Chapter M:4 Accounting HW
1.
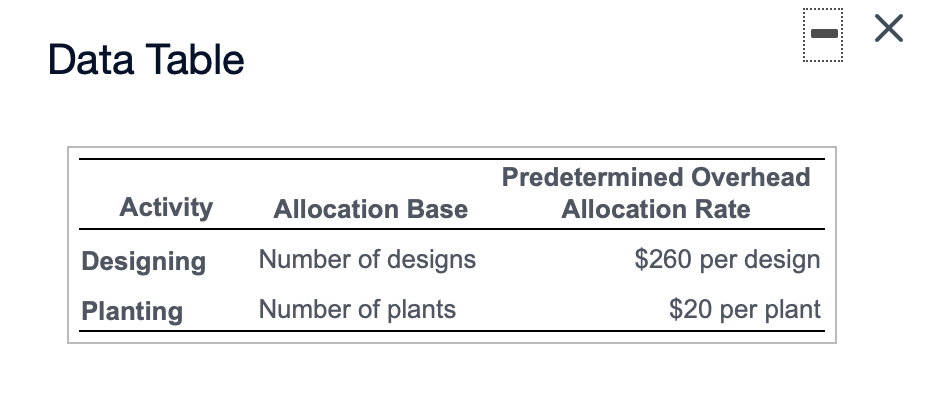
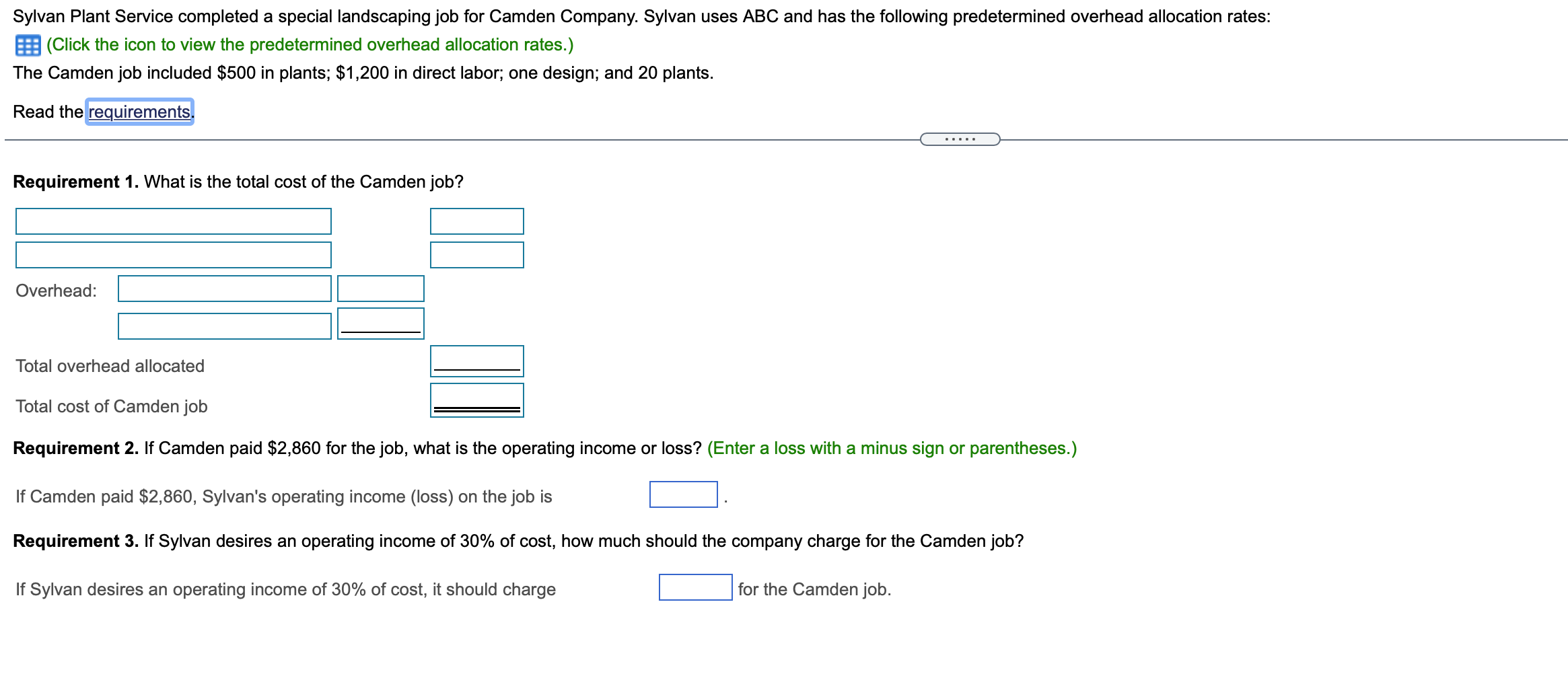
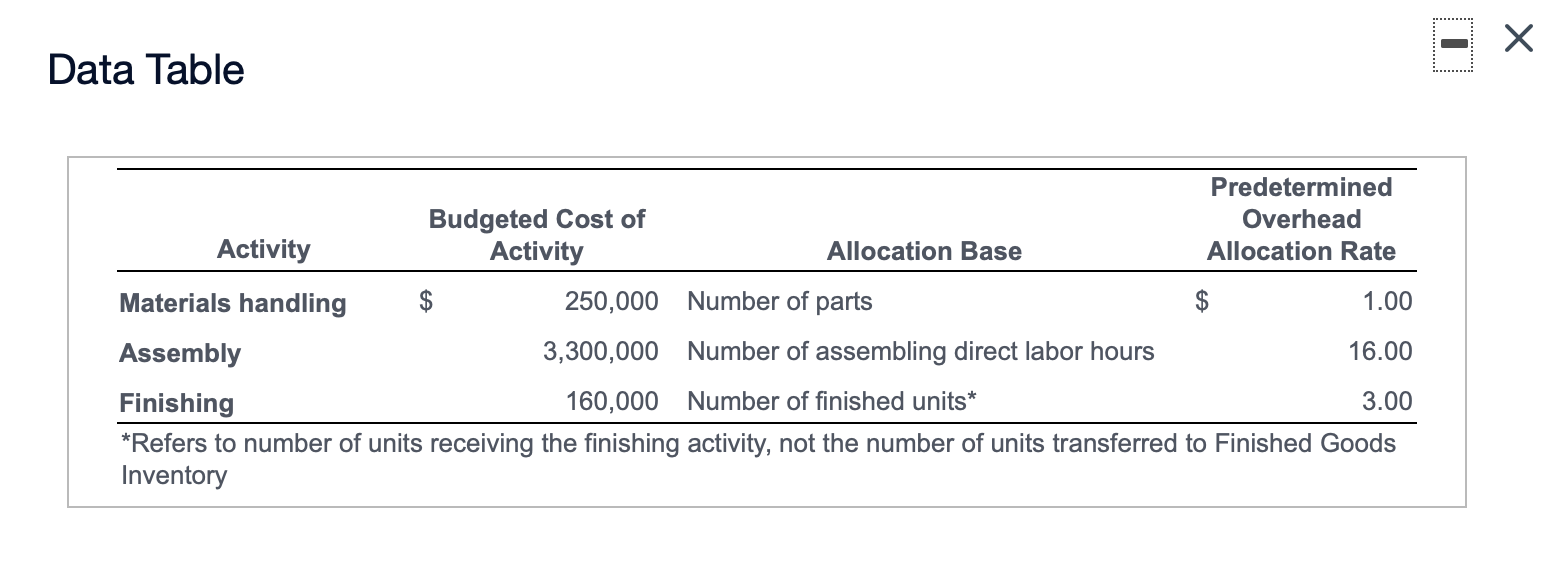
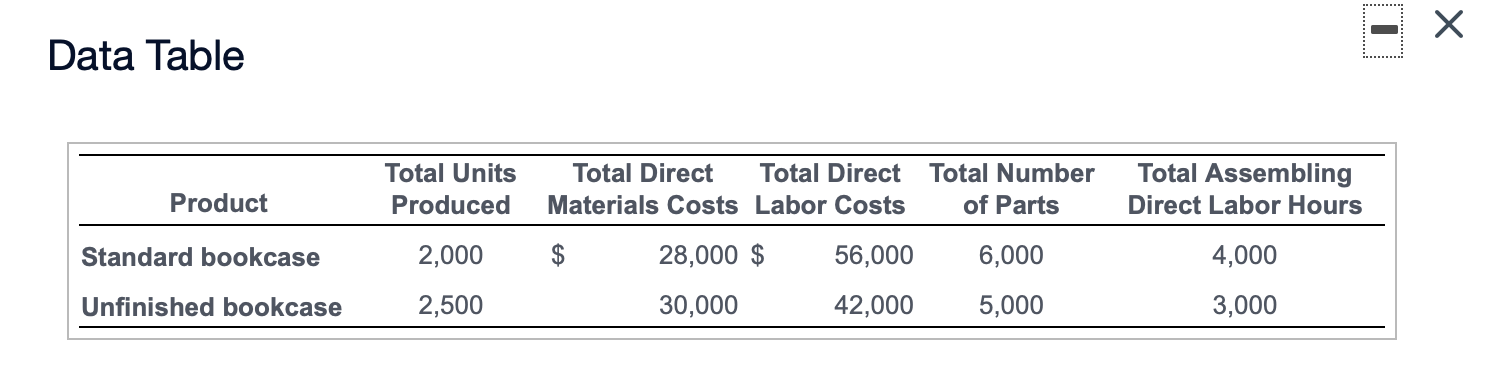
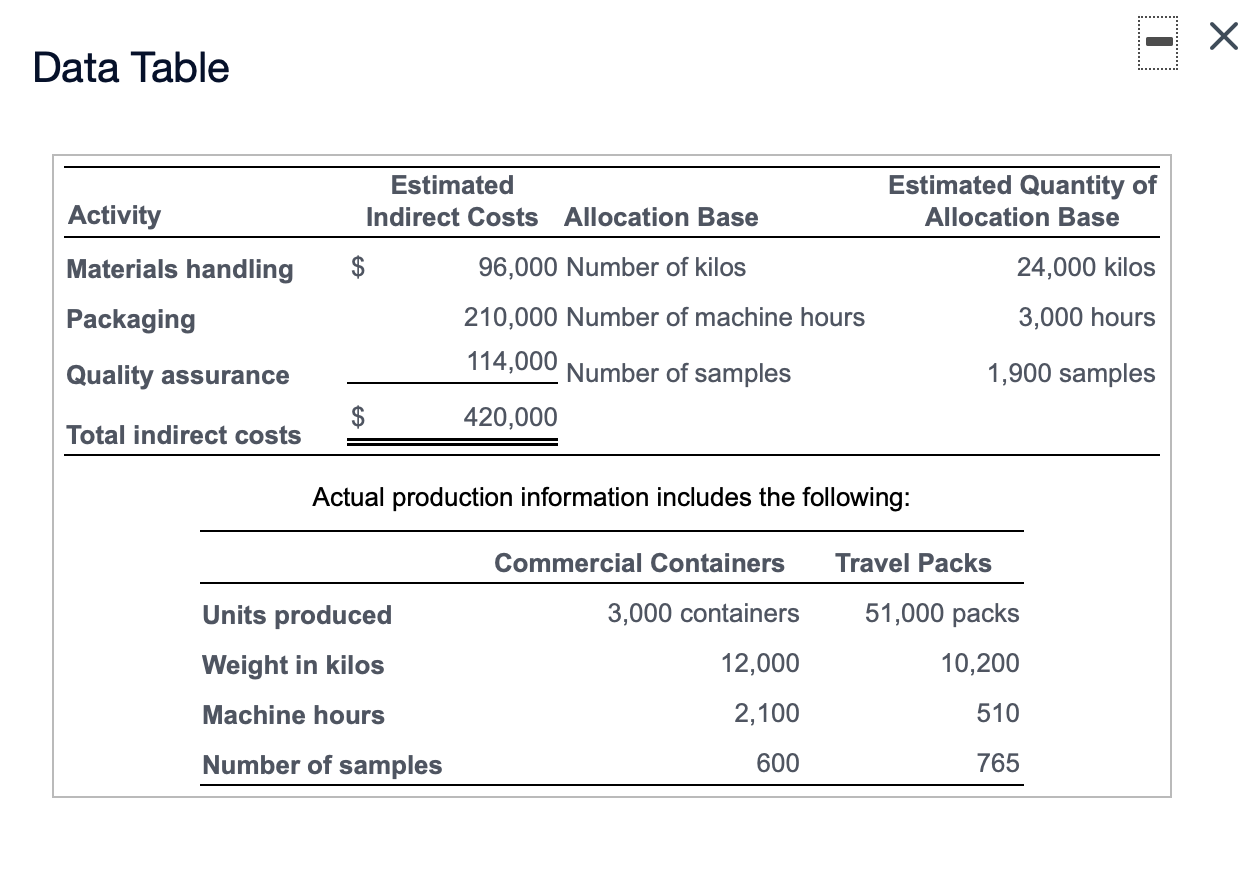
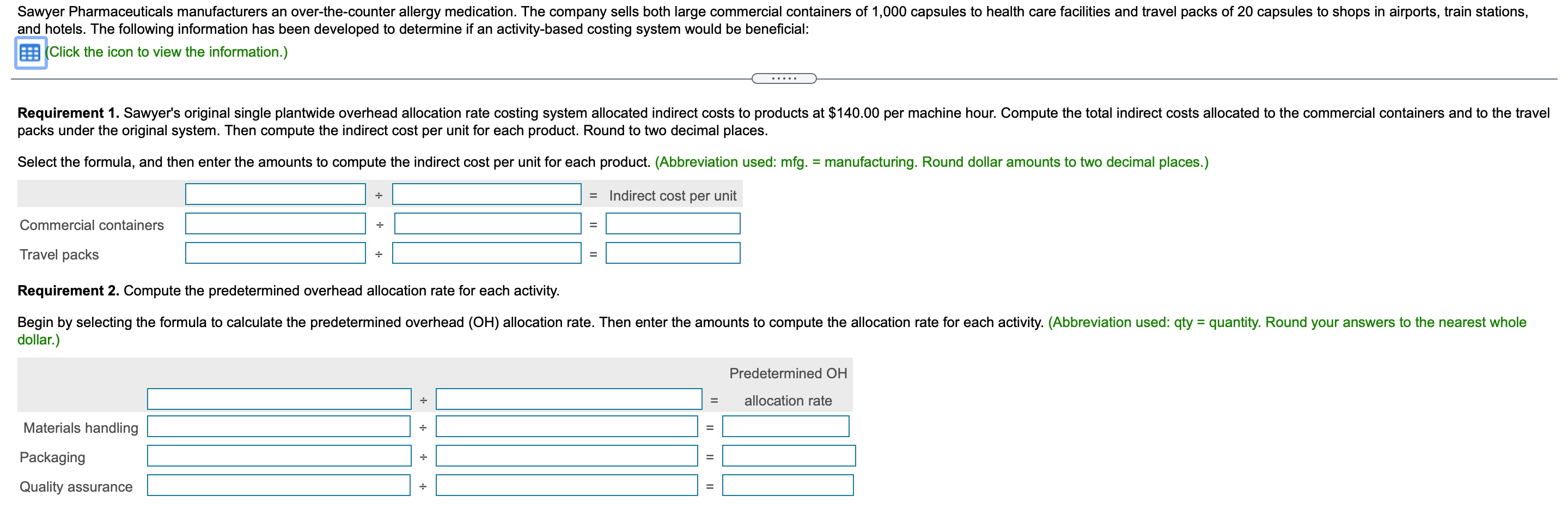
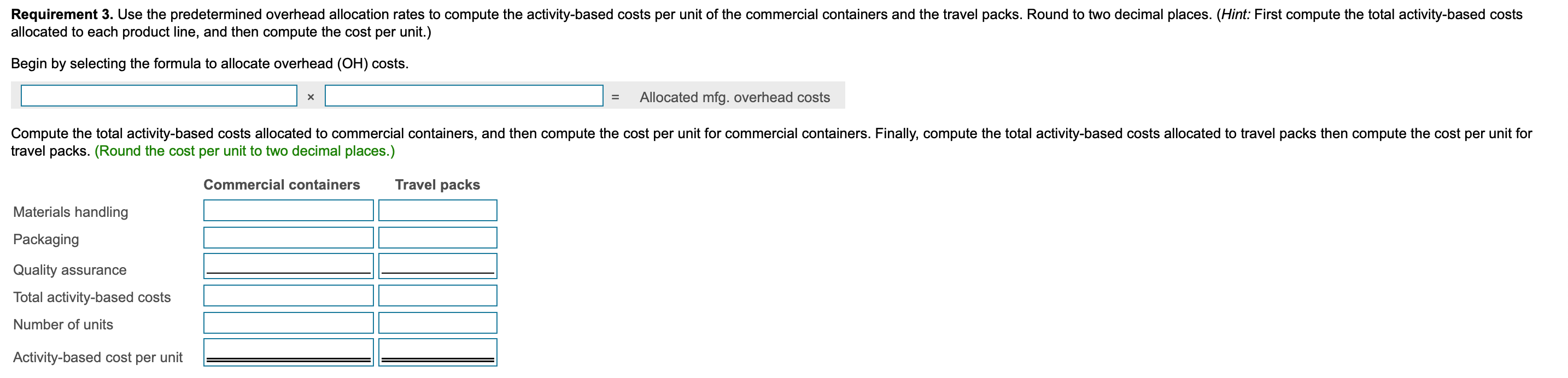
Data Table Predetermined Overhead Activity Allocation Base Allocation Rate Designing Number of designs $260 per design Planting Number of plants $20 per plant Sylvan Plant Service completed a special landscaping job for Camden Company. Sylvan uses ABC and has the following predetermined overhead allocation rates: a (Click the icon to view the predetermined overhead allocation rates.) The Camden job included $500 in plants; $1,200 in direct labor; one design; and 20 plants. Requirement 1. What is the total cost of the Camden job? Overhead: Total overhead allocated Total cost of Camden job Requirement 2. If Camden paid $2,860 for the job, what is the operating income or loss? (Enter a loss with a minus sign or parentheses.) If Camden paid $2,860, Sylvan's operating income (loss) on the job is Requirement 3. if Sylvan desires an operating income of 30% of