Question
Can someone help run me through this question? Having difficulty. Thanks 8. Consider the OLG model with capital. Each individual is endowed with y units
Can someone help run me through this question? Having difficulty. Thanks
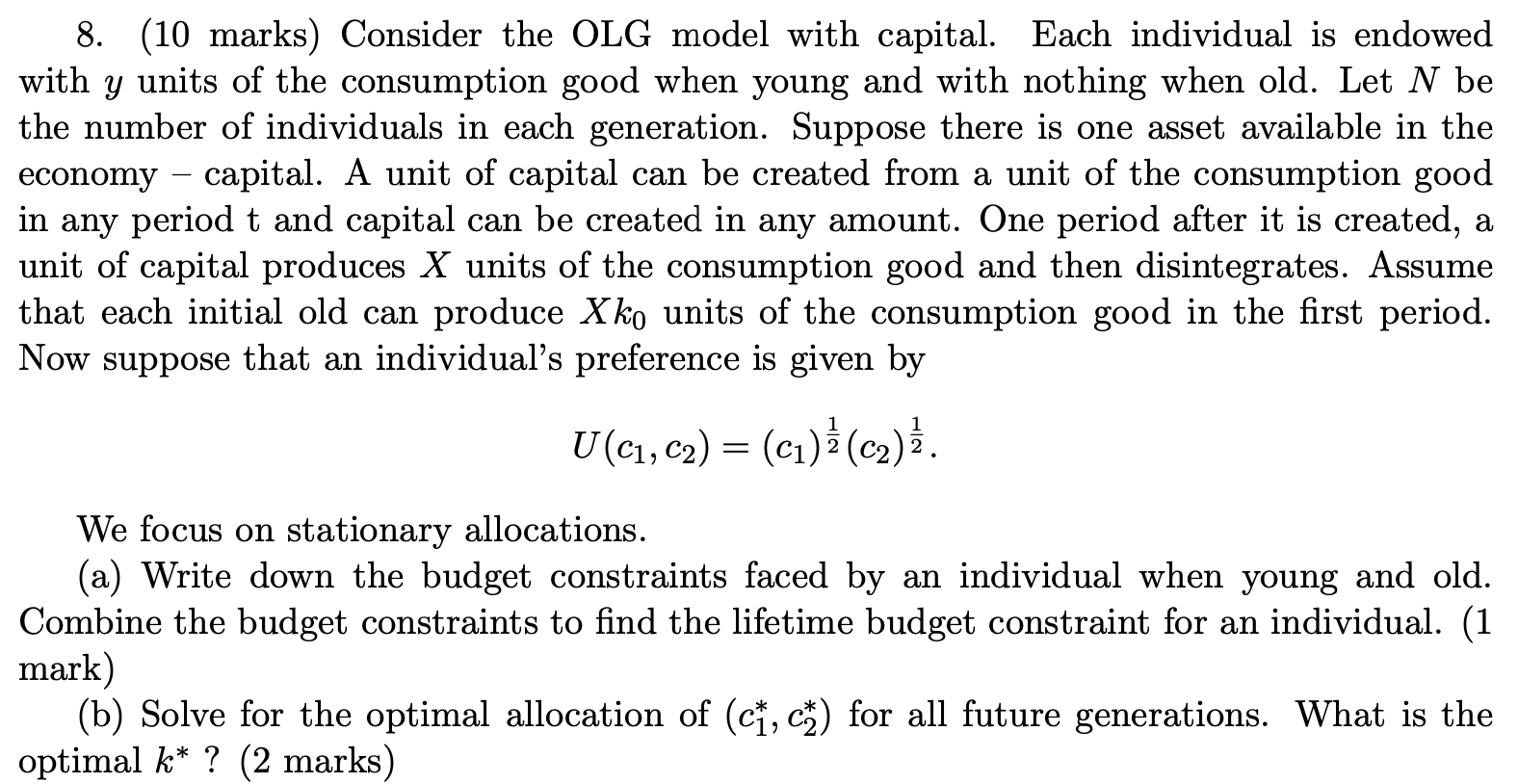
8. Consider the OLG model with capital. Each individual is endowed with y units of the consumption good when young and with nothing when old. Let N be the number of individuals in each generation. Suppose there is one asset available in the economy capital. A unit of capital can be created from a unit of the consumption good in any period t and capital can be created in any amount. One period after it is created, a unit of capital produces X units of the consumption good and then disintegrates. Assume that each initial old can produce Xk0 units of the consumption good in the first period. Now suppose that an individuals preference is given by
U(c1, c2) = (c1)^1/2 (c2)^1/2
8. (10 marks) Consider the OLG model with capital. Each individual is endowed with y units of the consumption good when young and with nothing when old. Let N be the number of individuals in each generation. Suppose there is one asset available in the economy - capital. A unit of capital can be created from a unit of the consumption good in any period t and capital can be created in any amount. One period after it is created, a unit of capital produces X units of the consumption good and then disintegrates. Assume that each initial old can produce Xk0 units of the consumption good in the first period. Now suppose that an individual's preference is given by U(c1,c2)=(c1)21(c2)21. We focus on stationary allocations. (a) Write down the budget constraints faced by an individual when young and old. Combine the budget constraints to find the lifetime budget constraint for an individual. ( 1 mark) (b) Solve for the optimal allocation of (c1,c2) for all future generations. What is the optimal k?(2 marks ) 8. (10 marks) Consider the OLG model with capital. Each individual is endowed with y units of the consumption good when young and with nothing when old. Let N be the number of individuals in each generation. Suppose there is one asset available in the economy - capital. A unit of capital can be created from a unit of the consumption good in any period t and capital can be created in any amount. One period after it is created, a unit of capital produces X units of the consumption good and then disintegrates. Assume that each initial old can produce Xk0 units of the consumption good in the first period. Now suppose that an individual's preference is given by U(c1,c2)=(c1)21(c2)21. We focus on stationary allocations. (a) Write down the budget constraints faced by an individual when young and old. Combine the budget constraints to find the lifetime budget constraint for an individual. ( 1 mark) (b) Solve for the optimal allocation of (c1,c2) for all future generations. What is the optimal k?(2 marks )Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


