Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Calculate: There are no acquisitions and dispositions of businesses during the year. There were no other comprehensive items during the year. All changes in deferred

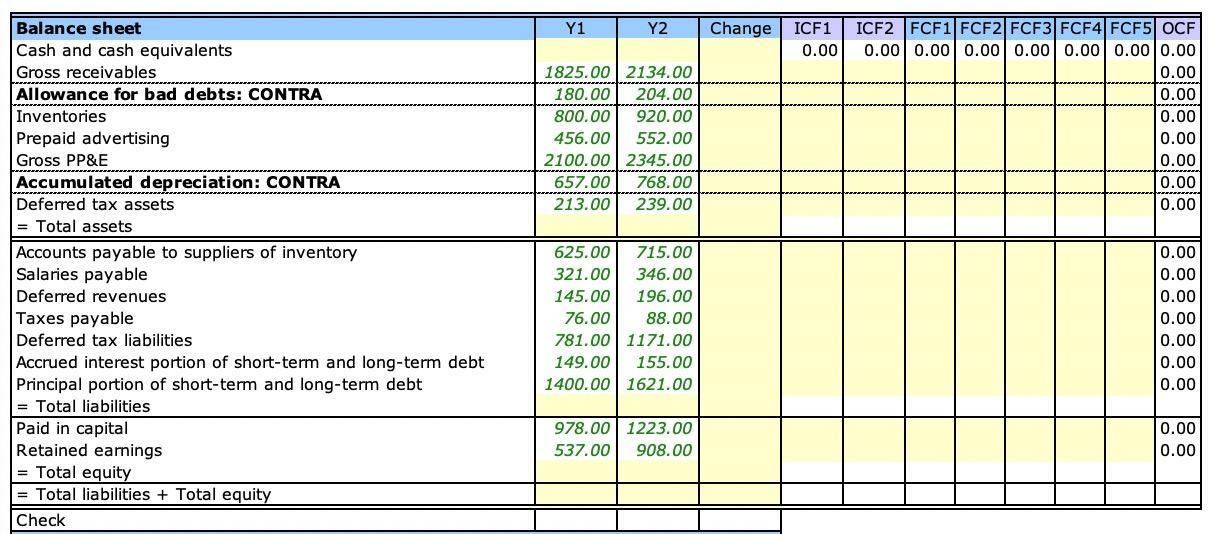
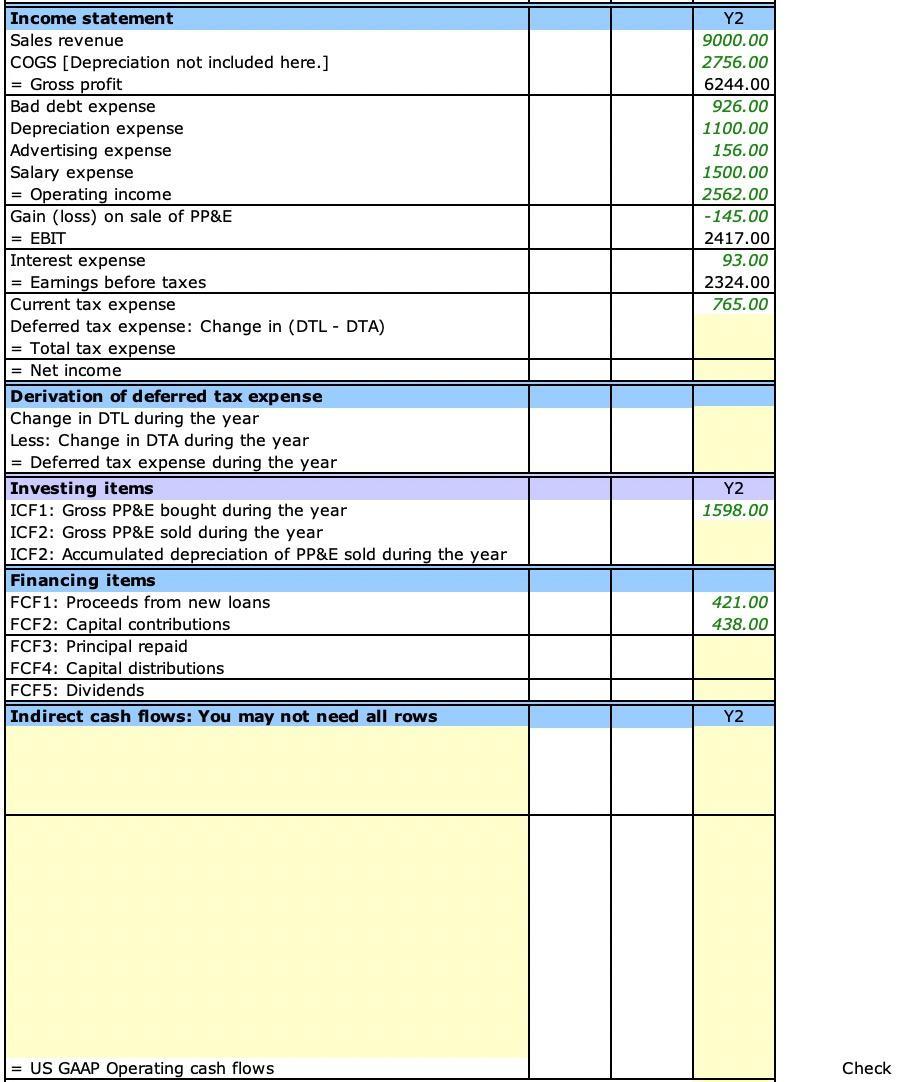
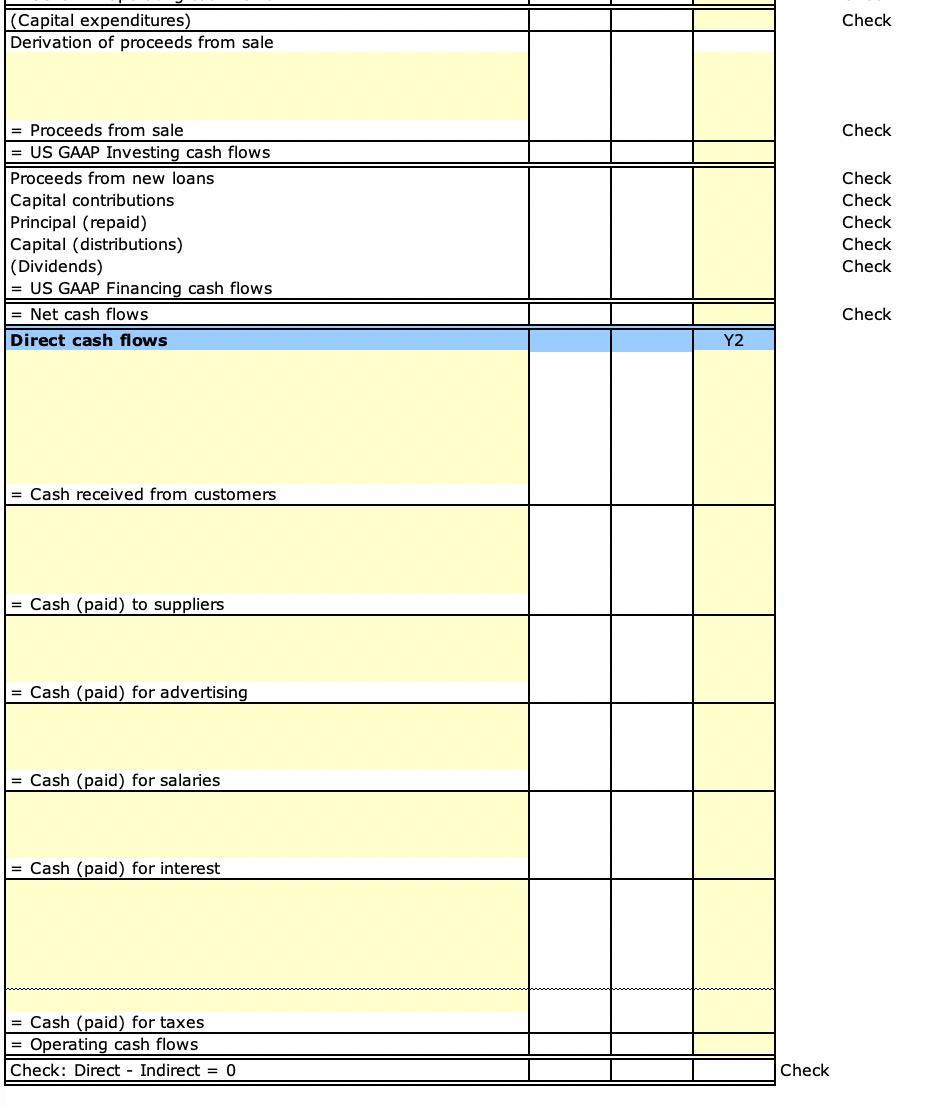
Calculate:
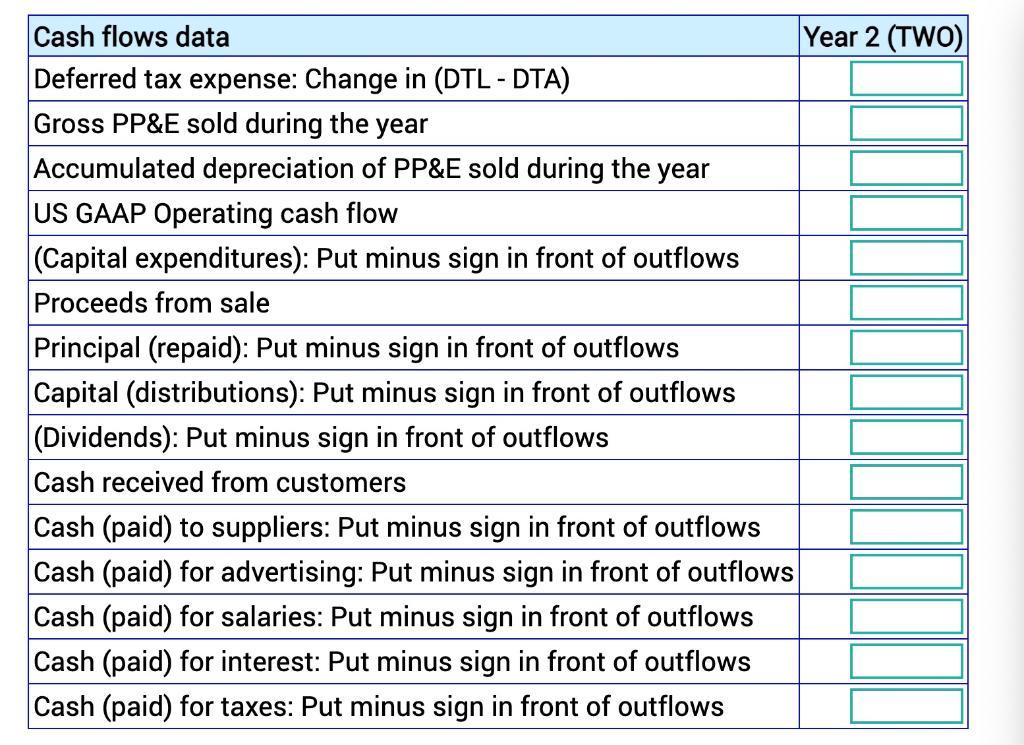
There are no acquisitions and dispositions of businesses during the year. There were no other comprehensive items during the year. All changes in deferred tax assets and liabilities appear as deferred tax expense on the income statement. You have to prepare the cash flow statement. You can do it your way, or you can follow the steps below: 1. Compute the cash balance for years 1 and 2. 2. The total change in accounts is given in the "change" column. 3. Change in cash = - Change in assets + Changes in contra-assets, liabilities, and equity. This formula is already entered for the change in cash in the ICF, FCF, and OCF columns. 