 Present Value of $1 4% 5% 6% 7% 8% 9% 10% 12% 14% 16% 20% 0.943396 0.889996 0.839619 0.909091 0.826446 0.751315 0.877193 0.769468 0.674972 0.862069 0.743163 0.925926 0.857339 0.793832 0.917431 0.841680 O.772183 0.892857 0.961538 2 0.924556 1 0.952381 0.934579 0.873439 0.816298 0.833333 0.694444 0.907029 0.797194 3 0.888996 0.863838 0.711780 0.640658 0.578704 4 0.854804 0.822702 0.792094 0.762895 O.735030 0.708425 0.683013 0.635518 0.592080 0.552291 0.482253 0.680583 5 0.821927 0.783526 0.747258 0.712986 0.649931 0.620921 0.567427 0.519369 0.476113 0.401878 0.666342 0.622750 0.596267 0.547034 0.501866 0.506631 0.452349 0.704961 0.630170 0.455587 0.410442 6 0.790315 0746215 0.564474 0.334898 0.513158 0.279082 7 0.759918 0.710681 0.665057 0.583490 0.399637 0.353830 0.350559 8 0.730690 0.676839 0.627412 0.582009 0.540269 0.466507 0.403883 0.305025 0.232568 0.193807 0.161506 9 0.702587 0.644609 0.591898 0.543934 0.500249 0.460428 0.424098 0.360610 0.307508 0.262953 10 0.675564 0.613913 0.558395 0.508349 0.463193 0.422411 0.385543 0.321973 0.269744 0.226684 0.526788 0.496969 0.649581 12 0.600574 0.577475 11 0.584679 0.475093 0.444012 0.428883 0.387533 0.355535 0.350494 0.318631 0.287476 0.256675 0.229174 0.236617 0.195417 0.168463 .134588 0.397114 0.112157 0.624597 0.556837 0.207559 13 0.530321 0.468839 0.414964 0.367698 0.326179 0.289664 0.182069 0.145227 0.093464 14 0.505068 0.442301 0.387817 0.340461 0.299246 0.263331 0.204620 0.159710 0.125195 0.077887 0.239392 0.362446 0.315242 0.182696 0.140096 0.107927 0.064905 15 0.555265 0.481017 0.417265 0.274538 0.093041 16 0.533908 17 0.458112 0.393646 0.338735 0.291890 0.251870 0.217629 0.163122 0.122892 0.054088 0.513373 0.436297 0.371364 0.316574 0.270269 0.231073 0.197845 0.145644 0.107800 0.080207 0.045073 18 0.493628 0.474642 0.415521 0.350344 0.295864 0.250249 0.231712 0.214548 0.211994 0.179859 0.130040 0.094561 0.069144 0.037561 19 0.395734 0.330513 0.276508 0.194490 0.163508 0.116107 0.082948 0.059607 0.031301 0.376889 0.258419 0.148644 0.103667 0.051385 0.026084 20 0.456387 0.311805 0.178431 0.072762 Present Value of an Annuity of $1 TABLE 2 4% 6% 7% 9% 14% 16% 5% 8% 10% 12% 20% n 0.961538 0.952381 0.943396 0.934579 0.925926 0.917431 0.909091 0.892857 0.877193 0.862069 0.833333 1.886095 1.783265 1.690051 1.605232 2 1.859410 1.833393 1.808018 1.759111 1.735537 1.646661 1.527778 2.486852 3.169865 2.106481 2.588735 2.990612 2.775091 2.723248 2.673012 2.624316 2.577097 2.531295 2.401831 2.321632 2.245890 3.54595 3.629895 3.465106 3.387211 3.312127 3.239720 3.037349 4 2.913712 2.798181 3.43308 5 4.451822 4.329477 4.212364 4.100197 3.992710 3.889651 3.790787 3.604776 3.274294 6 4.766540 4.622880 3.888668 3.684736 5.242137 5.075692 4.917324 4.485919 4.355261 4.111407 3.325510 5.58238 6.209794 7 6.002055 5.786373 5.389289 5.206370 5.032953 4.868419 4.563757 4.288305 4.038565 3.604592 6.732745 5.534819 3.837160 6.463213 5.971299 5.746639 5.334926 4.967640 5.328250 4.638864 4.343591 7.435332 7.107822 6.801692 6.515232 6.246888 5.995247 5.759024 4.946372 4.606544 4.030967 10 4.192472 8.110896 7.721735 7.360087 7.023582 6.710081 6.417658 .144567 5.650223 5.216116 4.833227 7.498674 11 8.760477 8.306414 886875 7.138964 6.805191 6.495061 5.937699 5.452733 5.028644 4.327060 7.536078 6.813692 12 9.385074 9.985648 10.563123 8.863252 8.383844 7.942686 7.160725 6.194374 5.660292 6.423548 5.842362 6.628168 5.197107 4.439217 13 9.393573 8.852683 8.357651 7.903776 7.486904 7.103356 7.366687 5.342334 4.532681 8.745468 9.898641 9.294984 8.244237 6.002072 5.467529 4.610567 14 7.786150 8.060688 15 11.118387 10.379658 9.712249 9.107914 8.559479 7.606080 6.81 0864 6.142168 5.575456 4.675473 11.652296 12.165669 10.105895 9.446649 8.851369 .121 638 8.312558 8.54363 8.755625 7.823709 16 10.837770 6.973986 6.265060 5.668497 4.729561 17 11.274066 10.477260 9.763223 8.021553 8.201412 7.119630 6.372859 5.748704 4.774634 12.659297 13.133939 20 18 11.689587 10.827603 10.059087 9.371887 7.249670 6.467420 6.550369 5.817848 4.812195 19 12.085321 11.158116 10.335595 9.603599 8.905115 8.364920 7.365777 5.877455 4.843496 12.462210 11.469921 9.128546 8.513564 4.869580 13.590326 10.594014 9.818147 7.469444 6.623131 5.928841











