Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
C++ For your second programming assignment, you will be writing an object-oriented C++ program that lets the user play against the computer in a variation
C++




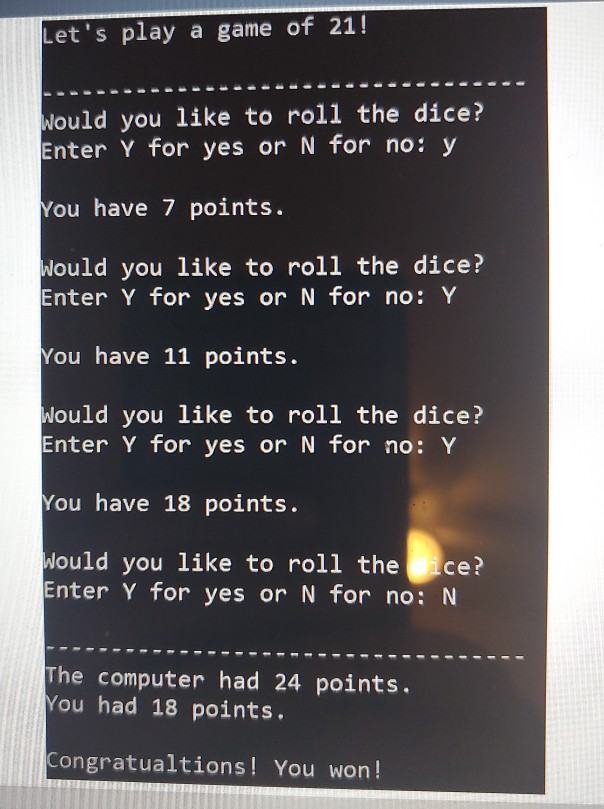
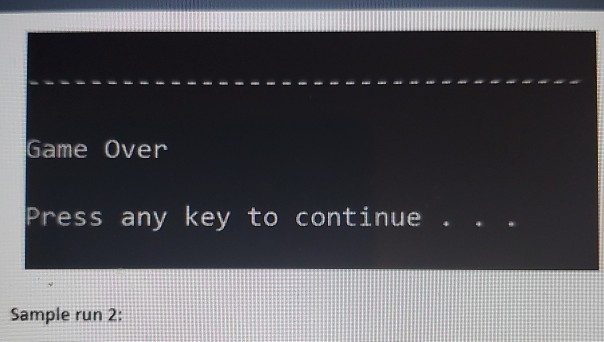
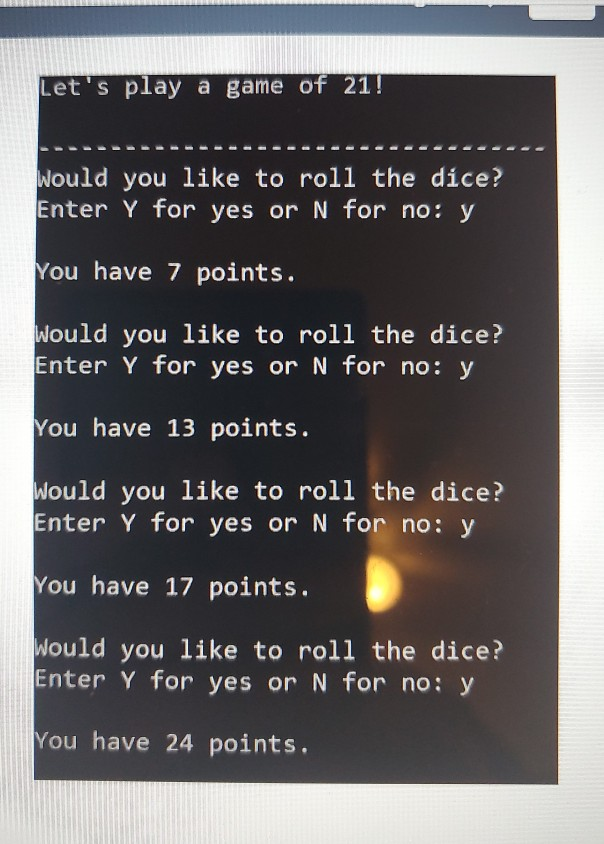
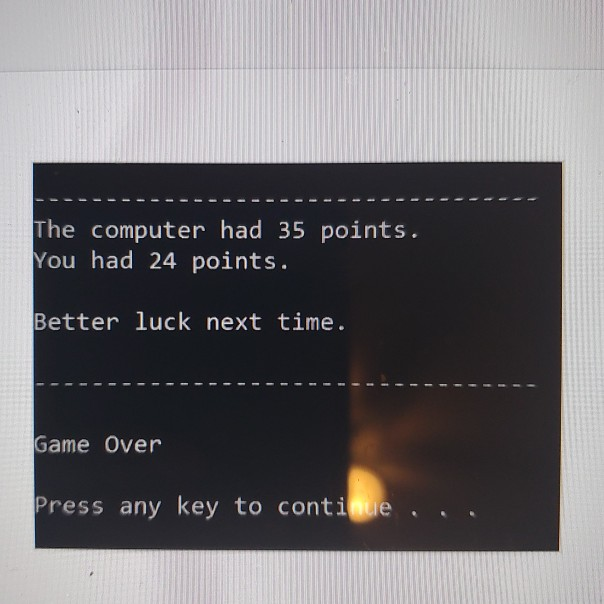
For your second programming assignment, you will be writing an object-oriented C++ program that lets the user play against the computer in a variation of the popular blackjack card game. In this variation of the game, two six-sided dice are used instead of cards. The dice are rolled, and the player tries to beat the computer's hidden total without going over 21. + Each round of the game is performed as an iteration of a loop that repeats as long as the player agrees to roll the dice, and the player's total does not exceed 21. + At the beginning of each round, the program will ask the user whether they want to roll the dice to accumulate points. During each round, the program simulates the rolling of two six-sided dice. It rolls the dice first for the computer, and then it asks the user if he or she wants to roll. + The loop keeps a running total of both the computer and the user's points. + The computer's total should remain hidden until the loop has finished. + After the loop has finished, the computer's total is revealed, and the player with the most points without going over 21 wins. Neither player wins if there is a tie or if both players go over 21. You will be implementing a class named Die (singular form of dice). Design the class from the following UML diagram: Die -sides: int // Number of sides on the die -value: int // The die's value > +Die(num Sides: int) +setSides(numSides: int) +rollo +getsides(): int +getValue(): int Here is a brief description of the constructor and member functions: > +Die(numSides: int) The constructor accepts an argument for the number of sides for the die and performs an initial roll of the die. +setSides(numSides: int) The setSides member function accepts an argument for the number of sides for the die and performs a roll of the die troll) The roll member function simulates the rolling of the die. For example, if the number of sides for the die is 6, then the die's value will be randomly chosen between 1-6 -sides: int // Number of sides on the die -value: int // The die's value > +Die(numSides: int) +setSides(numSides: int) +roll) +getSides(): int +getValue(): int Here is a brief description of the constructor and member