Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Calculation of theoretical braking ratio at different brake pipe pressures Use the previous values for brake cylinder pressure to calculate the braking force: P
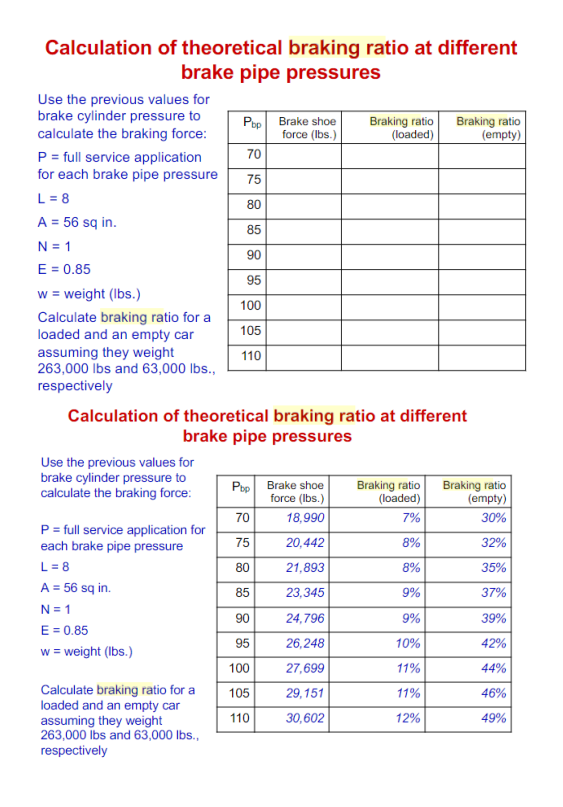
Calculation of theoretical braking ratio at different brake pipe pressures Use the previous values for brake cylinder pressure to calculate the braking force: P = full service application for each brake pipe pressure L = 8 A = 56 sq in. N = 1 E = 0.85 w = weight (lbs.) Calculate braking ratio for a loaded and an empty car assuming they weight 263,000 lbs and 63,000 lbs., respectively Use the previous values for brake cylinder pressure to calculate the braking force: P = full service application for each brake pipe pressure L = 8 A = 56 sq in. N=1 E = 0.85 w = weight (lbs.) Pbp Brake shoe force (lbs.) Calculation of theoretical braking ratio at different brake pipe pressures Calculate braking ratio for a loaded and an empty car assuming they weight 263,000 lbs and 63,000 lbs., respectively 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 110 Pop 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 110 Braking ratio Braking ratio (loaded) (empty) Brake shoe force (lbs.) 18,990 20,442 21,893 23,345 24,796 26,248 27,699 29,151 30,602 Braking ratio (loaded) 7% 8% 8% 9% 9% 10% 11% 11% 12% Braking ratio (empty) 30% 32% 35% 37% 39% 42% 44% 46% 49%
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


