Question
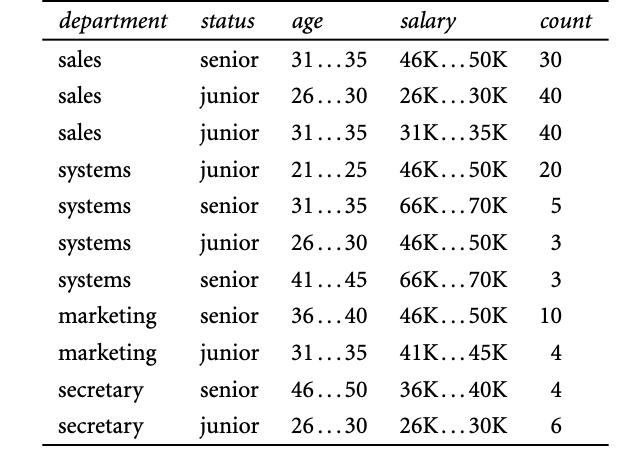
For this question, ignore the column count and treat each row as a single observation. We wish to classify a new employee from systems, who
For this question, ignore the column ‘count’ and treat each row as a single observation. We wish to classify a new employee from systems, who is 47 years old, and makes 70K into senior or junior.
(a) (1pts) Classify the employee using 3-nearest neighbors.
(b) (2pts) Build a decision tree as described in class and classify the employee using your decision tree. (
c) (2pts) Classify the employee using the Naive Bayes algorithm.
(d) How would you modify the basic decision tree algorithm to take into consideration the count of each generalized data tuple (i.e., of each row entry)?
(e) Use your algorithm to construct a decision tree from the given data.
(f) Given a data tuple having the values “systems,” “26 . . . 30,” and “46–50K” for the attributes department, age, and salary, respectively, what would a na¨ıve Bayesian classification of the status for the tuple be?
department status age salary senior 31...35 46K...50K 30 junior 26...30 26K...30K 40 junior 31...35 31K...35K 40 systems junior 21...25 46K...50K 20 systems senior 31...35 66K...70K 5 systems junior 26...30 46K...50K 3 systems senior 41...45 66K...70K 3 marketing senior 36...40 46K...50K 10 marketing junior 31...35 41K...45K 4 secretary senior 46...50 36K...40K 4 secretary junior 26...30 26K...30K 6 sales sales sales count
Step by Step Solution
3.38 Rating (151 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a 3Nearest Neighbors Classification To classify the new employee using 3nearest neighbors we need to find the three closest employees in the dataset b...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


