Question
channel leVels The producer and the final customer are part of every channel. We will use the number of intermediary levels to designate the length
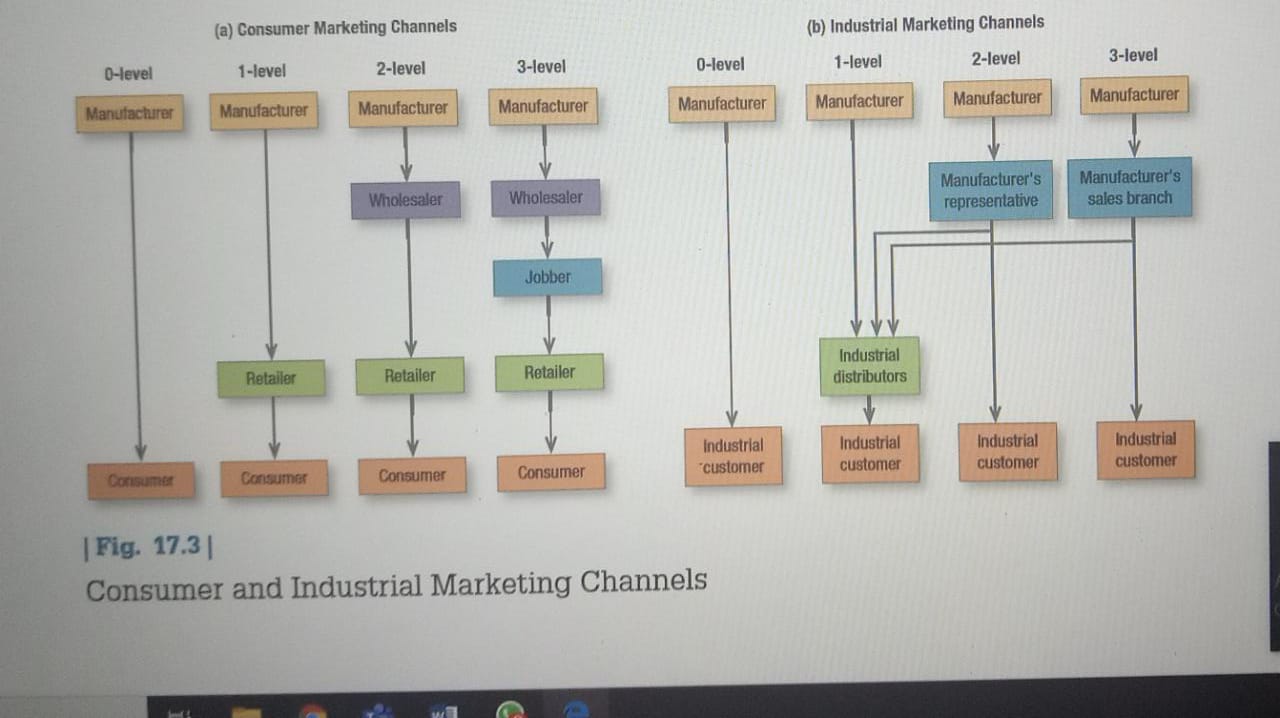
channel leVels The producer and the final customer are part of every channel. We will use the number of intermediary levels to designate the length of a channel. Figure 17.3(a) illustrates several consumer-goods marketing channels of different lengths. A zero-level channel, also called a direct marketing channel, consists of a manufacturer selling directly to the final customer. The major examples are mail order, online selling, TV selling, telemarketing, door-to-door sales, home parties, and manufacturer-owned stores. Traditionally, Franklin Mint sold collectibles through mail order; Red Envelope sold gifts online; Time-Life sold music and video collections through TV commercials or longer
"infomercials"; nonprofits and political organizations and candidates use the telephone to raise funds; Avon sales representatives sold cosmetics door to door; Tupperware sold its containers via in-home parties; and Apple sold computers and other consumer electronics through its own stores. Many of these firms now sell directly to customers online and via catalogs. Even traditional consumer-product firms are considering adding direct-to-consumer
e-commerce sites to their channel mix. Kimberly-Clark launched an online Kleenex Shop in the United Kingdom.27 A one-level channel contains one selling intermediary, such as a retailer. A two-level channel contains two intermediaries, typically a wholesaler and a retailer, and a three-level channel contains three. In the meatpacking industry, wholesalers sell to jobbers, essentially small-scale wholesalers, who sell to small retailers. In Japan, food distribution may include as many as six levels. Obtaining information about end users and exercising control become more difficult for the producer as the number of channel levels increases.
Figure 17.3(b) shows channels commonly used in B-to-B marketing. An industrial-goods manufacturer can use its sales force to sell directly to industrial customers, or it can sell to industrial distributors who sell to industrial customers, or it can sell through manufacturer's representatives or its own sales branches directly to industrial customers or indirectly to industrial customers through industrial distributors. Zero-, one-, and two-level marketing channels are quite common. Channels normally describe a forward movement of products from source to user, but reverse-flow channels are also important (1) to reuse products or containers (such as refillable chemical-carrying drums), (2) to refurbish products for resale (such as circuit boards or computers), (3) to recycle products, and (4) to dispose of products and packaging. Reverse-flow intermediaries include manufacturers' redemption centers, community groups, trash-collection specialists, recycling centers, trash-recycling brokers, and central processing warehousing.
QUESTION: Enlist the different channel levels and explain anyone them?
?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


