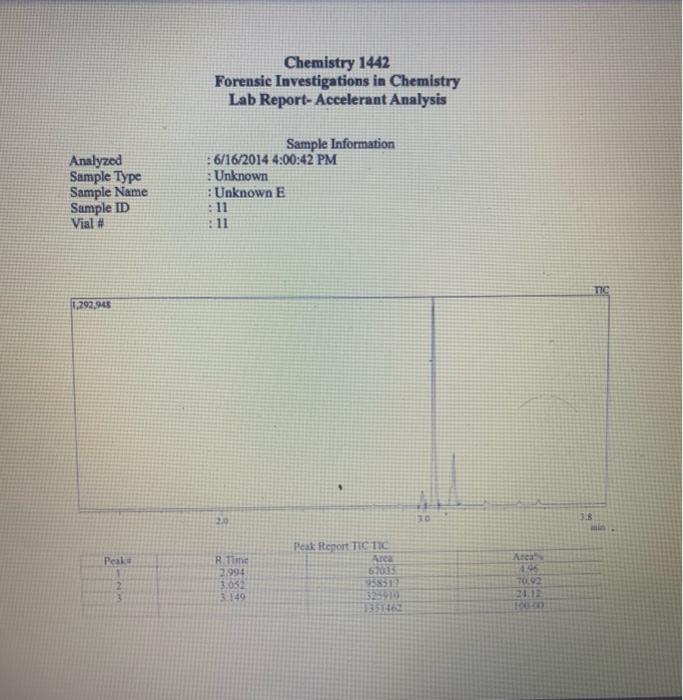
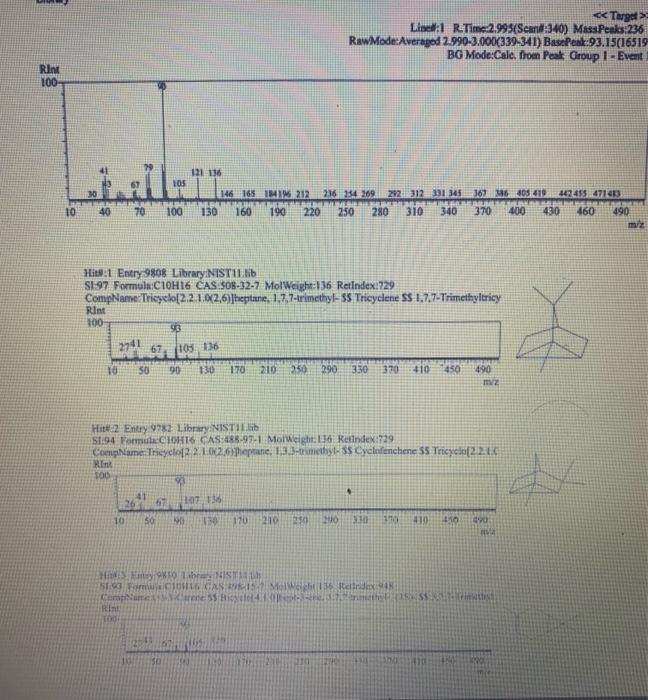
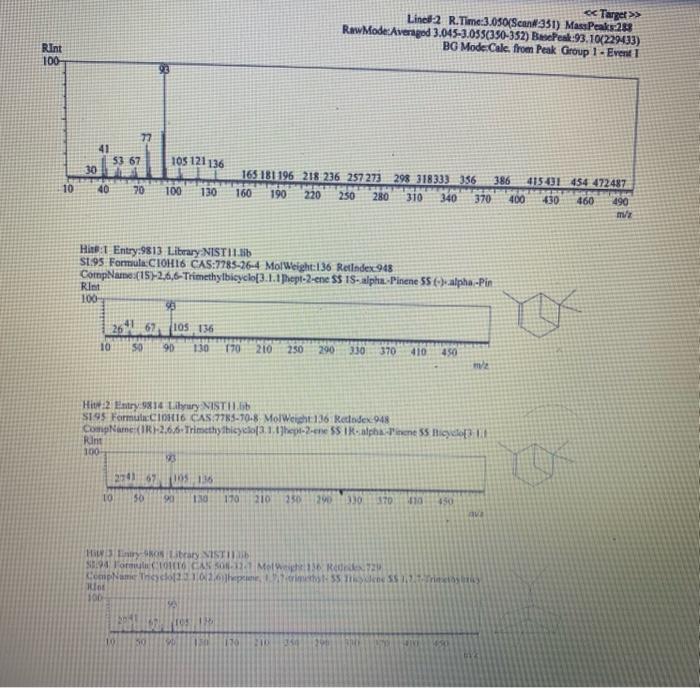
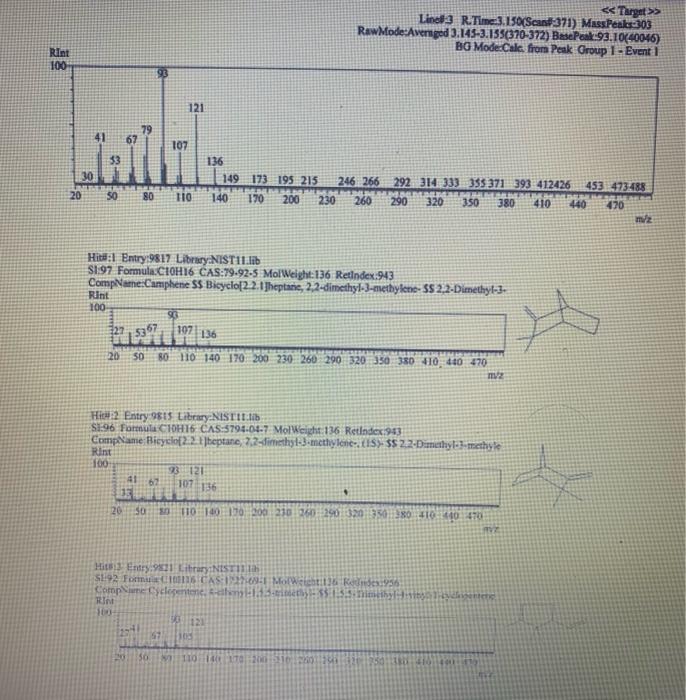
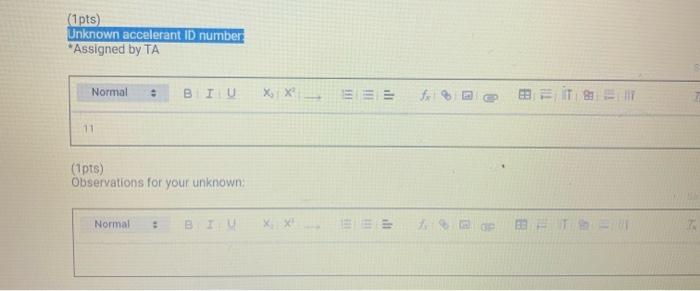
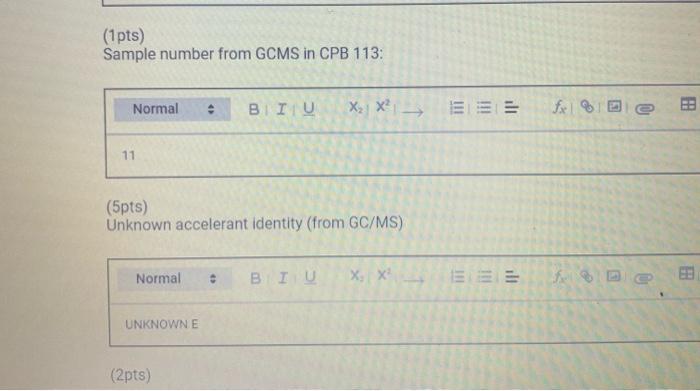
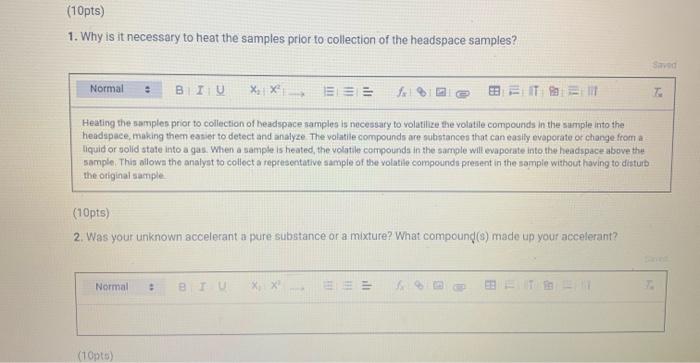
Chemistry 1442 Forensic Investigations in Chemistry Lab Report- Accelerant Analysis Sample Information AnalyzedSampleTypeSampleNameSampleIDVial#:6116/20144:00:42PM:Unknown:UnknownE:11:11 1,292,945 Peak fieport Ticix Peak 1 2 3 3 Histist Entry?ses LibraryiNiST11 ib St97 Formuln:C10H16 CAS S08-32-7 MolWeight 136 Retindexi729 CompName:Tricycho[2.2.1.0(2,6)]heptane, 1,7,7-1rimethy- 55 Tricyclene 551.7,7-Trimethyltricy Rint Hitu:2 Entry 9732 Libran NIST II Ilib S1:94 FomalecinH16 CAS:48g-97-1 Motweight:1.6 Kelindex:729 MInt Lined2 R.Time:3.050(Scann1351) MassPealssat? RawMode-Avengod 3.045-3.055(350-352) Buncieat:93. 10(229433) Hite: II Entry: 9813 Litrary NISTH1 ib St,95 Formula CiOH16 CAS:7785-76-4 MolWeighte136 Relindex-948 CotnpNarbe:(15-2,6,6-Trimethylbicyclo[3.1.1 pept-2-ene 5S is-alpha:-Pinene 55 (-) alpha -Pin Rlat Hite 2 Untry 9814 Lilyury NISTil.lib S19s Farmuliceiouti6 CAS:7785-70.8 MolWeight:136 Redosex 948 100ing Lindf-3 R.Tine3.150(Scan-371) Massheelese303 RawMlodesAventged 3.145-3.155(370-372) BasePoik.93.10(40046) Hicha Entrye 98 If LitraryeNisittitio \$1.96 Fortmula C10HIf CAS:5794.04-7. MorWeight 136 Rethdex:983 Rint Hits y ensty 9211 Litrarytisition Cing (1pts) Unknown accelerant ID numben "Assigned by TA (1pts) Sample number from GCMS in CPB 113: (5pts) Unknown accelerant identity (from GC/MS) 1. Why is it necessary to heat the samples prior to collection of the headspace samples? Heating the samples priof to collection of headspace samples is necessary to volatilize the volatile compounds in the sumple into the headipace. making them easier to detect and analyze. The volatile