Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
can i have help on this issue thank you :) sorry about that is this good information if not please let me know so i
can i have help on this issue thank you :) 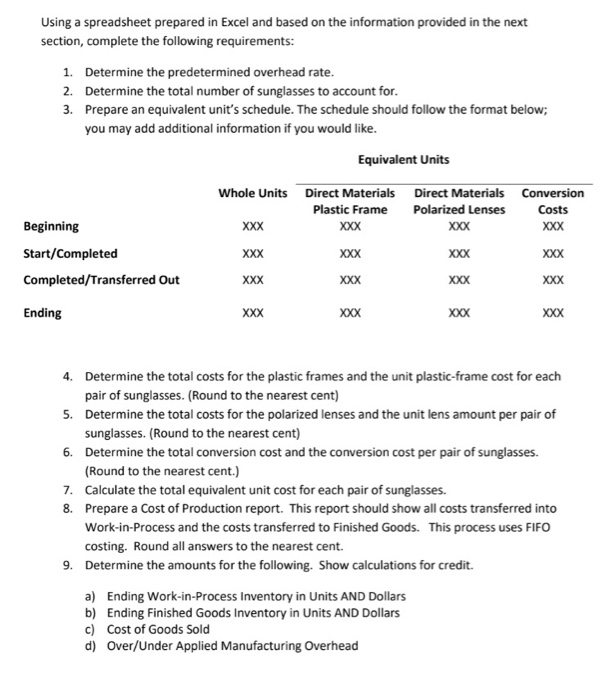

sorry about that is this good information if not please let me know so i can provide :)




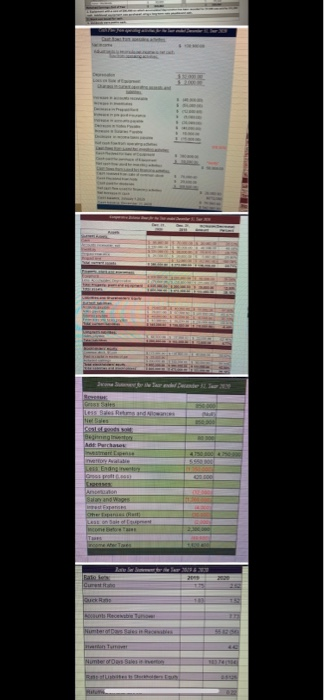
i am hoping just with starting this im not sure how to fix the bluryness
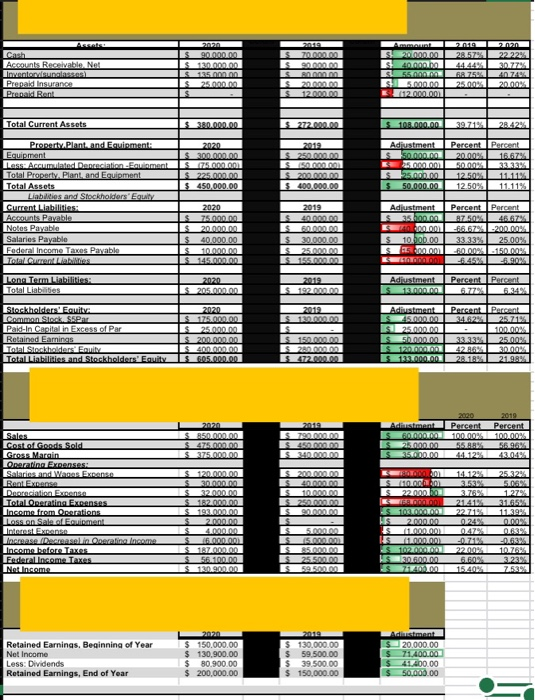
Using a spreadsheet prepared in Excel and based on the information provided in the next section, complete the following requirements: 1. Determine the predetermined overhead rate. 2. Determine the total number of sunglasses to account for. 3. Prepare an equivalent unit's schedule. The schedule should follow the format below; you may add additional information if you would like. Equivalent Units Beginning Start/Completed Completed/Transferred Out Whole Units Direct Materials Direct Materials Conversion Plastic Frame Polarized Lenses Costs XXX XXX XOX XXX XXX xxx XXX XXX XXX XXX XXX XXX Ending XXX xxx XXX xxx 4. Determine the total costs for the plastic frames and the unit plastic-frame cost for each pair of sunglasses. (Round to the nearest cent) 5. Determine the total costs for the polarized lenses and the unit lens amount per pair of sunglasses. (Round to the nearest cent) 6. Determine the total conversion cost and the conversion cost per pair of sunglasses. (Round to the nearest cent.) 7. Calculate the total equivalent unit cost for each pair of sunglasses. 8. Prepare a cost of Production report. This report should show all costs transferred into Work-in-Process and the costs transferred to Finished Goods. This process uses FIFO costing. Round all answers to the nearest cent. 9. Determine the amounts for the following. Show calculations for credit. a) Ending Work-in-Process Inventory in Units AND Dollars b) Ending Finished Goods Inventory in Units AND Dollars c) Cost of Goods Sold d) Over/Under Applied Manufacturing Overhead e) Gross Margin f) Income from Operations g) Net Income 10. Prepare the necessary Journal Entries related to the manufacturing cycle for this accounting period. Prepare journal entries for the accounting period. Use the account numbers in the chart of accounts, below, instead of the accounts names when writing the journal entries 10000 11000 12000 12100 14000 14100 15000 15050 16000 20000 40000 50000 Chart of Accounts Cash Accounts Receivable Plastic Material Inventory Lens Material Inventory Prepaid Rent Prepaid Insurance WIP FOH FG Wages Payable Sales COGS a. Record the purchase of the materials using cash b. Record the materials transferred to WIP C. Record the direct labor using cash d. Record the applied FOH e. Record the actual FOH using cash f. Record over or under applied FOH g. Record the transfer of goods from WIP to FG h. Record the sale of goods on account i. Record the cost of the inventory that was sold Blackboard Instructions for Part Two Add information concerning numbers here and enter into Blackboard as specified below a. When the answer is in units enter the number as is (See example below) i. 280 b. When the answer is for ratios (ie. %) and it has a decimal take the decimal out to two spaces (See example below) ii. 280.89 C. When ratios are in days/times take out to two decimal places (See example below) iii. 280.96 days d. When the answer is in dollars ALWAYS include a dollar sign and cents even if the cents is zero add.00 (See example below) iv. $280.00 or $3,800.00 e. When there is a single journal entry enter information EXACTLY as is below in the sequence of Dr/Cr, Account Number, and amount (note the signs, decimals, spaces, and capital