Question
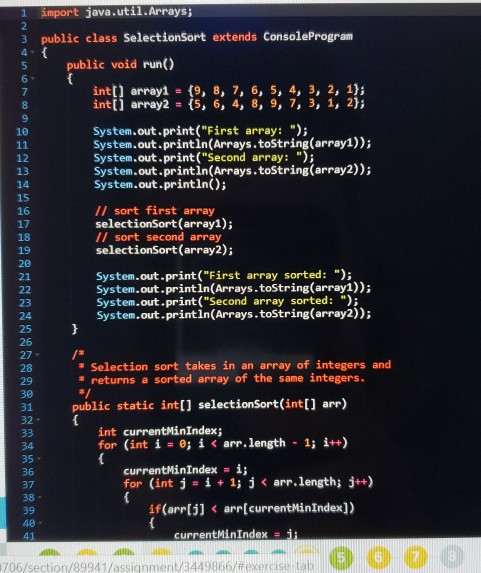
Code to copy: import java.util.Arrays; public class SelectionSort extends ConsoleProgram { public void run() { int[] array1 = {9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3,
Code to copy:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class SelectionSort extends ConsoleProgram { public void run() { int[] array1 = {9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1}; int[] array2 = {5, 6, 4, 8, 9, 7, 3, 1, 2}; System.out.print("First array: "); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array1)); System.out.print("Second array: "); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array2)); System.out.println();
// sort first array selectionSort(array1); // sort second array selectionSort(array2);
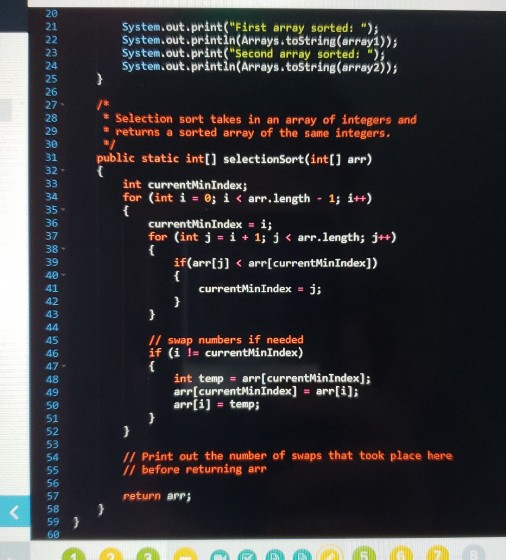
System.out.print("First array sorted: "); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array1)); System.out.print("Second array sorted: "); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array2)); } /* * Selection sort takes in an array of integers and * returns a sorted array of the same integers. */ public static int[] selectionSort(int[] arr) { int currentMinIndex; for (int i = 0; i RUN CODE TEST CASES ASSIGNMIT DOCS GRADE MORE 7 points Status: Not Submitted In this exercise, we will be looking at our example code for Selection Sort. However, while we are sorting we will also count the number of swaps taking place, then print them out once the array has been sorted. Add a print statement at the end of the selectionSort method that prints out the number of swaps that took place during the sort. You should not modify the run() method. Hint: where are items compared? Try writing out the steps in the algorithm on paper to help 1 import java.util.Arrays; 3 public class SelectionSort extends Console Program public void run() int[] array1 = {9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1); int[] array2 = {5, 6, 4, 8, 9, 7, 3, 1, 2); System.out.print("First array: "); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array:)); System.out.print("Second array: "); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array2)); System.out.println(); // sort first array selectionSort(array1); // sort second array selectionSort(array2); System.out.print("First array sorted: "); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); System.out.print("Second array sorted: "); .println(Arrays.toString(array2)); * Selection sort takes in an array of integers and * returns a sorted array of the same integers. public static int[] selectionSort(int[] arr) int currentMinIndex; for (int i = ; i
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


