Question
class BinarySearchTree: def __init__(self, data, left=None, right=None): self.data = data self.left = left self.right = right def get_left(self): return self.left def get_right(self): return self.right def
class BinarySearchTree: def __init__(self, data, left=None, right=None): self.data = data self.left = left self.right = right
def get_left(self): return self.left
def get_right(self): return self.right
def get_data(self): return self.data
def set_data(self, data): self.data = data
def set_left(self, left): self.left = left
def set_right(self, right): self.right = right
def print_tree(t, level): print(' ' * (level*4) + str(t.get_data())) if t.get_left() != None: print('(l)', end = '') print_tree(t.get_left(), level + 1) if t.get_right() != None: print('(r)', end = '') print_tree(t.get_right(), level + 1)
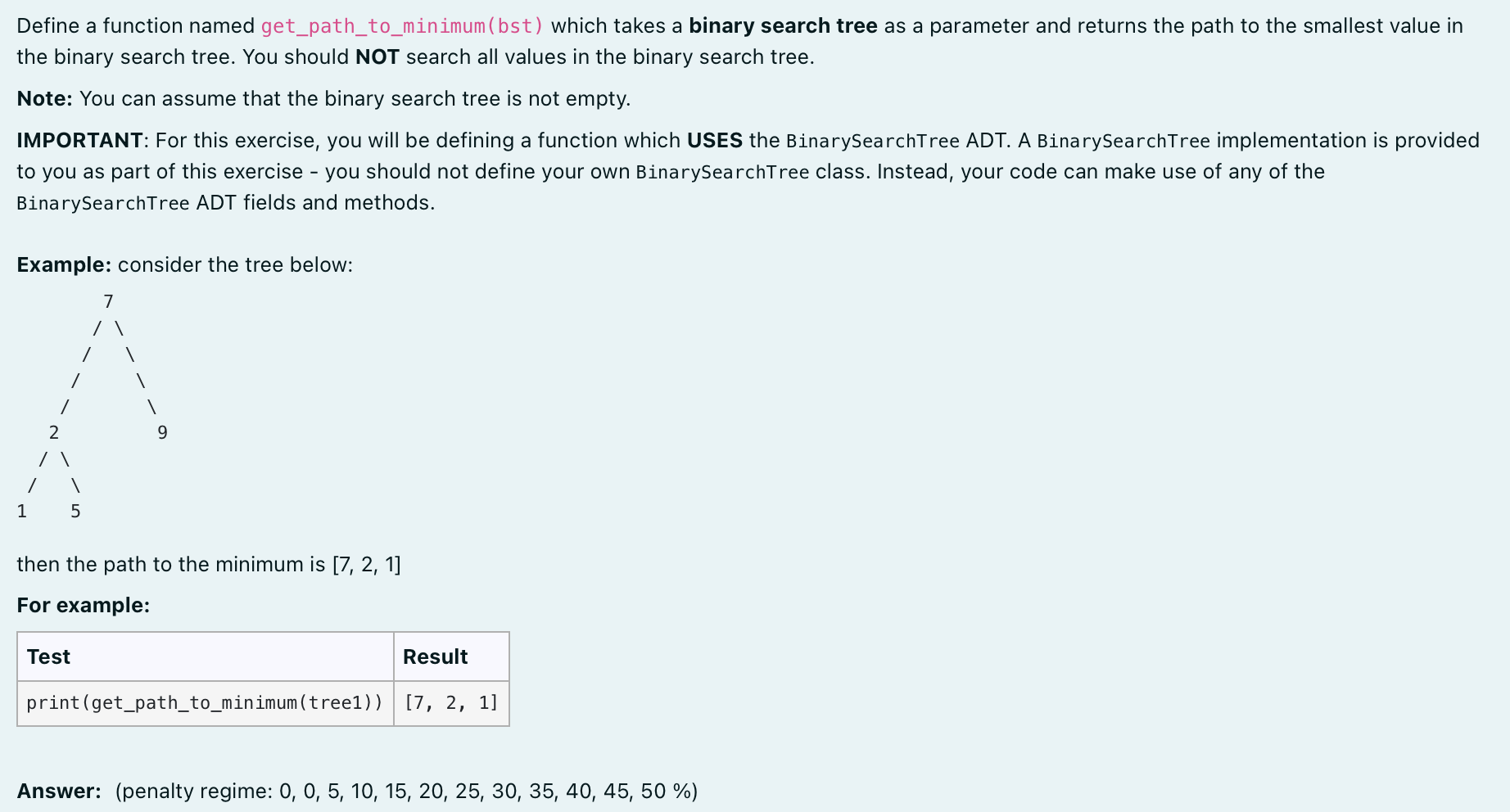
Define a function named get_path_to_minimum (bst) which takes a binary search tree as a parameter and returns the path to the smallest value in the binary search tree. You should NOT search all values in the binary search tree. Note: You can assume that the binary search tree is not empty. IMPORTANT: For this exercise, you will be defining a function which USES the BinarySearchTree ADT. A BinarySearchTree implementation is provided to you as part of this exercise - you should not define your own BinarySearchTree class. Instead, your code can make use of any of the BinarysearchTree ADT fields and methods. Example: consider the tree below: then the path to the minimum is [7,2,1] For example: Answer: (penalty regime: 0,0,5,10,15,20,25,30,35,40,45,50% )Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


