Question
C++ Playing cards have been in existence in various forms for more than 600 years. They are used for a large number of games of
C++
Playing cards have been in existence in various forms for more than 600 years. They are used for a large number of games of chance and are a favorite subject for exercises in math, statistics, and computer science.
In Europe, and the West, there is a standard card set, called a deck, which is familiar to most people. It consists of 52 cards, divided into 4 subsets, called suits . Each suit consists of 13 cards designated by the names: A (Ace), 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, T (Ten), J (Jack), Q (Queen), K (King). Many card games begin by supplying each player with a small set of cards (randomly extracted from the deck) called a hand.
In this exercise, you design data types to represent a deck and a hand of cards. Later you will revisit these classes to elaborate the rules and add graphics. Figure 6.7 suggests one way of representing these classes.
Figure 6.7. Card Game UML
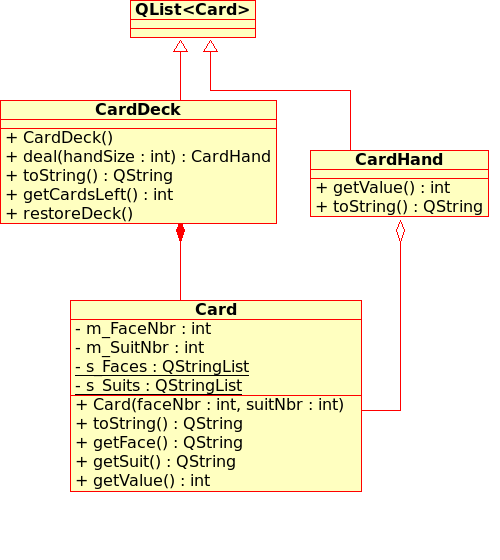
Following are some hints:
The CardDeck constructor generates a complete deck of cards in a convenient order.
CardDeck::deal(int k) should use the random() function from
Initialize the random() function from the system clock so that the results will be different each time you run the application. The syntax is
srandom(time(0));
Evaluate the hand, using the rules of the game of bridge : Ace = 4, King = 3, Queen = 2, Jack = 1; all other cards have zero value. You can use this formula to calculate the return values for the getValue() functions.
Example 6.29 is a piece of client code that you can start with, for testing your classes.
Example 6.29. src/cardgame/datastructure/cardgame-client.cpp
[ . . . . ] #include "carddeck.h" #include#include int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { QApplication app(argc, argv); QTextStream cout(stdout); CardDeck deck; CardHand hand; int handSize, playerScore, progScore; cout progScore)?"You":"I") QList CardDeck +CardDeck() + deal(handSize: int) : CardHand +toString): QString + getCardsLeft): int + restoreDeck) CardHand +getValue): int +toString) QString Card - m FaceNbr: int - m SuitNbr int - S Faces: QStringList s Suits: QStringList + Card(faceNbr : int, suitNbr int) +toString): QString + getFace() : QString + getSuit() : QString + getValue): int QList CardDeck +CardDeck() + deal(handSize: int) : CardHand +toString): QString + getCardsLeft): int + restoreDeck) CardHand +getValue): int +toString) QString Card - m FaceNbr: int - m SuitNbr int - S Faces: QStringList s Suits: QStringList + Card(faceNbr : int, suitNbr int) +toString): QString + getFace() : QString + getSuit() : QString + getValue): int
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


