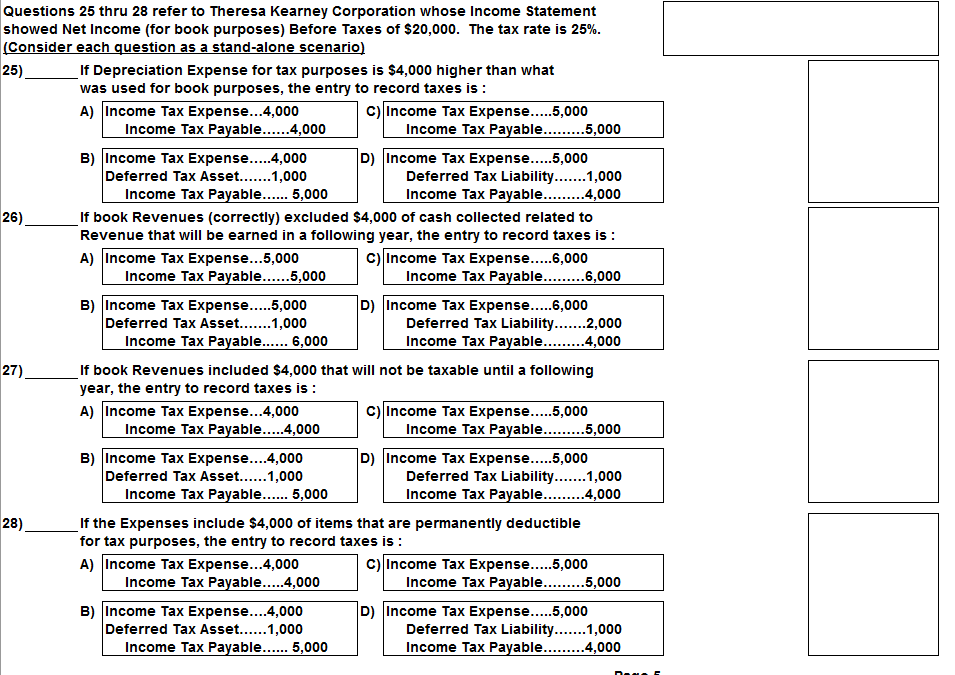
Question
C1. A. Should the yield of a corporate bond be higher or lower than a Treasury which has the same maturity date but a lower



C1. A. Should the yield of a corporate bond be higher or lower than a Treasury which has the same maturity date but a lower coupon? Why? [2 points]
C1. B. Suppose the yield of the Treasury is 2%, the likelihood of default in the next year of the corporate is 1.5%, and the expected recovery rate conditional on default is 40%. Ignoring liquidity issues, what is your best estimate of the yield of a bond issued by this corporate? [4 points]
C2. A Treasury bond has a coupon rate of 9%, a face value of 100$ and matures 10 years from now. For a treasury bond, the interest on the bond is a paid in semiannual installments. The current risk interest rate is 12%.
a) What is the current price of the bond? [3 points]
b) If you buy the bond at this price, under what circumstances do you make money? [2 points]
c) Let's suppose you buy the Treasury Bond described above. Just after you buy, the riskless interest rate decreases to 9%. What would be the new market price? [2 points]
Project 2
John Levitt owns a popular burger stand on a trendy section of Melrose Boulevard. Following the success of his first burger stand, "Johnny's Burgers," which has been in operations for five years, John is now considering opening a second burger stand in another trendy location, on Sunset Boulevard in the Silver Lake area. John's market research shows that the clientele in both areas is similar: young professionals, typically without children, who like the traditional aspect of eating burgers, but also relish his gourmet, specially manufactured low-fat burgers and the healthy side dishes his stand also sells. John's overall plan is to get the second stand up and running for four years, and then sell both stands off to a new owner and retire to Santa Barbara.
John estimates that the cost of starting up a second stand will be as follows:
Purchase of retail kiosk (mobile retail food outlet) $750,000
Specialized kitchen equipment $60,000
Installation of the kitchen equipment $20,000
Furniture and fittings $50,000
John estimates that annual operating costs of the new location would be identical to those of his current stand:
Labor costs, inclusive of all overhead costs:
Kitchen and service staff (5 people) $200,000
License and rent costs $150,000
Raw materials:
Burgers (275 per day x 7 days x 52 weeks), see burgers' cost below
Drinks $38,400
Other food supplies $145,800
Nonfood supplies $50,200
The revenues at his current location are as follows:
Sales of burgers $6 per burger Price per unit
Average daily sales 275 burgers
Other food items $270,000
Drinks $190,000
In addition to contributing profits, John expects that opening a second stand will decrease the cost of purchasing gourmet burgers from $1.5 cents to $1.35 cents in both locations. This is due to economies of scale. John also expects that he will be able to manage both locations himself, avoiding hiring a manager for the new location.
Assume that:
Increase in the receivables (AR) is expected to be equal to 12% of gross sales; the project will require additional cash (for giving change to the stand's customers paying cash) in the amount of 5% of gross sales. There will be no considerable investment in inventory as John implements "just-in-time" inventory system to keep the products fresh. Increase in payables associated with the new stand is estimated to be equal to 15% of the cost of raw products
Net working capital is fully recovered (i.e., reduced to zero) at the end of year 4
The marginal tax rate is 34 percent.
Cost of Capital is 10 percent.
Cost of the stand (kiosk), together with the cost of the equipment and the installation, is depreciated over five years according to the straight-line method.
Note: The definition of an asset's cost is all costs that are necessary to get an asset in place and ready for use. Therefore, the cost of the installation labor (wages and related fringe benefits) is part of the cost of the asset (and not an immediate expense of the accounting period).
The stand (together with the kitchen equipment) is expected to be worth $300,000 after four years of service.
1. Construct a model in Excel to evaluate the project.
You may use "Home Net" spreadsheet for inspiration. DO NOT follow it literally though as this is a different project with its own unique features.
2. What is the NPV of this investment?
3. Consider several values of cost of capital (for example, check values between 7% and 13% with 1% step) and compute NPV for each of these values. Use "Data Table" Construct NPV profile: Let cost of capital be your X-variable and NPV be your Y-variable.
4. Set some goal value for NPV (choose a value yourself) and use "goal seek" to find number of burgers that the new stand must sell annually to achieve the goal. To learn how to use "goal seek" please see tutorial video (my own tutorial video is available with the project)
5. Suppose that you are unsure about the price John would be able to charge. John would like to generate at least $200,000 in NPV with the new kiosk. Using "goal seek" find price per burger necessary to achieve this goal





Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


