Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Calculus 3 Sections 12.1 and 12.2 Reading Assignment: 3D Coordinates and Vectors Answer Only Exercise 3 by using a screenshot provided Calculus Pearson textbook. Make

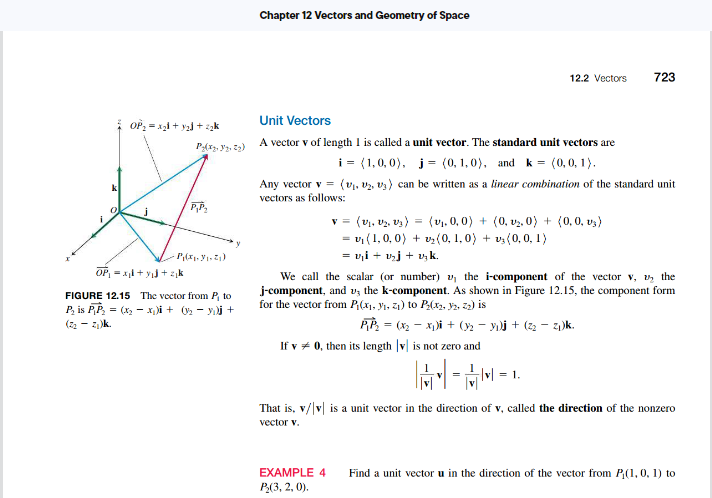
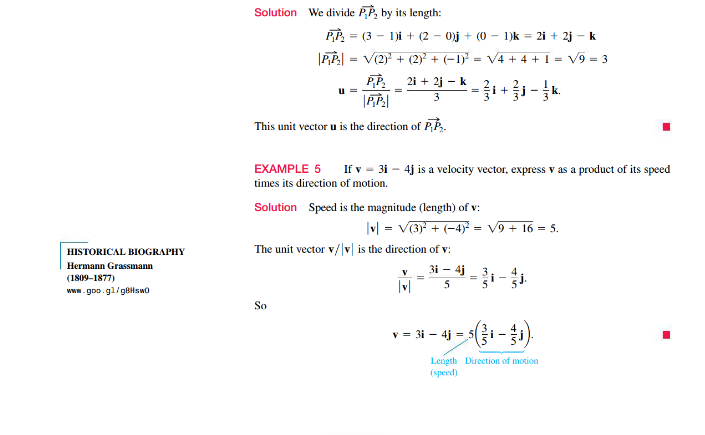
Calculus 3 Sections 12.1 and 12.2 Reading Assignment: 3D Coordinates and Vectors
Answer Only Exercise 3 by using a screenshot provided Calculus Pearson textbook. Make sure you read these three questions very carefully and see on what it is asking for and what is really about. Please be very serious careful with this assignment of exercise #3.
References: Thomas' Calculus: Early Transcendentals | Calculus | Calculus | Mathematics | Store | Pearson+

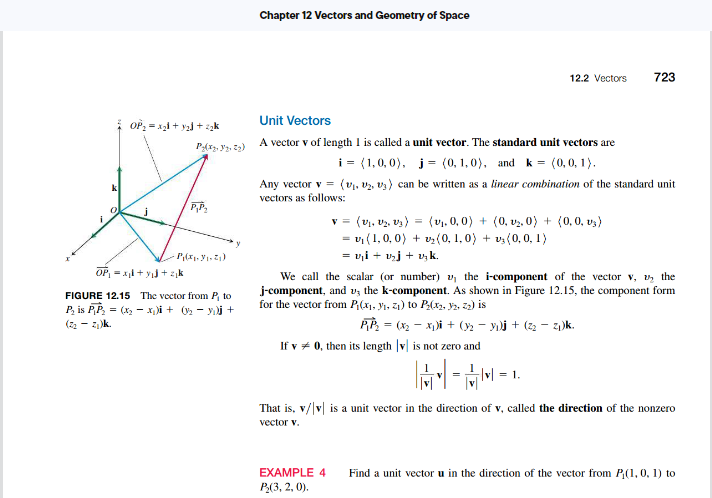
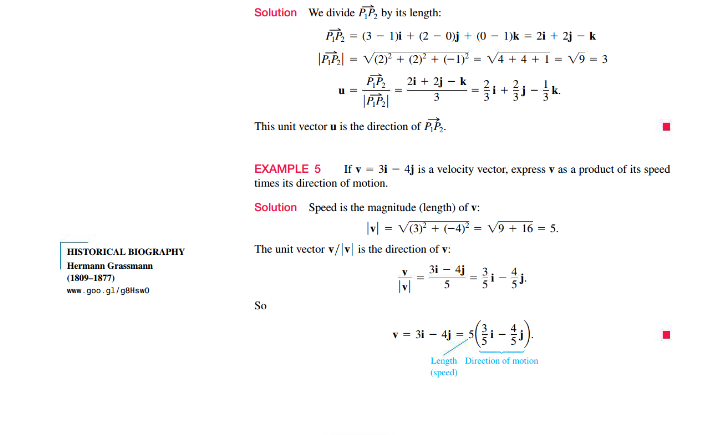
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
To complete Exercise 3 lets focus on the standard unit vectors and how they are used to express any ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


