Question: C++ PROGRAMMING Hello, I'm working on c++ and I just need to make changes with DateImp.cpp so that it prints out the right output when
C++ PROGRAMMING
Hello, I'm working on c++ and I just need to make changes with DateImp.cpp so that it prints out the right output when the user inputs something that's not an integer. Please DO NOT modify date.h and main.cpp file!!!
Prompt:
Develop an implementation file (call it DateImp.cpp) for the modified Date.h. DO NOT MODIFY THE DATE.h OR MAIN.cpp FILES!!! Your solution should have the following overloaded operators:
++ Prefix and postfix increment operators. These operators should increment the objects day member.
-- Prefix and postfix decrement operators. These operators should decrement the objects day member.
- Subtraction operator. If one Date object is subtracted from another, the operator should give the number of days between the two dates. For example, if April 10, 2014 is subtracted from April 18, 2014, the result will be 8.
coutss stream insertion operator. This operator should cause the date to be displayed in the form: April 18. 2014
>> cins stream extraction operator. This operator should prompt the user for a date to be stored in a Date object.
The class should detect the following SPECIAL conditions and handle them accordingly:
When a date is set to the last day of the month and incremented, it should become the first day of the following month.
When a date is set to December 31 and incremented, it should become January 1 of the following year.
When a date is set to the first day of the month and decremented, it should become the last day of the previous month.
When a date is set to January 1 and decremented, it should become December 31 of the previous year.
Input validation: The overloaded >> operator should not accept invalid dates. For example:
The date 13/45/2014 should not be accepted.
Valid year range: 1900
Dont forget to validate the 12 months of the year
Dont forget to validate the days of each month
Restrictions: No global variables, No labels or go-to statements, No infinite loops, No break statements
Here are the given date.h and main.cpp files:
Date.h
#ifndef DATE_H
#define DATE_H
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Date;
// Constants
const int NUM_MONTHS = 12;
// Declaration of the Date class
class Date
{
public:
// Constructors
Date();
Date(int, int, int);
// Mutators
void setMonth(int m);
void setDay(int d);
void setYear(int y);
// Other member functions
void showDate1();
void showDate2();
void showDate3();
bool isLeapYear(int);
// Overloaded operators
Date operator ++(); // Prefix ++
Date operator ++(int); // Postfix ++
Date operator --(); // Prefix --
Date operator --(int); // Postfix --
int operator -(const Date &); // Subtraction operator
friend ostream &operator
friend istream &operator >> (istream &, Date &); // Overloaded >> operator
private:
int month; // To hold the month
int day; // To hold the day
int year; // To hold the year
// An array of strings to hold
// the names of the months
string names[NUM_MONTHS];
// An array to hold the number of days
// that each month has.
int numDays[NUM_MONTHS];
// Private member function to assign
// the month names to the names array
void setNames();
// Private member function to assign
// the numbers of days to the numDaus array
void setDays();
};
#endif
main.cpp
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#include "Date.h"
//*************************************
// Function main *
//*************************************
int main()
{
// Demonstrate the overloaded - and
Date d1(2, 2, 2006);
Date d2(11, 10, 2003);
int days = d1 - d2;
cout
// Demonstrate the overloaded ++ operators.
cout
cout
cout
d1.setDay(31);
d1.setMonth(12);
cout
// Demonstrate the overloaded -- operators.
d1.setDay(10);
d1.setMonth(7);
d1.setYear(2003);
cout
cout
cout
d1.setDay(1);
d1.setMonth(1);
d1.setYear(2004);
cout
// Demonstrate the overloaded >> operator.
cin >> d1;
cout
system("pause");
return 0;
}
MY dateImp.cpp FILE (this needs help to be fixed..)