compounds are aubatances that can easily evaporate or change from a liquid or solid state into a gas. When a sample is heated, the volatile corpounds in the sample will evaporate into the headspace above the sample. This allowa the analyat to collect a representative sample of the volatile compounds present in the sample without having to diaturb the otiginal sample (10pts) 2. Was your unknown accelerant a pure substance or a mixture? What compoun(s) made up your accelerant? 3. Based on your accelerant identification, do the compounds you observe in the GC-MS match to expected compounds for this substance? (refer to Table 1) (10pis) 4. If the GC/MS chromatographic elution peaks in the sample are far apart and analysis takes a relatively long time. should you increase or decrease the column temperature program to improve analysis time? Explain your reasoning. (10pto). 5. Can paper chromatography be used to determine conclusively whether two ink maris came from the same pen? 5. Can paper chromatography be used to determine conclusively whether two ink marks came from the same pen? (10p+s) 6. Compare the retention factors of the spots from the different pens. Do any of the pens contain the same components in their black ink? Explain your reasoning. (10pts) 7. Identify the brand of the unknovn pen. Explain your reasoning 7. Identify the brand of the unknown pen. Explain your reasoning. Figure 6: Schematic Diagram of GC/MS. The numbers in the diagram are referred in the main text. Table 1: Retention times of common household accelerants. II. Ink Analysis Paper Chromatography We are not always able to classify something as a pure substance or a mixture based on visual inspection. If we are given a material, how can we determine if it is a pure substance or a mixture? Chromatography is a technique used to separate and identify the components of a mixture. The mechanism of separation