Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
A 0.8 m-diameter pool of ethanol is ignited at floor level in a room with a normal door opening. After a while the smoke

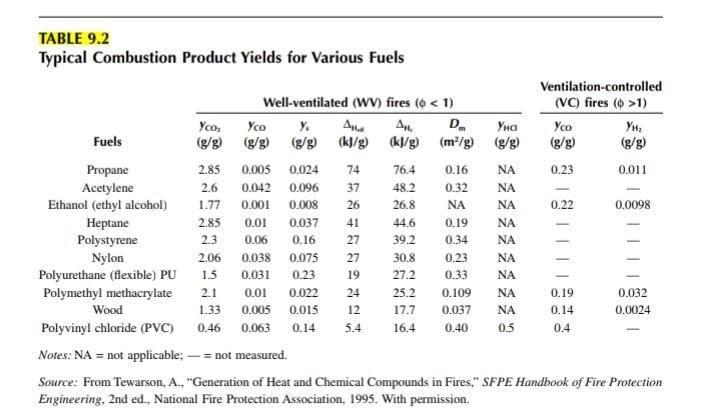
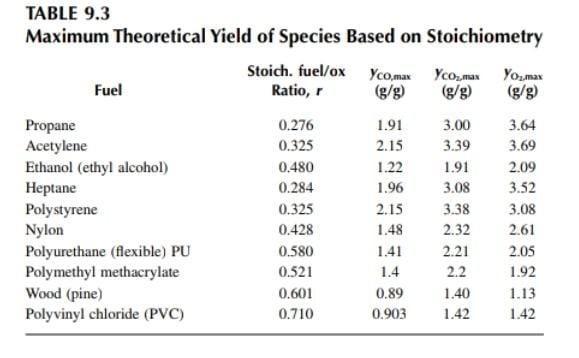
A 0.8 m-diameter pool of ethanol is ignited at floor level in a room with a normal door opening. After a while the smoke layer stabilizes at a height of 1.5 m from the floor. Calculate the CO, concentration in the hot layer. Suggested answer: Using equations and tables from Chapter 3, we find m = 0.0075 kg/s, m, roughly 0.8 kg/s, o = 0.086, yco, = 1.77 g/g (Table 9.2), f = 0.0094, and Yco, = 1.7%. 9.3 A pool of ethanol is ignited in the scenario described in Problem 9.2, but now the door is closed. There is a well-specified leakage opening at floor level. The upper layer is now O00 by CRC Press LLC much hotter and the mass loss rate is measured to be m; = 0.05 kg/s. The mass flow rate in through the leakage opening is measured to be 0.3 kg/s. Estimate the concentration of CO, and O, in the hot layer. Suggested answer: The equivalence ratio is found to be o = 1.51. Table 9.3 gives yo, max = 2.09 and yco, max = 1.91. Therefore yo, = 2.09/1.51 = 1.38 g/g and yco, = 1.26 g/g. Fuel mixture fraction is f= 0.05/(0.05 + 0.3) = 0.143, so Yco, = 1.26 - 0.143 18.0% and Yo, = 1.38 0.143 = 19.7%. = 1.91/1.51 %3D TABLE 9.2 Typical Combustion Product Yields for Various Fuels Ventilation-controlled Well-ventilated (WV) fires (6 < 1) (VC) fires ( >1) D. (kl/g) (m/g) (g/g) Yco, Yco Y. Yco Fuels (g/g) (g/g) (g/g) (k)/g) (g/g) (g/g) 0.005 0.024 Propane Acetylene Ethanol (ethyl alcohol) Heptane Polystyrene Nylon Polyurethane (flexible) PU 2.85 74 76.4 0.16 NA 0.23 0.011 2.6 0.042 0.096 37 48.2 0.32 NA 1.77 0.001 0.008 26 26.8 NA NA 0.22 0.0098 2.85 0.01 0.037 41 44.6 0.19 NA 2.3 0.06 0.16 27 39.2 0.34 NA 2.06 0.038 0.075 27 30.8 0.23 NA 1.5 0.031 0.23 19 27.2 0.33 NA Polymethyl methacrylate 2.1 0.01 0.022 24 25.2 0.109 NA 0.19 0.032 Wood 1.33 0.005 0.015 12 17.7 0.037 NA 0.14 0.0024 Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) 0.46 0.063 0.14 5.4 16.4 0.40 0.5 0.4 Notes: NA = not applicable; -= not measured. Source: From Tewarson, A., "Generation of Heat and Chemical Compounds in Fires," SFPE Handbook of Fire Protection Engineering, 2nd ed., National Fire Protection Association, 1995. With permission. TABLE 9.3 Maximum Theoretical Yield of Species Based on Stoichiometry Stoich. fuel/ox Yco,max Yco,mas Ratio, r Youmax (g/g) Fuel (g/g) (g/g) Propane Acetylene Ethanol (ethyl alcohol) ptane Polystyrene Nylon Polyurethane (flexible) PU Polymethyl methacrylate Wood (pine) Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) 0.276 1.91 3.00 3.64 0.325 2.15 3.39 3.69 0.480 1.22 1.91 2.09 0.284 1.96 3.08 3.52 0.325 2.15 3.38 3.08 0.428 1.48 2.32 2.61 0.580 1.41 2.21 2.05 0.521 1.4 2.2 1.92 0.601 0.89 1.40 1.13 0.710 0.903 1.42 1.42
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.42 Rating (152 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Mass loss rate 005kgs Mass flow rate through leakage 03kg...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