letter) v. Dr 10000 $280.00 Cr 20000 $280.00 f. When there is a journal entry requiring two debits or credits enter information EXACTLY as is below in the sequence of Dr/Cr, Account Number, amount, and always put the smaller account number FIRST (note the signs, decimals, spaces, capital letters and order of the accounts) vi. Dr 10000 $280.00 Dr 60000 $40.00 Cr 20000 $300.00 vii. Dr 10000 $300.00 Cr 20000 $280.00 Cr 90000 $40.00 viii. Dr 10000 $280.00 Dr 60000 $40.00 Cr 70000 $290.00 Cr 90000 $10.00 8. When there is a sale enter the sale first and then add the COGS and the transfer of Inventory i. Dr 10000 $10,368.00 Cr 40000 $10,000.00 Cr 26833 $368.00 Dr 50000 $70,000.00 Cr 12000 $50,000.00 Cr 12100 $20,000.00 h. Follow examples exactly as are! Do NOT copy and paste from Excel into Blackboard. If your entry is formatted incorrectly it will be counted wrong. Manufacturing Process Information Sally's Sunglasses, a corporation, started a small manufacturing plant that fabricates polarized sunglasses. The manufacturing process starts by placing hot melted plastic in molds for the frames. After the molds are cooled, the frames are then prepared for the placement of the lenses. The lens material is a polarized plastic and each sheet of polarized plastic makes one lens. Once the polarized plastic for the lenses is fabricated for the sunglasses the lenses are then secured into the frame, the sunglasses are then inspected, next they are transferred to finished goods. This process is completely automated. Direct material, plastic-frames is added 100% at the beginning of the process. Lenses are added 100% at the end of the process. Conversion costs are added equally throughout the process. Conversion costs are 35% complete for ending inventory in work in process and the lenses are 0% complete as to ending inventory. At the beginning of the accounting period, Sally's Sunglasses estimated that production would be 20,000 sunglasses. Our predetermined factory overhead rate is based on an estimated FOH of $40,000 and the production of 20,000 sunglasses. This information is to be used to determine the application rate for factory overhead. Estimated and actual direct labor costs totaled $28,050. Actual factory overhead costs totaled $36,000. The following information is available concerning direct materials. Direct Materials-Plastic Beginning Inventory O pounds @ $7.00 per pound Purchase of plastic 10,000 pounds @ $7.00 per pound Ending Inventory O pounds @ $7.00 per pound Each pair of sunglasses contains a half pound of plastic for the frames. The company starts 20,000 sunglasses for the period. Direct Materials-Lenses Beginning Inventory O sheets of polarized plastic @ 8.31 per sheet Purchases 40,000 sheets of polarized plastic @ 8.31 per sheet Ending Inventory 4,000 sheets of polarized plastic @ 8.31 per sheet 1 sheet of polarized plastic makes one lens. The Work-in-process account has the following information Beginning Work-in-process contains 0 frames Ending Work-in-Process contains 2,000 frames The Finished Goods account has the following Information Beginning Finished Goods contains 5,400 sunglasses Ending Finished Goods contains 5,900 sunglasses The selling price is $50.00 for each pair of sunglasses. Selling and Administrative Costs totaled $180,000 and the tax rate is 30%. $ Cash Accounts Receivable Net Inwentarus) Prepaid Insurance Prepaid Bani $ 90.000.00 $ 120.000 $135.onnon $25.000 70.000.00 0.000 B 20.00 12.00 mat 20.000.00 40 55 500 112.000.00 28.57% 44449 68.75 25.00% 2020 2222 3077 AZUA 20.00 s Total Current Assets $_380.000.00 100.000,00 39.7194 28.42 Adiustment 50.000.00 2020 $ 300.000.00 $75.000 $225.00 $450,000.00 S_250 S0000 $ 200 $400,000.00 Percent Percent 20.00% 