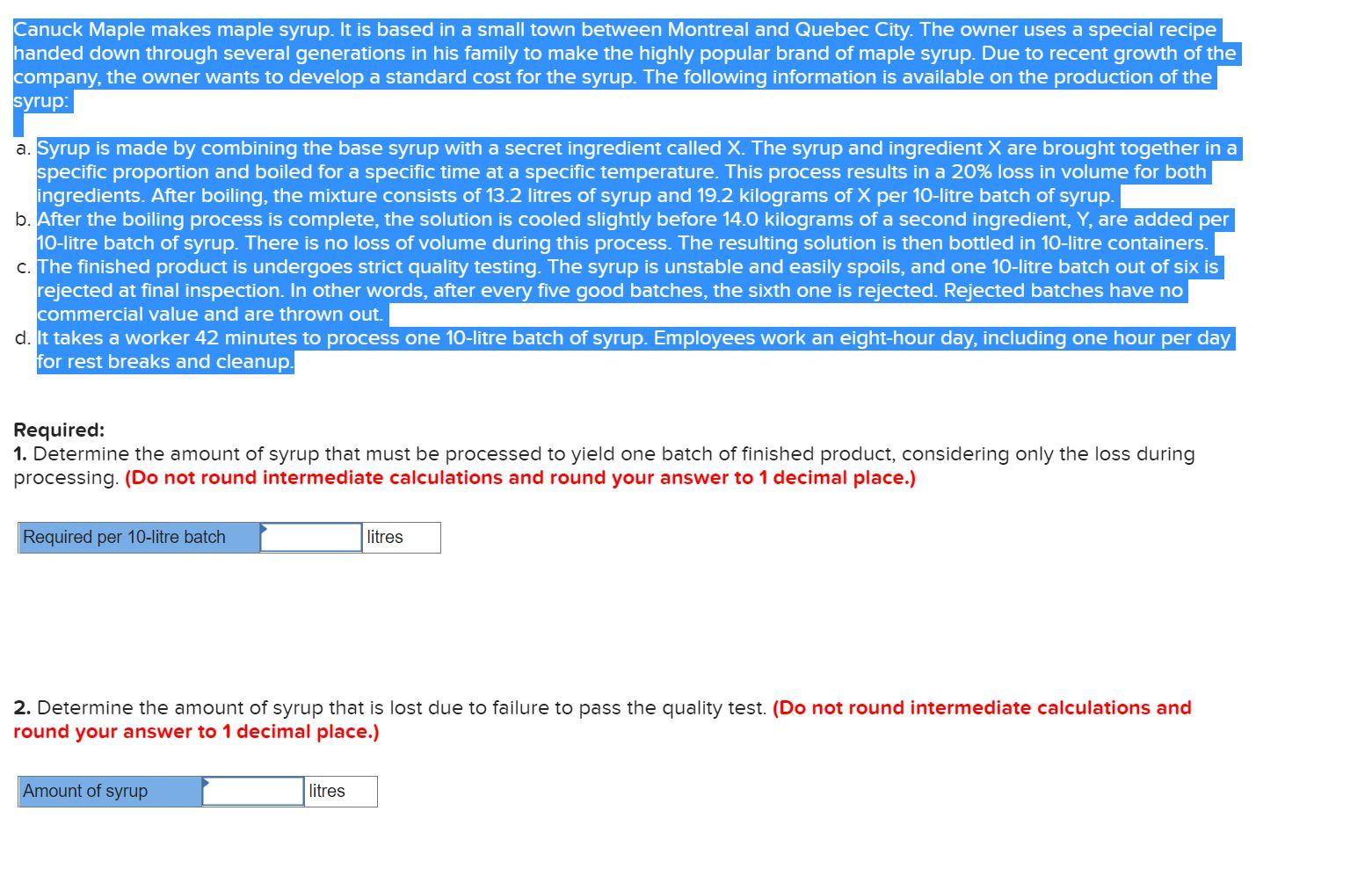

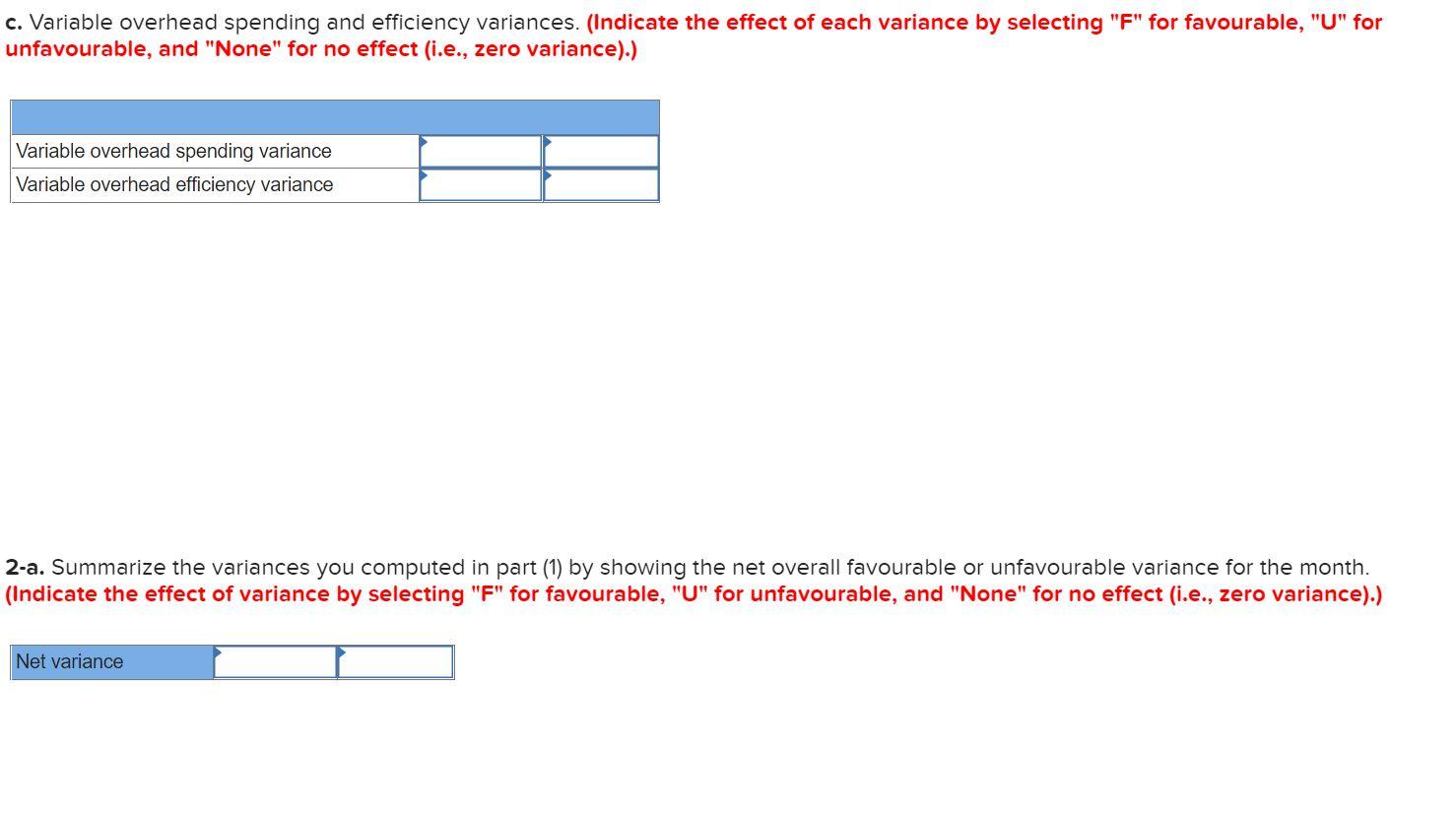
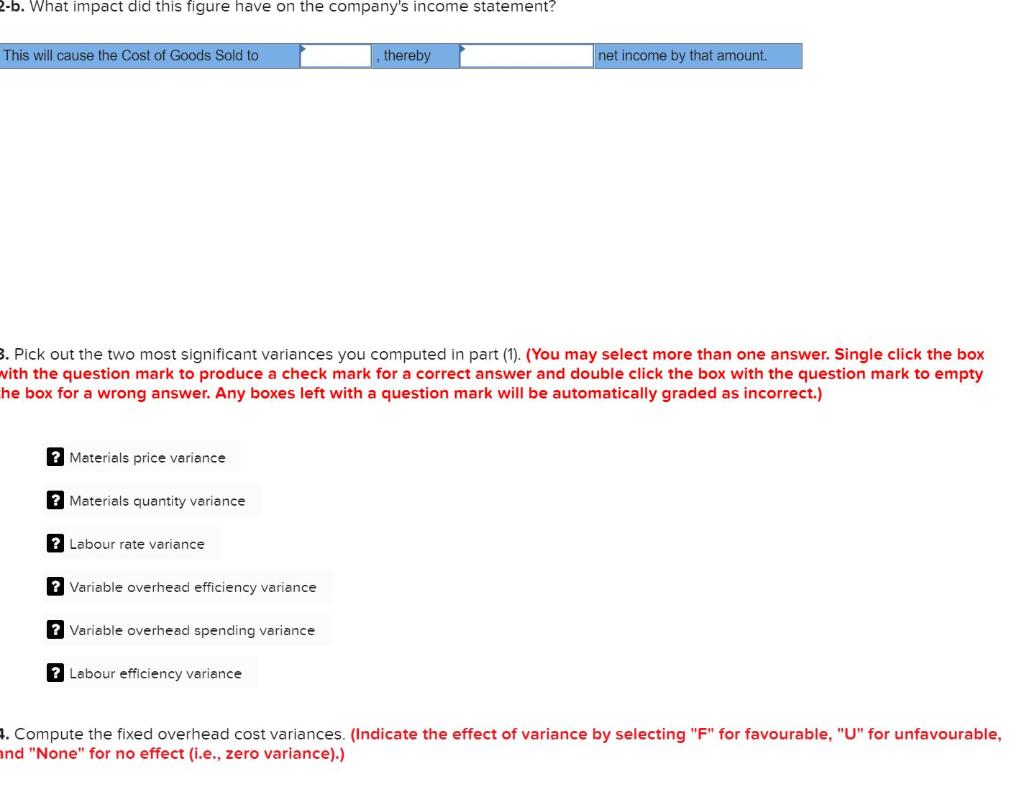

Canuck Maple makes maple syrup. It is based in a small town between Montreal and Quebec City. The owner uses a special recipe handed down through several generations in his family to make the highly popular brand of maple syrup. Due to recent growth of the company, the owner wants to develop a standard cost for the syrup. The following information is available on the production of the syrup: a. Syrup is made by combining the base syrup with a secret ingredient called X. The syrup and ingredient X are brought together in a specific proportion and boiled for a specific time at a specific temperature. This process results in a 20% loss in volume for both ingredients. After boiling, the mixture consists of 13.2 litres of syrup and 19.2 kilograms of X per 10-litre batch of syrup. b. After the boiling process is complete, the solution is cooled slightly before 14.0 kilograms of a second ingredient, Y, are added per 10-litre batch of syrup. There is no loss of volume during this process. The resulting solution is then bottled in 10-litre containers. C. The finished product is undergoes strict quality testing. The syrup is unstable and easily spoils, and one 10-litre batch out of six is rejected at final inspection. In other words, after every five good batches, the sixth one is rejected. Rejected batches have no commercial value and are thrown out. d. It takes a worker 42 minutes to process one 10-litre batch of syrup. Employees work an eight-hour day, including one hour per day for rest breaks and cleanup. Required: 1. Determine the amount of syrup that must be processed to yield one batch of finished product, considering only the loss during processing. (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 1 decimal place.) Required per 10-litre batch litres 2. Determine the amount of syrup that is lost due to failure