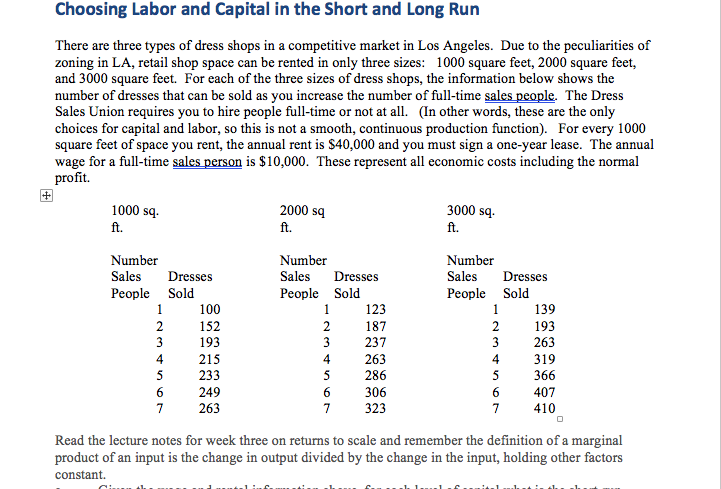

Choosing Labor and Capital in the short and Long Run There are three types of dress shops in a competitive market in Los Angeles. Due to the peculiarities of zoning in LA, retail shop space can be rented in only three sizes: 1000 square feet, 2000 square feet, and 3000 square feet. For each of the three sizes of dress shops, the information below shows the number of dresses that can be sold as you increase the number of full-time sales people. The Dress Sales Union requires you to hire people full-time or not at all. In other words, these are the only choices for capital and labor, so this is not a smooth, continuous production function). For every 1000 square feet of space you rent, the annual rent is $40,000 and you must sign a one-year lease. The annual wage for a full-time sales person is $10,000. These represent all economic costs including the normal profit. 1000 sq. ft. 2000 sq ft. 3000 sq. ft. Number Sales Dresses People Sold 1 100 2 152 3 4 215 5 233 6 249 7 263 193 Number Sales Dresses People Sold 1 123 2 187 3 237 4 263 5 286 6 306 7 323 Number Sales Dresses People Sold 1 139 2 193 3 263 4 319 S 366 6 407 7 410 Read the lecture notes for week three on returns to scale and remember the definition of a marginal product of an input is the change in output divided by the change in the input, holding other factors constant. a. b. Given the wage and rental information above, for each level of capital what is the short-run average total cost of producing 263 units of output? (3 points) What is the long-run average total cost of producing 263 units of output? (2 points) [Hint: Remember that the short run average total cost is equal to the averaged fixed cost plus average variable cost at that level of output. For long run average total cost look at the section on Economies of Scale in the notes and remember that you are looking for the long run average total cost at a specific quantity.] Explain in words why you chose each answer. For firms with each amount of capital at each amount of labor, determine variable cost, total cost, average variable cost per dress, average total cost per dress, and the marginal cost of an additional dress. (4 points) Due to differences in the periods of the leases that the various dress shops have signed, all three types of dress shops are currently in the market. If the net price to the dress shop (retail price minus wholesale price) of a dress is $500, what is the optimal number of workers to hire for each level of capital? What profits are earned in the dress shops for each type of capital? Explain why you made each choice in words. (8 points). Consider the long run situation in the market where there will strong price competition, dress shops can change their size, and dress shops enter and exit the market. What do you anticipate will be the net price of a dress in the long run? Based on that net price, what will be the optimal choice of shop size and number of employees in the long run? Explain why you come to these conclusions. (3 points). d. Choosing Labor and Capital in the short and Long Run There are three types of dress shops in a competitive market in Los Angeles. Due to the peculiarities of zoning in LA, retail shop space can be rented in only three sizes: 1000 square feet, 2000 square feet, and 3000 square feet. For each of the three sizes of dress shops, the information below shows the number of dresses that can be sold as you increase the number of full-time sales people. The Dress Sales Union requires you to hire people full-time or not at all. In other words, these are the only choices for capital and labor, so this is not a smooth, continuous production function). For every 1000 square feet of space you rent, the annual rent is $40,000 and you must sign a one-year lease. The annual wage for a full-time sales person is $10,000. These represent all economic costs including the normal profit. 1000 sq. ft. 2000 sq ft. 3000 sq. ft. Number Sales Dresses People Sold 1 100 2 152 3 4 215 5 233 6 249 7 263 193 Number Sales Dresses People Sold 1 123 2 187 3 237 4 263 5 286 6 306 7 323 Number Sales Dresses People Sold 1 139 2 193 3 263 4 319 S 366 6 407 7 410 Read the lecture notes for week three on returns to scale and remember the definition of a marginal product of an input is the change in output divided by the change in the input, holding other factors constant. a. b. Given the wage and rental information above, for each level of capital what is the short-run average total cost of producing 263 units of output? (3 points) What is the long-run average total cost of producing 263 units of output? (2 points) [Hint: Remember that the short run average total cost is equal to the averaged fixed cost plus average variable cost at that level of output. For long run average total cost look at the section on Economies of Scale in the notes and remember that you are looking for the long run average total cost at a specific quantity.] Explain in words why you chose each answer. For firms with each amount of capital at each amount of labor, determine variable cost, total cost, average variable cost per dress, average total cost per dress, and the marginal cost of an additional dress. (4 points) Due to differences in the periods of the leases that the various dress shops have signed, all three types of dress shops are currently in the market. If the net price to the dress shop (retail price minus wholesale price) of a dress is $500, what is the optimal number of workers to hire for each level of capital? What profits are earned in the dress shops for each type of capital? Explain why you made each choice in words. (8 points). Consider the long run situation in the market where there will strong price competition, dress shops can change their size, and dress shops enter and exit the market. What do you anticipate will be the net price of a dress in the long run? Based on that net price, what will be the optimal choice of shop size and number of employees in the long run? Explain why you come to these conclusions. (3 points). d