cost, how much should the company charge for the Camden job? If Sylvan desires an operating income of 30% of cost, it should charge for the Camden job. X Data Table Predetermined Budgeted Cost of Overhead Activity Activity Allocation Base Allocation Rate Materials handling $ 250,000 Number of parts $ 1.00 Assembly 3,300,000 Number of assembling direct labor hours 16.00 Finishing 160,000 Number of finished units* 3.00 *Refers to number of units receiving the finishing activity, not the number of units transferred to Finished Goods InventoryData Table Total Units Total Direct Total Direct Total Number Total Assembling Product Produced Materials Costs Labor Costs of Parts Direct Labor Hours Standard bookcase 2,000 $ 28,000 $ 56,000 6,000 4,000 Unfinished bookcase 2,500 30,000 42,000 5,000 3,000 Allen, Inc. manufactures bookcases and uses an activity-based costing system. Allen's activity areas and related data follow: (Click the icon to view the activity areas and related data.) Allen produced two styles of bookcases in October: the standard bookcase and an unfinished bookcase, which has fewer parts and requires no finishing. The totals for quantities, direct materials costs, and other data follow: (Click the icon to view the totals for quantities, direct materials costs, and other data.) Requirement 1. Compute the manufacturing product cost per unit of each type of bookcase. (Enter a "0" for any zero-balances.) Standard Bookcase Unfinished Bookcase Total manufacturing cost Manufacturing cost per unitRequirement 2. Suppose that pre-manufacturing activities, such as product design, were assigned to the standard bookcases at $4 each and to the unfinished bookcases at $3 each. Similar analyses were conducted of post-manufacturing activities such as distribution, marketing, and customer service. The post-manufacturing costs were $23 per standard bookcase and $14 per unfinished bookcase. Compute the full product costs per unit. Standard Bookcase Unfinished Bookcase Full product cost per unit Requirement 3. Which product costs are reported in the external financial statements? Which costs are used for management decision making? Explain the difference. V, which include 7, are reported in the financial statements. Managers use , which include V, for decisions such as pricing and product emphasis. Requirement 4. What price should Allen's