#include
#include
#include "Date.h"
using namespace std;
// Default constructor
Date::Date()
{
setNames();
setDays();
}
// Overloaded constructor
Date::Date(int m, int d, int y)
{
setMonth(m);
setDay(d);
setYear(y);
setNames();
setDays();
}
// Private member function setNames assigns the names of the months to the names array
void Date::setNames()
{
names[0] = "January";
names[1] = "February";
names[2] = "March";
names[3] = "April";
names[4] = "May";
names[5] = "June";
names[6] = "July";
names[7] = "August";
names[8] = "September";
names[9] = "October";
names[10] = "November";
names[11] = "December";
}
// Member function setMonth
void Date::setMonth(int m)
{
if (m >= 1 && m
month = m;
else
{
cout
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
// Member function setDay
void Date::setDay(int d)
{
if (d >= 1 && d
day = d;
else
{
cout
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
// Member function setYear
void Date::setYear(int y)
{
if (y >= 1900 && y
year = y;
else
{
cout
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
// Member function showDate1 : Ex. MM/DD/YY
void Date::showDate1()
{
cout
}
// Member function showDate2 : Ex. December 25, 2014
void Date::showDate2()
{
cout
}
// Member function showDate3 : Ex. 25 December, 2014
void Date::showDate3()
{
cout
}
// Member function isLeapYear
bool Date::isLeapYear(int y)
{
bool leap = false;
if ((y % 400 == 0 || y % 100 != 0) && (y % 4 == 0))
leap = true;
return leap;
}
// Prefix increment operator
Date Date::operator ++()
{
++day;
return *this;
}
// Postfix increment operator
Date Date::operator ++(int)
{
Date temp(month, day, year);
day++;
return temp;
}
// Prefix decrement operator
Date Date::operator --()
{
--day;
return *this;
}
// Postfix decrement operator
Date Date::operator --(int)
{
Date temp(month, day, year);
day--;
return temp;
}
// Subtraction operator:
//If one Date object is subtracted from another, the operator
//gives the number of days between the two dates
int Date::operator -(const Date &right)
{
int days = 0;
int ltotal = 0;
int rtotal = 0;
//get total days of left object
for (int i = 1900; i
ltotal += (isLeapYear(i)) ? 366 : 365;
for (int m = 0; m
{
ltotal += numDays[m];
if (isLeapYear(year) && m == 1)
ltotal++;
}
ltotal += day;
//get total days of right object
for (int i = 1900; i
rtotal += (isLeapYear(i)) ? 366 : 365;
for (int m = 0; m
{
rtotal += right.numDays[m];
if (isLeapYear(right.year) && m == 1)
rtotal++;
}
rtotal += right.day;
//subtract right from left;
days = ltotal - rtotal;
return days;
}
// Overloaded
// Operator causes date to display in the form: April 18, 2014
ostream &operator
{
int m = (obj.month - 1
string outMonth = obj.names[m];
strm
return strm;
}
// Overloaded >> operator - cins stream extraction operator
// Operator prompts user for a date to be stored in a Date object
istream &operator >> (istream &strm, Date &obj)
{
cout
strm >> obj.day;
while (obj.day 31)
{
cout
cout
strm >> obj.day;
}
cout
strm >> obj.month;
while (obj.month 12)
{
cout
cout
strm >> obj.month;
}
cout
strm >> obj.year;
while (obj.year 9999)
{
cout
cout
strm >> obj.year;
}
return strm;
}
// Private member function to assign numbers of days to the numDays array
void Date::setDays()
{
numDays[0] = 31;
int m = isLeapYear(year) ? 29 : 28;
numDays[1] = m;
numDays[2] = 31;
numDays[3] = 30;
numDays[4] = 31;
numDays[5] = 30;
numDays[6] = 31;
numDays[7] = 31;
numDays[8] = 30;
numDays[9] = 31;
numDays[10] = 30;
numDays[11] = 31;
}
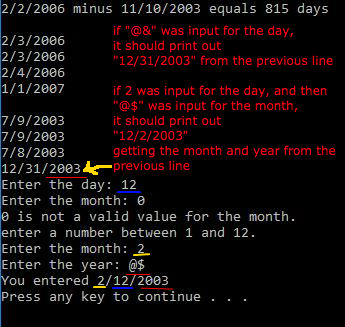
2/2/2006 minus 11/10/2003 equals 815 days 2/3/2006 2/3/2006 2/4/2006 1/1/2007 if"@&" was input for the day, it should print out "12/31/2003" from the previous line if 2 was input for the day, and thern 7/9/2003 7/9/2003 7/8/2003 " was input for the month, it should print out "12/2/2003" getting the month and year from the 12/31/2003previous line Enter the day: 12 Enter the month: 0 0 is not a valid value for the month. enter a number between 1 and 12. Enter the month 2 Enter the year: @$ You entered 2/12/2003 Press any key to continue
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


