Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
c. What is the project's NPV if the project's cost of capital is 10% ? NPV (at 10% cost of capital) d. Use the NPV
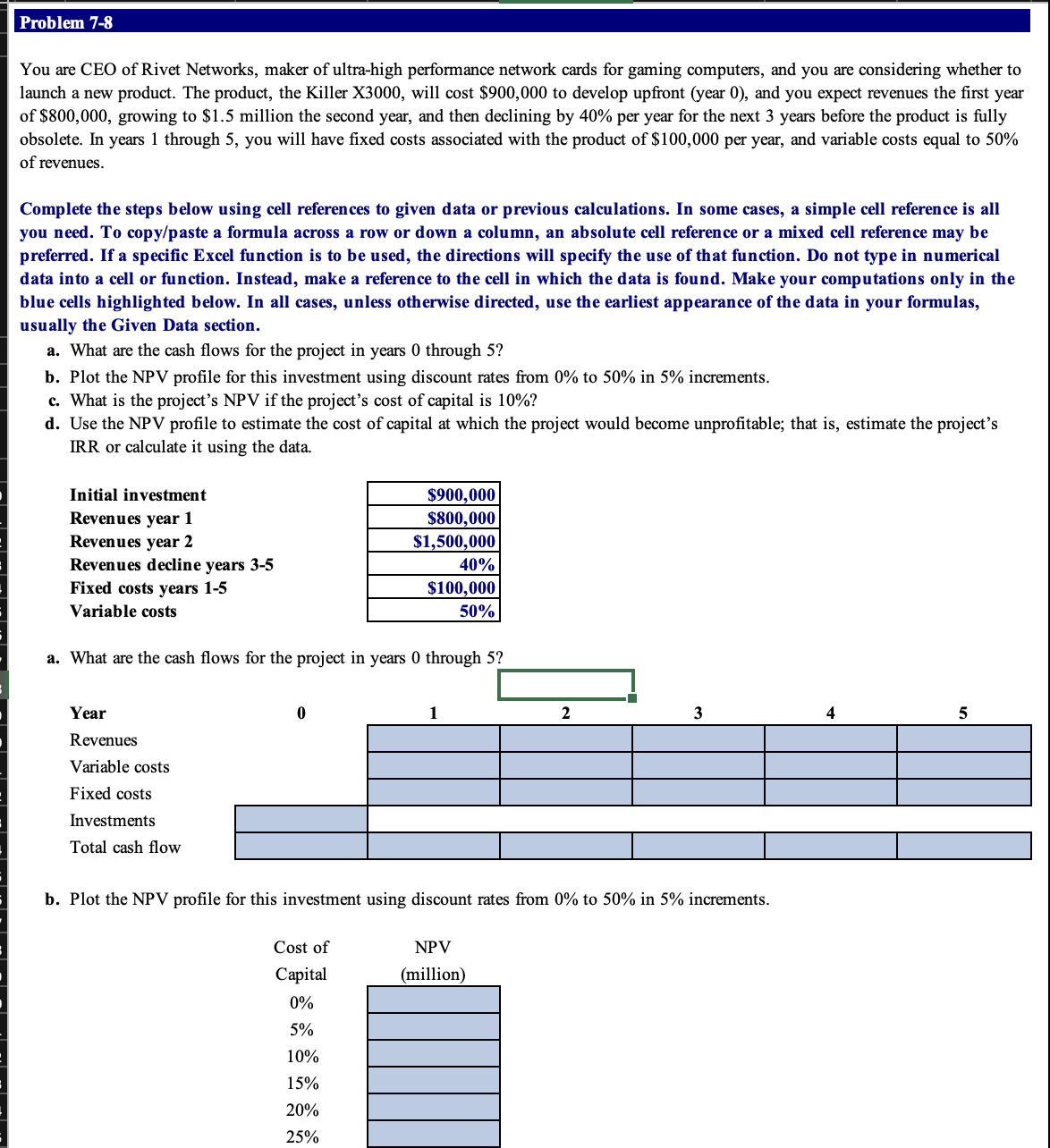

 c. What is the project's NPV if the project's cost of capital is 10% ? NPV (at 10% cost of capital) d. Use the NPV profile to estimate the cost of capital at which the project would become unprofitable; that is, estimate the project's IRR or calculate it using the data. Calculated IRR 1. Start Excel - completed. 2. In cells E20:I20, by using a cell reference, calculate the revenues of the project for years 1 to 5 , respectively (5 pt.). 3. In cells E21:I21, by using cell references, calculate the variable costs of the project for years 1 to 5 , respectively (5 pt.). Note: The outputs of the expression or function you typed in these cells are expected as negative numbers. 4. In cells E22:I22, by using a cell reference, calculate the fixed costs of the project for years 1 to 5 , respectively (5 pt.). Note: The outputs of the expression or function you typed in these cells are expected as negative numbers. 5. In cell D23, by using a cell reference, calculate the investments of the project for year 0 (1 pt.). Note: The output of the expression or function you typed in this cell is expected as a negative number. 6. In cells D24:I24, by using cell references and the function SUM, calculate the total cash flows of the project for years 0 to 5 , respectively (6 pt.). 7. In cell range E30:E40, by using cell references and the function NPV, calculate the NPV of the investment opportunity for cost of capital 0% to 50%, respectively (11 pt.). 8. In cells C42:G53, insert a Line Chart to plot the NPV profile of the investment opportunity. Inserting a Chart You are CEO of Rivet Networks, maker of ultra-high performance network cards for gaming computers, and you are considering whether to launch a new product. The product, the Killer X3000, will cost $900,000 to develop upfront (year 0), and you expect revenues the first year of $800,000, growing to $1.5 million the second year, and then declining by 40% per year for the next 3 years before the product is fully obsolete. In years 1 through 5 , you will have fixed costs associated with the product of $100,000 per year, and variable costs equal to 50% of revenues. Complete the steps below using cell references to given data or previous calculations. In some cases, a simple cell reference is all you need. To copy/paste a formula across a row or down a column, an absolute cell reference or a mixed cell reference may be preferred. If a specific Excel function is to be used, the directions will specify the use of that function. Do not type in numerical data into a cell or function. Instead, make a reference to the cell in which the data is found. Make your computations only in the blue cells highlighted below. In all cases, unless otherwise directed, use the earliest appearance of the data in your formulas, usually the Given Data section. a. What are the cash flows for the project in years 0 through 5 ? b. Plot the NPV profile for this investment using discount rates from 0% to 50% in 5% increments. c. What is the project's NPV if the project's cost of capital is 10% ? d. Use the NPV profile to estimate the cost of capital at which the project would become unprofitable; that is, estimate the project's IRR or calculate it using the data. a. What are the cash flows for the project in years 0 through 5 ? b. Plot the NPV profile for this investment using discount rates from 0% to 50% in 5% increments. 1. Start Excel - completed. 2. In cells E20:I20, by using a cell reference, calculate the revenues of the project for years 1 to 5 , respectively (5 pt.). 3. In cells E21:I21, by using cell references, calculate the variable costs of the project for years 1 to 5 , respectively (5 pt.). Note: The outputs of the expression or function you typed in these cells are expected as negative numbers. 