managers set for unfinished bookcases to earn a net profit of $15 per bookcase? To earn a net profit of $15 per bookcase, Allen's managers should chargeData Table Estimated Estimated Quantity of Activity Indirect Costs Allocation Base Allocation Base Materials handling $ 96,000 Number of kilos 24,000 kilos Packaging 210,000 Number of machine hours 3,000 hours Quality assurance Number of samples 1,900 samples Total indirect costs 420,000 Actual production information includes the following: Commercial Containers Travel Packs Units produced 3,000 containers 51,000 packs Weight in kilos 12,000 10,200 Machine hours 2,100 510 Number of samples 600 765 Sawyer Pharmaceuticals manufacturers an over-the-counter allergy medication. The company sells both large commercial containers of 1,000 capsules to health care facilities and travel packs of 20 capsules to shops in airports. train stations. and hotels. The following information has been developed to determine if an activity-based costing system would be benecial: lick the icon to view the information.) Requlrement 1. Sawyers original single plantvvide overhead allocation rate costing system allocated indirect costs to products at $140.00 per machine hour. Compute the total indirect costs allocated to the commercial containers and to the travel packs under the original system. Then compute the indirect cost per unit for each product. Round to two decimal places. Select the fon'nula. and then enter the amounts to compute the indirect cost per unit for each product. (Abbreviation used: mfg. = manufacturing. Round dollar amounts to two decimal places.) + = Indirect cost per unit Commercial containers + = Travel packs + = Requlrement 2. Compute the predetermined overhead allocation rate for each activity. Begin by selecting the formula to calculate the predetermined overhead (OH) allocation rate. Then enter the amounts to compute the allocation rate for each activity. (Abbreviation used: qty = quantity. Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar.) Predetennined OH + = allocation rate Materials handling + = Packaging + = Quality assurance + Requirement 3. Use the predetermined overhead allocation rates to compute the activity-based costs per unit of the commercial containers and the travel packs. Round to two decimal places. (Hint: First compute the total activity-based costs allocated to each product line, and then compute the cost per unit) Begin by selecting the formula to allocate overhead (0H) costs. x = Allocated mfg, overhead costs Compute the total activity-based costs allocated to commercial containers, and then compute the cost per unit for commercial containers Finally. compute the total activity-based costs allocated to travel packs then compute the cost per unit for travel packs. (Round the cost per unit to two decimal places.) Commercial containers Travel packs Materials handling Packaging Quality assurance Total activity-based costs Number of units Activity-based cost per unit Requirement 4. Compare the indirect activity-based costs per unit to the indirect costs per unit from the traditional system. How have the unit costs changed? Explain why the costs changed. Relative to activity-based costing (ABC), the traditional system V the commercial containers and l the travel packs. The traditional system allocates overhead costs solely on Activity-based costing (ABC) reoognizes that although commercial containers require 7 machine hours per unit than travel packs, they proportion of material handling and quality assurance. 7 the same