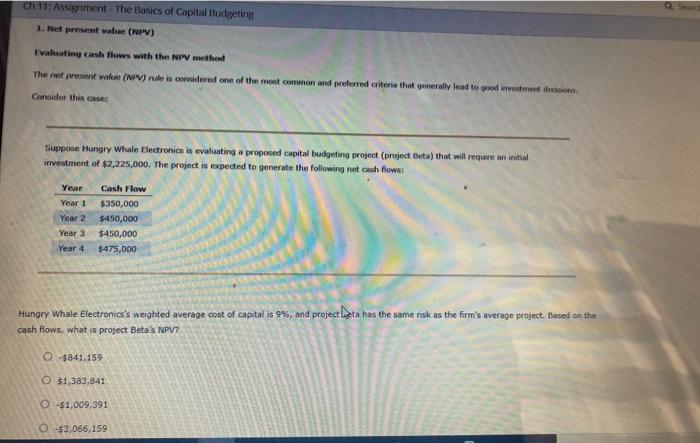
Ch 11: Assignment - The Basics of Capital Budgeting 1. Net present value (NPV) Evaluating cash flows with the NIV mited The net present watu (NIV) rule in considered one of the ment common and preferred criteria that generally lead to yood investment decision Consider this caset Suppose Hungry Whale Electronics is evaluating a proposed capital budgeting project (project Beta) that will require an initial investment of $2,225,000. The project is expected to generate the following net cash flows Year Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Cash Flow $350,000 $450,000 $450,000 $475,000 Hungry Whale Electronics's weighted average cost of capital is 9%, and project bata has the same risk as the firm's average project. Based on the cash flows, what is project Beta's NPV? O $841,159 O $1,383,841 -$1,009,391 0 $3,066,159 Making the accept or reject decision cess Tips DE YOU Hungry Whale Electronics's decision to aceptor reject project Betas independent of a cons on other projects. If the firm follows the NPV method, it should project Beta Tools troductory Suppose your bonect you to analyse two mutuely exclusive projecte project and projects. Both projects require the same investment amount and the accepta intlows of Project A la larger than the sum of cash flows of project. 8. A coworker told you that you don't need to do NPV analysis or her because you already know that project will have a larger Ny than proje 8. Do you agree with your coworkers statenrent? No the NPV calculation is based on percentage returns to the son project's cash flows does not affect a project's NPV. Yes, project A will always have the largest NPV because ts cash intlows are greater than project B's cash flows. No, the NPV calculation will take into account not only the projects cashinews but also the timing of cashindows and outflow. Consequently, project could have a larger NPV than project A even though project has larger cash now Making the accept or reject decision Hungry Whale Electronics's decision to accept or reject project. Beta is independent of its decisions on other projects. If the firm follows the NPV method, it should project Beta. 5 Suppose your boss has asked you to analyze two mutually exclusive projects-project A and project 6. Hoth projects require the same investment amount, and the sum of cash inflows of Project A is larger than the sum of cash inflows of project B. A coworker told you that you don't need to do an NPV analysis of the projects because you already know that project A will have a larger NPV than project 8. Do you agree with your coworker's statement? No, the NPV calculation is based on percentage returns, so the size of a project's cash flows does not affect a project's NPM/ ctory Yes, project A will always have the largest IPV, because its cash inflows are greater than project B's cash inflows. No, the NPV calculation will take into account not only the projects' cash inflows but also the timing of cash inflows and outflows. Consequently, project B could have a larger NPV than project A, even though project A has larger cash inflows