4. ICF1: Identify changes in non-cash accounts due to purchase of PP&E. You have to use the supplemental information provided at the bottom of the balance sheet. 5. ICF2: Identify changes in non-cash accounts due to sale of PP&E. You have to use the supplemental information provided at the bottom of the balance sheet. 6. FCF1: Identify changes in non-cash accounts due to borrowings. You have to use the supplemental information provided at the bottom of the balance sheet. 7. FCF2: Identify changes in non-cash accounts due to capital contributions. You have to use the supplemental information provided at the bottom of the balance sheet. 8. FCF3: Identify changes in non-cash accounts due to principal repaid. You have to use the supplemental information provided at the bottom of the balance sheet. 9. FCF4: Identify changes in non-cash accounts due to stock buyback. You have to use the supplemental information provided at the bottom of the balance sheet. 10. FCF5: Identify changes in non-cash accounts due to dividends. You have to use the supplemental information provided at the bottom of the balance sheet. 11. Subtract changes due to investing and financing activities from the total change to arrive at changes due to operating activities. This formula is already entered in the OCF column. 12. Use this information to prepare the cash flow statement. 13. If your computations have errors, then the check cells will not be blank. 14. Direct cash flows: Now you have to think how to adjust each row on the income statement to arrive at corresponding cash flows.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.29 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
To prepare the cash flow statement we will follow the provided steps and compute the cash balance for years 1 and 2 then proceed to calculate the necessary adjustments for the indirect method of cash ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