4. In cells E22:I22, by using a cell reference, calculate the fixed costs of the project for years 1 to 5 , respectively (5 pt.). Note: The outputs of the expression or function you typed in these cells are expected as negative numbers. 5. In cell D23, by using a cell reference, calculate the investments of the project for year 0 (1 pt.). Note: The output of the expression or function you typed in this cell is expected as a negative number. 6. In cells D24:I24, by using cell references and the function SUM, calculate the total cash flows of the project for years 0 to 5 , respectively (6 pt.). 7. In cell range E30:E40, by using cell references and the function NPV, calculate the NPV of the investment opportunity for cost of capital 0% to 50%, respectively (11 pt.). 8. In cells C42:G53, insert a Line Chart to plot the NPV profile of the investment opportunity. Inserting a Chart On the Insert tab, in the Charts group, click the arrow next to Insert Line or Area Chart and choose Line Chart. Selecting Data Series Then in Select Data Source window, delete any series created automatically. Add new series for the NPV profile of the investment opportunity using cells E30:E40 for the series values. Do not name the series. Edit Chart Elements Then in Select Data Source window, edit Horizontal Axis Labels using cells D30:D40. Add a chart title and choose the Above Chart option. Replace Chart Title with NPV Profile. Add axis titles. Replace Axis Title for the horizontal axis with Cost of Capital and Axis Title for the vertical axis with NPV. (3 pt.) 9. In cell E57, by using cell references, calculate the NPV of the investment opportunity for a 10% cost of capital (1 pt.). 10. In cell E61, by using cell references and the function IRR, calculate the IRR of the investment opportunity (1 pt.). Note: Do not enter any value for the Guess argument of the function IRR. 11. Save the workbook. Close the workbook and then exit Excel. Submit the workbook as directed
c. What is the project's NPV if the project's cost of capital is 10% ? NPV (at 10% cost of capital) d. Use the NPV profile to estimate the cost of capital at which the project would become unprofitable; that is, estimate the project's IRR or calculate it using the data. Calculated IRR 1. Start Excel - completed. 2. In cells E20:I20, by using a cell reference, calculate the revenues of the project for years 1 to 5 , respectively (5 pt.). 3. In cells E21:I21, by using cell references, calculate the variable costs of the project for years 1 to 5 , respectively (5 pt.). Note: The outputs of the expression or function you typed in these cells are expected as negative numbers. 4. In cells E22:I22, by using a cell reference, calculate the fixed costs of the project for years 1 to 5 , respectively (5 pt.). Note: The outputs of the expression or function you typed in these cells are expected as negative numbers. 5. In cell D23, by using a cell reference, calculate the investments of the project for year 0 (1 pt.). Note: The output of the expression or function you typed in this cell is expected as a negative number. 6. In cells D24:I24, by using cell references and the function SUM, calculate the total cash flows of the project for years 0 to 5 , respectively (6 pt.). 7. In cell range E30:E40, by using cell references and the function NPV, calculate the NPV of the investment opportunity for cost of capital 0% to 50%, respectively (11 pt.). 