in paper chromatography is similar to that of gas chromatography (GC). In paper chromatography, a very small amount of a sample (a mixture to Chemistry 1442 Forensic Investigations in Chemistry Lab Report- Accelerant Analysis Sample Information AnalyzedSampleTypeSampleNameSampleIDVial#:6116/20144:00:42PM:Unknown:UnknownE:11:11 1,292,945 Peak fieport Ticix Peak 1 2 3 3 Histist Entry?ses LibraryiNiST11 ib St97 Formuln:C10H16 CAS S08-32-7 MolWeight 136 Retindexi729 CompName:Tricycho[2.2.1.0(2,6)]heptane, 1,7,7-1rimethy- 55 Tricyclene 551.7,7-Trimethyltricy Rint Hitu:2 Entry 9732 Libran NIST II Ilib S1:94 FomalecinH16 CAS:48g-97-1 Motweight:1.6 Kelindex:729 MInt Lined2 R.Time:3.050(Scann1351) MassPealssat? RawMode-Avengod 3.045-3.055(350-352) Buncieat:93. 10(229433) Hite: II Entry: 9813 Litrary NISTH1 ib St,95 Formula CiOH16 CAS:7785-76-4 MolWeighte136 Relindex-948 CotnpNarbe:(15-2,6,6-Trimethylbicyclo[3.1.1 pept-2-ene 5S is-alpha:-Pinene 55 (-) alpha -Pin Rlat Hite 2 Untry 9814 Lilyury NISTil.lib S19s Farmuliceiouti6 CAS:7785-70.8 MolWeight:136 Redosex 948 100ing Lindf-3 R.Tine3.150(Scan-371) Massheelese303 RawMlodesAventged 3.145-3.155(370-372) BasePoik.93.10(40046) Hicha Entrye 98 If LitraryeNisittitio \$1.96 Fortmula C10HIf CAS:5794.04-7. MorWeight 136 Rethdex:983 Rint Hits y ensty 9211 Litrarytisition Cing (1pts) Unknown accelerant ID numben "Assigned by TA (1pts) Sample number from GCMS in CPB 113: (5pts) Unknown accelerant identity (from GC/MS) 1. Why is it necessary to heat the samples prior to collection of the headspace samples? Heating the samples priof to collection of headspace samples is necessary to volatilize the volatile compounds in the sumple into the headipace. making them easier to detect and analyze. The volatile compounds are aubatances that can easily evaporate or change from a liquid or solid state into a gas. When a sample is heated, the volatile