to pass the quality test. (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 1 decimal place.) Amount of syrup litres Required: 1. Compute the following variances for June: a. Direct materials price and quantity variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance).) Material price variance Material quantity variance b. Direct labour rate and efficiency variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance).) Labour rate variance Labour efficiency variance c. Variable overhead spending and efficiency variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance).) Variable overhead spending variance Variable overhead efficiency variance 2-a. Summarize the variances you computed in part (1) by showing the net overall favourable or unfavourable variance for the month. (Indicate the effect of variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance).) Net variance 2-b. What impact did this figure have on the company's income statement? This will cause the cost of Goods Sold to thereby net income by that amount. 3. Pick out the two most significant variances you computed in part (1). (You may select more than one answer. Single click the box with the question mark to produce a check mark for a correct answer and double click the box with the question mark to empty he box for a wrong answer. Any boxes left with a question mark will be automatically graded as incorrect.) ? Materials price variance ? Materials quantity variance ? Labour rate variance ? Variable overhead efficiency variance ? Variable overhead spending variance ? Labour efficiency variance 4. Compute the fixed overhead cost variances. (Indicate the effect of variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance).) 4. Compute the fixed overhead cost variances. (Indicate the effect of variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance).) Fixed overhead budget variance Fixed overhead volume variance 5. This part of the question is not part of your Connect assignment. Canuck Maple makes maple syrup. It is based in a small town between Montreal and Quebec City. The owner uses a special recipe handed down through several generations in his family to make the highly popular brand of maple syrup. Due to recent growth of the company, the owner wants to develop a standard cost for the syrup. The following information is available on the production of the syrup: a. Syrup is made by combining the base syrup with a secret ingredient called X. The syrup and ingredient X are brought together in a specific proportion and boiled for a specific time at a specific temperature. This process results in a 20% loss in volume for both ingredients. After boiling, the mixture consists of 13.2 litres of syrup and 19.2 kilograms of X per 10-litre batch of syrup. b. After the boiling process is complete, the solution is cooled slightly before 14.0 kilograms of a second ingredient, Y, are added per 10-litre batch of syrup. There is no loss of volume during this process. The resulting solution is then bottled in 10-litre containers. C. The finished product is undergoes strict quality testing. The syrup is unstable and easily spoils, and one 10-litre batch out of six is rejected at final inspection. In other words, after every five good batches, the sixth one is rejected. Rejected batches have no commercial value and are thrown out. d. It takes a worker 42 minutes to process one 10-litre batch of syrup. Employees work an eight-hour day, including one hour per day for rest breaks and cleanup. Required: 1. Determine the amount of syrup that must be processed to yield one batch of finished product, considering only the loss during processing. (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 1 decimal place.) Required per 10-litre batch litres 2. Determine the amount of syrup that is lost due to failure to pass the quality test. (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 1 decimal