8. In cells C42:G53, insert a Line Chart to plot the NPV profile of the investment opportunity. Inserting a Chart You are CEO of Rivet Networks, maker of ultra-high performance network cards for gaming computers, and you are considering whether to launch a new product. The product, the Killer X3000, will cost $900,000 to develop upfront (year 0), and you expect revenues the first year of $800,000, growing to $1.5 million the second year, and then declining by 40% per year for the next 3 years before the product is fully obsolete. In years 1 through 5 , you will have fixed costs associated with the product of $100,000 per year, and variable costs equal to 50% of revenues. Complete the steps below using cell references to given data or previous calculations. In some cases, a simple cell reference is all you need. To copy/paste a formula across a row or down a column, an absolute cell reference or a mixed cell reference may be preferred. If a specific Excel function is to be used, the directions will specify the use of that function. Do not type in numerical data into a cell or function. Instead, make a reference to the cell in which the data is found. Make your computations only in the blue cells highlighted below. In all cases, unless otherwise directed, use the earliest appearance of the data in your formulas, usually the Given Data section. a. What are the cash flows for the project in years 0 through 5 ? b. Plot the NPV profile for this investment using discount rates from 0% to 50% in 5% increments. c. What is the project's NPV if the project's cost of capital is 10% ? d. Use the NPV profile to estimate the cost of capital at which the project would become unprofitable; that is, estimate the project's IRR or calculate it using the data. a. What are the cash flows for the project in years 0 through 5 ? b. Plot the NPV profile for this investment using discount rates from 0% to 50% in 5% increments. 1. Start Excel - completed. 2. In cells E20:I20, by using a cell reference, calculate the revenues of the project for years 1 to 5 , respectively (5 pt.). 3. In cells E21:I21, by using cell references, calculate the variable costs of the project for years 1 to 5 , respectively (5 pt.). Note: The outputs of the expression or function you typed in these cells are expected as negative numbers. 4. In cells E22:I22, by using a cell reference, calculate the fixed costs of the project for years 1 to 5 , respectively (5 pt.). Note: The outputs of the expression or function you typed in these cells are expected as negative numbers. 5. In cell D23, by using a cell reference, calculate the investments of the project for year 0 (1 pt.). Note: The output of the expression or function you typed in this cell is expected as a negative number. 6. In cells D24:I24, by using cell references and the function SUM, calculate the total cash flows of the project for years 0 to 5 , respectively (6 pt.). 7. In cell range E30:E40, by using cell references and the function NPV, calculate the NPV of the investment opportunity for cost of capital 0% to 50%, respectively (11 pt.). 8. In cells C42:G53, insert a Line Chart to plot the NPV profile of the investment opportunity. Inserting a Chart On the Insert tab, in the Charts group, click the arrow next to Insert Line or Area Chart and choose Line Chart. Selecting Data Series Then in Select Data Source window, delete any series created automatically. Add new series for the NPV profile of the investment opportunity using cells E30:E40 for the series values. Do not name the series. Edit Chart Elements Then in Select Data Source window, edit Horizontal Axis Labels using cells D30:D40. Add a chart title and choose the Above Chart option. Replace Chart Title with NPV Profile. Add axis titles. Replace Axis Title for the horizontal axis with Cost of Capital and Axis Title for the vertical axis with NPV. (3 pt.) 9. In cell E57, by using cell references, calculate the NPV of the investment opportunity for a 10% cost of capital (1 pt.). 10. In cell E61, by using cell references and the function IRR, calculate the IRR of the investment opportunity (1 pt.). Note: Do not enter any value for the Guess argument of the function IRR. 11. Save the workbook. Close the workbook and then exit Excel. Submit the workbook as directed Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


