
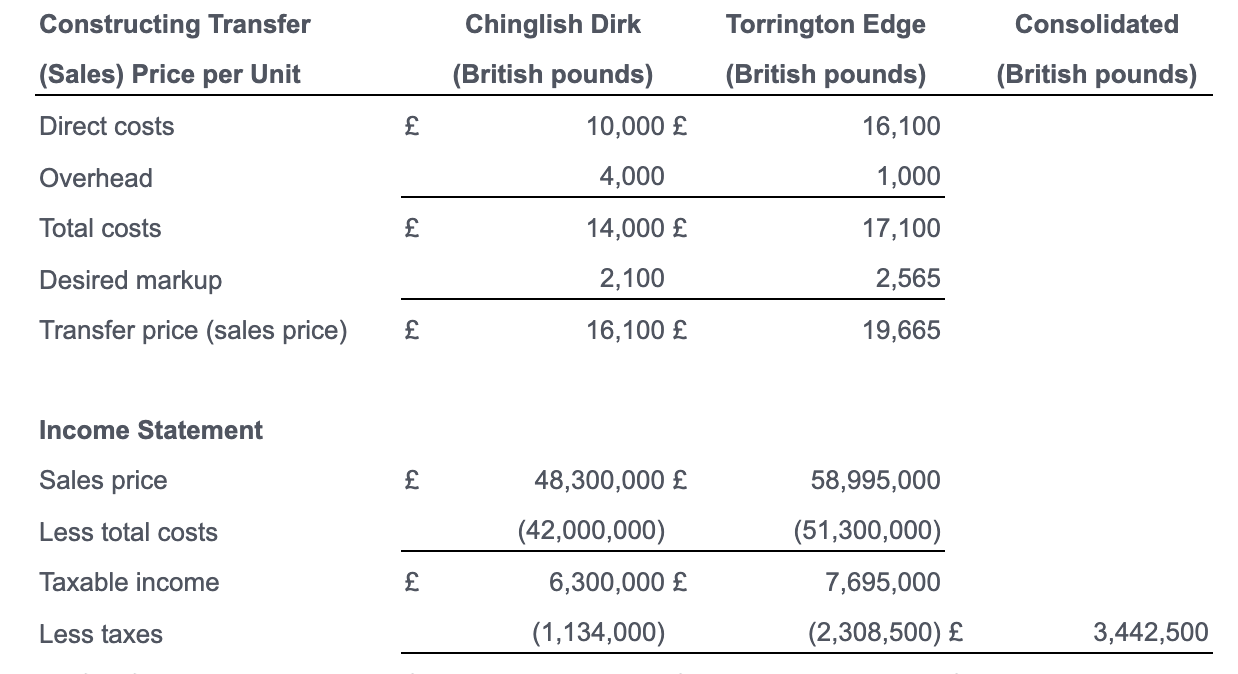
Chinglish Dirk (B). Chinglish Dirk Company (Hong Kong) exports razor blades to its wholly owned parent company, Torrington Edge (Great Britain). Hong Kong tax rates are 18% and British tax rates are 30%. The markup was 15% and the sales volume was 3,000 units. Chinglish calculates its profit per container as follows (all values in British pounds); Corporate management of Torrington Edge wishes to reposition profit in Hong Kong. It is, however, facing two constraints. First, the final sales price in Great Britain must be 20,000 or less to remain competitlve. Secondly, the British tax authorities in working with Torrington Edge's cost accounting staff-has established a maximum transfer price allowed (from Hong Kong) of 17.800. Prove that the optimal combination of markups is a 25.0% markup at Chinglish and an 8.1% markup in Torrington Edge. What is the impact of this repositioning on consolidated after-tax profits and total tax payments? Calculate the profits of Chinglish Dirk and Torrington Edge, and the consolidated results of both, if the markup at Chinglish was increased to 25.0% and the markup at Torrington was reduced to 8.1% in the following table: (Round to the nearest cent.) Consolidated Constructing Transfer (Sales) Price per Unit Torrington Edge (British pounds) (British pounds) Chinglish Dirk (British pounds) 10,000 4.000 14,000 Direct costs Overhead Total costs Desired markup Transfer price (sales price) 1,000 $ Income Statement Sales price Less total costs Taxable income Less taxes Profit, after-tax Consolidated Constructing Transfer (Sales) Price per Unit Chinglish Dirk (British pounds) Torrington Edge (British pounds) (British pounds) Direct costs 10,000 16,100 Overhead 4,000 1,000 Total costs 14,000 17,100 2,100 2,565 Desired markup Transfer price (sales price) 16,100 19,665 Income Statement Sales price 48,300,000 58,995,000 Less total costs (42,000,000) (51,300,000) Taxable income 6,300,000 7,695,000 (2,308,500) Less taxes (1,134,000) 3,442,500 Chinglish Dirk (B). Chinglish Dirk Company (Hong Kong) exports razor blades to its wholly owned parent company, Torrington Edge (Great Britain). Hong Kong tax rates are 18% and British tax rates are 30%. The markup was 15% and the sales volume was 3,000 units. Chinglish calculates its profit per container as follows (all values in British pounds); Corporate management of Torrington Edge wishes to reposition profit in Hong Kong. It is, however, facing two constraints. First, the final sales price in Great Britain must be 20,000 or less to remain competitlve. Secondly, the British tax authorities in working with Torrington Edge's cost accounting staff-has established a maximum transfer price allowed (from Hong Kong) of 17.800. Prove that the optimal combination of markups is a 25.0% markup at Chinglish and an 8.1% markup in Torrington Edge. What is the impact of this repositioning on consolidated after-tax profits and total tax payments? Calculate the profits of Chinglish Dirk and Torrington Edge, and the consolidated results of both, if the markup at Chinglish was increased to 25.0% and the markup at Torrington was reduced to 8.1% in the following table: (Round to the nearest cent.) Consolidated Constructing Transfer (Sales) Price per Unit Torrington Edge (British pounds) (British pounds) Chinglish Dirk (British pounds) 10,000 4.000 14,000 Direct costs Overhead Total costs Desired markup Transfer price (sales price) 1,000 $ Income Statement Sales price Less total costs Taxable income Less taxes Profit, after-tax Consolidated Constructing Transfer (Sales) Price per Unit Chinglish Dirk (British pounds) Torrington Edge (British pounds) (British pounds) Direct costs 10,000 16,100 Overhead 4,000 1,000 Total costs 14,000 17,100 2,100 2,565 Desired markup Transfer price (sales price) 16,100 19,665 Income Statement Sales price 48,300,000 58,995,000 Less total costs (42,000,000) (51,300,000) Taxable income 6,300,000 7,695,000 (2,308,500) Less taxes (1,134,000) 3,442,500








