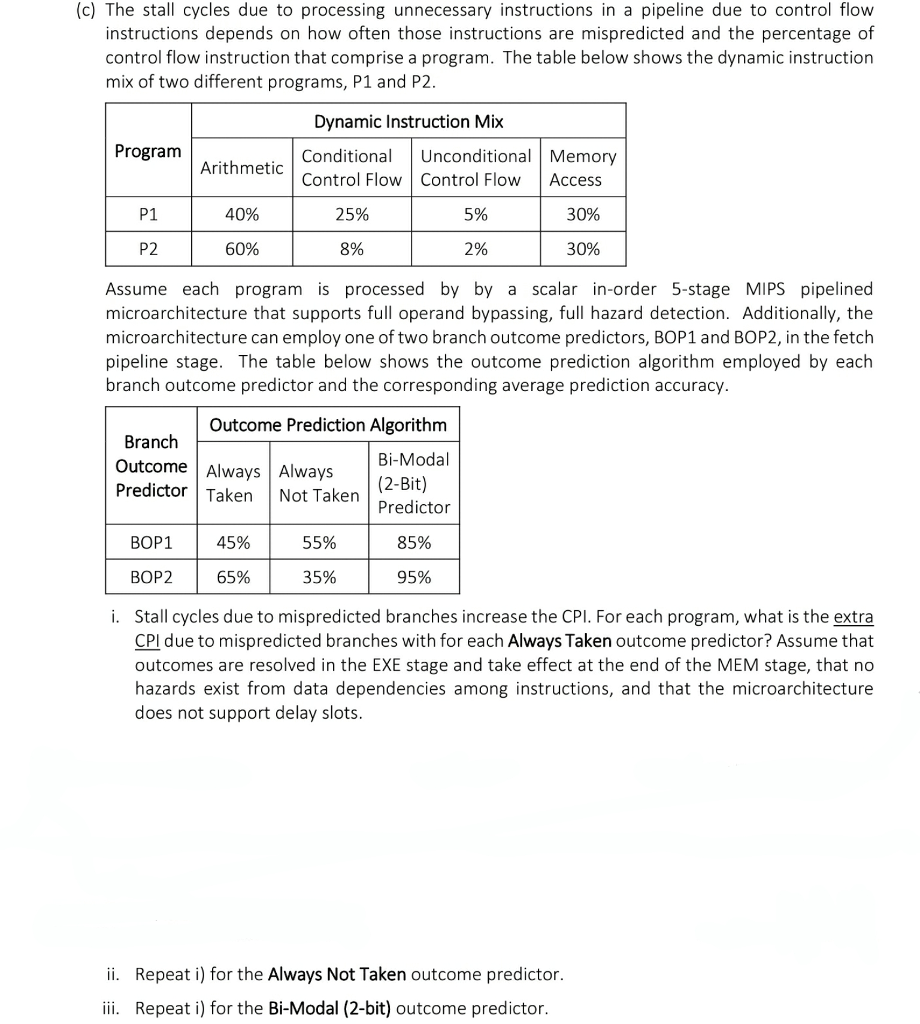
(c) The stall cycles due to processing unnecessary instructions in a pipeline due to control flow instructions depends on how often those instructions are mispredicted and the percentage of control flow instruction that comprise a program. The table below shows the dynamic instruction mix of two different programs, PI and P2. Assume each program is processed by a scalar in-order 5-stage MIPS pipelined microarchitecture that supports full operand bypassing, full hazard detection. Additionally, the microarchitecture can employ one of two branch outcome predictors, BOP1 and BOP2, in the fetch pipeline stage. The table below shows the outcome prediction algorithm employed by each branch outcome predictor and the corresponding average prediction accuracy. i. Stall cycles due to mispredicted branches increase the CPI. For each program, what is the extra CPI due to mispredicted branches with for each Always Taken outcome predictor? Assume that outcomes are resolved in the EXE stage and take effect at the end of the MEM stage, that no hazards exist from data dependencies among instructions, and that the microarchitecture does not support delay slots. ii. Repeat i) for the Always Not Taken outcome predictor. iii. Repeat i) for the Bi-Modal (2-bit) outcome predictor. (c) The stall cycles due to processing unnecessary instructions in a pipeline due to control flow instructions depends on how often those instructions are mispredicted and the percentage of control flow instruction that comprise a program. The table below shows the dynamic instruction mix of two different programs, PI and P2. Assume each program is processed by a scalar in-order 5-stage MIPS pipelined microarchitecture that supports full operand bypassing, full hazard detection. Additionally, the microarchitecture can employ one of two branch outcome predictors, BOP1 and BOP2, in the fetch pipeline stage. The table below shows the outcome prediction algorithm employed by each branch outcome predictor and the corresponding average prediction accuracy. i. Stall cycles due to mispredicted branches increase the CPI. For each program, what is the extra CPI due to mispredicted branches with for each Always Taken outcome predictor? Assume that outcomes are resolved in the EXE stage and take effect at the end of the MEM stage, that no hazards exist from data dependencies among instructions, and that the microarchitecture does not support delay slots. ii. Repeat i) for the Always Not Taken outcome predictor. iii. Repeat i) for the Bi-Modal (2-bit) outcome predictor