16.67% $0.00 12.50 12.50% 11.11% $ $ 35.000.00 50,000.00 Property. Plant and Eainment Equipment Less Accumulated Depreciation Equiment Total Property. Plant, and Equipment Total Assets Liabilities and Stockholdors' Equity Current Liabilities Accounts Pavable Notes Payable Salaries Payable Federal Income Taxes Payable Total Current Liabilities 2020 $ 75.000.00 20.000.00 $ 40.000,00 10.000.00 145.00 2019 ennen 60.000.00 $ 30,000.00 25.RO $_155. Adjustment $_35 hann EER S 10.000.00 S12.00 EC Percent Percent 87.60 46.67 -66.679.200.00% 33.33% 25.00% 60.002.150.00% -5.900 Long Term Liabilities: Total Liabilities 2020 $ 205.000.00 S 192.000.00 Adjustment 10.000.00 Percent percent 6.77 Stockholders' Equity Common Stock Par Paid-In Capital in Excess of Par Retained Earnings Total Stockholders' Eauit Total Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity 2020 S_175.000 L$25.000.00 $200.00 $ 4.0 S_605.000.00 S150.00 Adiustment 25.000.00 SI 25.000.00 $ sha. $ 1200 S132.000.00 Percent Percent 34.628 25.71135 100M 33 25.00% 42 BARA 30.00 28.18% 21.98% S472.000.00 Sanon $ 475 S_375.000 790 $450 S 340.000.00 2000 2019 Adiuustment Percent Percent $ 0.000000 100.00% 100.00% 25.000.00 55.82 6.6.96 35000.00 4412 40.4 14.12 SOLAR Sales Cost of Goods Sold Gross Mazgin Operating Expenses Salaries and Wanes Expanse Rent Expense Depreciation Expense TotalLoperating EXROSS Income from Operations LASSAN Sales Emman Interest Expens lacrease Decrease in Online forme Income before Taxes Federal Income Taxes Net Income S200.000.00 ES ennnnn 10.000.000 $_250RR S90.000 $120.000 30.000 32.000.0 182.000.00 $ 193.000.00 2000 4.000.00 16.000.00 S1870000 56.100.00 120.900.00 3.78% 21414 22.71% TEMALARI STORA 2.000.00 25.32% 5.06 12784 31165 11.39% ANAS 5.000 s SARAI $_35 100M 102 1.600.00 7.00 22.00% 6.602 15.40 06 107 3.23 75 $59.5 Retained Earnings, Beginning of Year Net Income Less: Dividends Retained Earnings, End of Year 2020 $ 150,000.00 $ 130,900.00 $ 80.900.00 $ 200,000.00 2012 $ 130,000.00 $ 59,500.00 $39.500.00 $ 150,000.00 Adiestiment 20.000.00 71.400.00 S 41400.00 50.000.00 Using a spreadsheet prepared in Excel and based on the information provided in the next section, complete the following requirements: 1. Determine the predetermined overhead rate. 2. Determine the total number of sunglasses to account for. 3. Prepare an equivalent unit's schedule. The schedule should follow the format below; you may add additional information if you would like. Equivalent Units Beginning Start/Completed Completed/Transferred Out Whole Units Direct Materials Direct Materials Conversion Plastic Frame Polarized Lenses Costs XXX XXX XOX XXX XXX xxx XXX XXX XXX XXX XXX XXX Ending XXX xxx XXX xxx 4. Determine the total costs for the plastic frames and the unit plastic-frame cost for each pair of sunglasses. (Round to the nearest cent) 5. Determine the total costs for the polarized lenses and the unit lens amount per pair of sunglasses. (Round to the nearest cent) 6. Determine the total conversion cost and the conversion cost per pair of sunglasses. (Round to the nearest cent.) 7. Calculate the total equivalent unit cost for each pair of sunglasses. 8. Prepare a cost of Production report. This report should show all costs transferred into Work-in-Process and the costs transferred to Finished Goods. This process uses FIFO costing. Round all answers to the nearest cent. 9. Determine the amounts for the following. Show calculations for credit. a) Ending Work-in-Process Inventory in Units AND Dollars b) Ending Finished Goods Inventory in Units AND Dollars c) Cost of Goods Sold d) Over/Under Applied Manufacturing Overhead e) Gross Margin f) Income from Operations g) Net Income 10. Prepare the necessary Journal Entries