corpounds in the sample will evaporate into the headspace above the sample. This allowa the analyat to collect a representative sample of the volatile compounds present in the sample without having to diaturb the otiginal sample (10pts) 2. Was your unknown accelerant a pure substance or a mixture? What compoun(s) made up your accelerant? 3. Based on your accelerant identification, do the compounds you observe in the GC-MS match to expected compounds for this substance? (refer to Table 1) (10pis) 4. If the GC/MS chromatographic elution peaks in the sample are far apart and analysis takes a relatively long time. should you increase or decrease the column temperature program to improve analysis time? Explain your reasoning. (10pto). 5. Can paper chromatography be used to determine conclusively whether two ink maris came from the same pen? 5. Can paper chromatography be used to determine conclusively whether two ink marks came from the same pen? (10p+s) 6. Compare the retention factors of the spots from the different pens. Do any of the pens contain the same components in their black ink? Explain your reasoning. (10pts) 7. Identify the brand of the unknovn pen. Explain your reasoning 7. Identify the brand of the unknown pen. Explain your reasoning. Figure 6: Schematic Diagram of GC/MS. The numbers in the diagram are referred in the main text. Table 1: Retention times of common household accelerants. II. Ink Analysis Paper Chromatography We are not always able to classify something as a pure substance or a mixture based on visual inspection. If we are given a material, how can we determine if it is a pure substance or a mixture? Chromatography is a technique used to separate and identify the components of a mixture. The mechanism of separation in paper chromatography is similar to that of gas chromatography (GC). In paper chromatography, a very small amount of a sample (a mixture to