functions: > +Die(numSides: int) The constructor accepts an argument for the number of sides for the die and performs an initial roll of the die. +setSides(num Sides: int) The setSides member function accepts an argument for the number of sides for the die and performs a roll of the die. trollo) The roll member function simulates the rolling of the die. For example, if the number of sides for the die is 6, then the die's value will be randomly chosen between 1-6. +getSides(): int The getSides member function returns the number of sides for the die. +getValue(): int The getValue member function returns the die's value. After you create the Die class, then you can start working on the logic of the game itself. You can either implement all of the game logic in the main function, or you can create other functions ("regular" functions that aren't part of the Die class). The first thing you need to do is create two Die objects, because two six-sided dice are needed to play the game. NOTE: It's important to keep in mind that this Die class could be used for other applications besides this Blackjack game that you are implementing. For example, it could be used to implement a game that requires three dice, each with ten sides. If the Die class is implemented correctly following the UML diagram, it could be used for any game that uses any number of dice with any number of sides. The code in main is the application in this case a game) that uses the Die class. But the die class is a reusable class that can be used for any game involving dice. Sample Run 1: Let's play a game of 21! Would you like to roll the dice? Enter Y for yes or N for no: y You have 7 points. Would you like to roll the dice? Enter Y for yes or N for no: Y You have 11 points. Would you like to roll the dice? Enter Y for yes or N for no: Y You have 18 points. Would you like to roll the ice? Enter Y for yes or N for no: N The computer had 24 points. You had 18 points. Congratualtions! You won! Game Over Press any key to continue... Sample run 2 Let's play a game of 21! Would you like to roll the dice? Enter Y for yes or N for no: y You have 7 points. Would you like to roll the dice? Enter y for yes or N for no: y You have 13 points. Would you like to roll the dice? Enter y for yes or N for no: y You have 17 points. Would you like to roll the dice? Enter y for yes or N for no: y You have 24 points. ------------ The computer had 35 points. You had 24 points. Better luck next time. Game Over Press any key to continues
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