place.) Amount of syrup litres Required: 1. Compute the following variances for June: a. Direct materials price and quantity variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance).) Material price variance Material quantity variance b. Direct labour rate and efficiency variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance).) Labour rate variance Labour efficiency variance c. Variable overhead spending and efficiency variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance).) Variable overhead spending variance Variable overhead efficiency variance 2-a. Summarize the variances you computed in part (1) by showing the net overall favourable or unfavourable variance for the month. (Indicate the effect of variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance).) Net variance 2-b. What impact did this figure have on the company's income statement? This will cause the cost of Goods Sold to thereby net income by that amount. 3. Pick out the two most significant variances you computed in part (1). (You may select more than one answer. Single click the box with the question mark to produce a check mark for a correct answer and double click the box with the question mark to empty he box for a wrong answer. Any boxes left with a question mark will be automatically graded as incorrect.) ? Materials price variance ? Materials quantity variance ? Labour rate variance ? Variable overhead efficiency variance ? Variable overhead spending variance ? Labour efficiency variance 4. Compute the fixed overhead cost variances. (Indicate the effect of variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance).) 4. Compute the fixed overhead cost variances. (Indicate the effect of variance by selecting "F" for favourable, "U" for unfavourable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance).) Fixed overhead budget variance Fixed overhead volume variance 5. This part of the question is not part of your Connect assignment