related to the manufacturing cycle for this accounting period. Prepare journal entries for the accounting period. Use the account numbers in the chart of accounts, below, instead of the accounts names when writing the journal entries 10000 11000 12000 12100 14000 14100 15000 15050 16000 20000 40000 50000 Chart of Accounts Cash Accounts Receivable Plastic Material Inventory Lens Material Inventory Prepaid Rent Prepaid Insurance WIP FOH FG Wages Payable Sales COGS a. Record the purchase of the materials using cash b. Record the materials transferred to WIP C. Record the direct labor using cash d. Record the applied FOH e. Record the actual FOH using cash f. Record over or under applied FOH g. Record the transfer of goods from WIP to FG h. Record the sale of goods on account i. Record the cost of the inventory that was sold Blackboard Instructions for Part Two Add information concerning numbers here and enter into Blackboard as specified below a. When the answer is in units enter the number as is (See example below) i. 280 b. When the answer is for ratios (ie. %) and it has a decimal take the decimal out to two spaces (See example below) ii. 280.89 C. When ratios are in days/times take out to two decimal places (See example below) iii. 280.96 days d. When the answer is in dollars ALWAYS include a dollar sign and cents even if the cents is zero add.00 (See example below) iv. $280.00 or $3,800.00 e. When there is a single journal entry enter information EXACTLY as is below in the sequence of Dr/Cr, Account Number, and amount (note the signs, decimals, spaces, and capital letter) v. Dr 10000 $280.00 Cr 20000 $280.00 f. When there is a journal entry requiring two debits or credits enter information EXACTLY as is below in the sequence of Dr/Cr, Account Number, amount, and always put the smaller account number FIRST (note the signs, decimals, spaces, capital letters and order of the accounts) vi. Dr 10000 $280.00 Dr 60000 $40.00 Cr 20000 $300.00 vii. Dr 10000 $300.00 Cr 20000 $280.00 Cr 90000 $40.00 viii. Dr 10000 $280.00 Dr 60000 $40.00 Cr 70000 $290.00 Cr 90000 $10.00 8. When there is a sale enter the sale first and then add the COGS and the transfer of Inventory i. Dr 10000 $10,368.00 Cr 40000 $10,000.00 Cr 26833 $368.00 Dr 50000 $70,000.00 Cr 12000 $50,000.00 Cr 12100 $20,000.00 h. Follow examples exactly as are! Do NOT copy and paste from Excel into Blackboard. If your entry is formatted incorrectly it will be counted wrong. Manufacturing Process Information Sally's Sunglasses, a corporation, started a small manufacturing plant that fabricates polarized sunglasses. The manufacturing process starts by placing hot melted plastic in molds for the frames. After the molds are cooled, the frames are then prepared for the placement of the lenses. The lens material is a polarized plastic and each sheet of polarized plastic makes one lens. Once the polarized plastic for the lenses is fabricated for the sunglasses the lenses are then secured into the frame, the sunglasses are then inspected, next they are transferred to finished goods. This process is completely automated. Direct material, plastic-frames is added 100% at the beginning of the process. Lenses are added 100% at the end of the process. Conversion costs are added equally throughout the process. Conversion costs are 35% complete for ending inventory in work in process and the lenses are 0% complete as to ending inventory. At the beginning of the accounting period, Sally's Sunglasses estimated that production would be 20,000 sunglasses. Our predetermined factory overhead rate is based on an estimated FOH of $40,000 and the production of 20,000 sunglasses. This information is to be used to determine the application rate for factory overhead. Estimated and actual direct labor costs totaled $28,050. Actual factory overhead costs totaled $36,000. The following information is available concerning direct materials. Direct Materials-Plastic Beginning Inventory O pounds @ $7.00 per pound Purchase of plastic 10,000 pounds @ $7.00 per pound Ending Inventory O pounds @ $7.00 per pound Each pair of sunglasses contains a half pound of plastic for the frames. The company starts 20,000 sunglasses for the period. Direct Materials-Lenses Beginning Inventory O sheets of polarized plastic @ 8.31 per sheet Purchases 40,000 sheets of polarized plastic @ 8.31 per sheet Ending Inventory 4,000 sheets of polarized plastic @ 8.31 per sheet 1 sheet of polarized plastic makes one lens. The Work-in-process account has the following information Beginning Work-in-process contains 0 frames Ending Work-in-Process contains 2,000 frames The Finished Goods account has the following Information Beginning Finished Goods contains 5,400 sunglasses Ending Finished Goods contains 5,900 sunglasses The selling price is $50.00 for each pair of sunglasses. Selling and Administrative Costs totaled $180,000 and the tax rate is 30%. $ Cash Accounts Receivable Net Inwentarus) Prepaid Insurance Prepaid Bani $ 90.000.00 $ 120.000 $135.onnon $25.000 70.000.00 0.000 B 20.00 12.00 mat 20.000.00 40 55 500 112.000.00 28.57% 44449 68.75 25.00% 2020 2222 3077 AZUA 20.00 s Total Current Assets $_380.000.00 100.000,00 39.7194 28.42 Adiustment 50.000.00 2020 $ 300.000.00 $75.000 $225.00 $450,000.00 S_250 S0000 $ 200 $400,000.00 Percent Percent 20.00% 16.67% $0.00 12.50 12.50% 11.11% $ $ 35.000.00 50,000.00 Property. Plant and Eainment Equipment Less Accumulated Depreciation Equiment Total Property. Plant, and Equipment Total Assets Liabilities and Stockholdors' Equity Current Liabilities Accounts Pavable Notes Payable Salaries Payable Federal Income Taxes Payable Total Current Liabilities 2020 $ 75.000.00 20.000.00 $ 40.000,00 10.000.00 145.00 2019 ennen 60.000.00 $ 30,000.00 25.RO $_155. Adjustment $_35 hann EER S 10.000.00 S12.00 EC Percent Percent 87.60 46.67 -66.679.200.00% 33.33% 25.00% 60.002.150.00% -5.900 Long Term Liabilities: Total Liabilities 2020 $ 205.000.00 S 192.000.00 Adjustment 10.000.00 Percent percent 6.77 Stockholders' Equity Common Stock Par Paid-In Capital in Excess of Par Retained Earnings Total Stockholders' Eauit Total Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity 2020 S_175.000 L$25.000.00 $200.00 $ 4.0 S_605.000.00 S150.00 Adiustment 25.000.00 SI 25.000.00 $ sha. $ 1200 S132.000.00 Percent Percent 34.628 25.71135 100M 33 25.00% 42 BARA 30.00 28.18% 21.98% S472.000.00 Sanon $ 475 S_375.000 790 $450 S 340.000.00 2000 2019 Adiuustment Percent Percent $ 0.000000 100.00% 100.00% 25.000.00 55.82 6.6.96 35000.00 4412 40.4 14.12 SOLAR Sales Cost of Goods Sold Gross Mazgin Operating Expenses Salaries and Wanes Expanse Rent Expense Depreciation Expense TotalLoperating EXROSS Income from Operations LASSAN Sales Emman Interest Expens lacrease Decrease in Online forme Income before Taxes Federal Income Taxes Net Income S200.000.00 ES ennnnn 10.000.000 $_250RR S90.000 $120.000 30.000 32.000.0 182.000.00 $ 193.000.00 2000 4.000.00 16.000.00 S1870000 56.100.00 120.900.00 3.78% 21414 22.71% TEMALARI STORA 2.000.00 25.32% 5.06 12784 31165 11.39% ANAS 5.000 s SARAI $_35 100M 102 1.600.00 7.00 22.00% 6.602 15.40 06 107 3.23 75 $59.5 Retained Earnings, Beginning of Year Net Income Less: Dividends Retained Earnings, End of Year 2020 $ 150,000.00 $ 130,900.00 $ 80.900.00 $ 200,000.00 2012 $ 130,000.00 $ 59,500.00 $39.500.00 $ 150,000.00 Adiestiment 20.000.00 71.400.00 S 41400.00 50.000.00 
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


