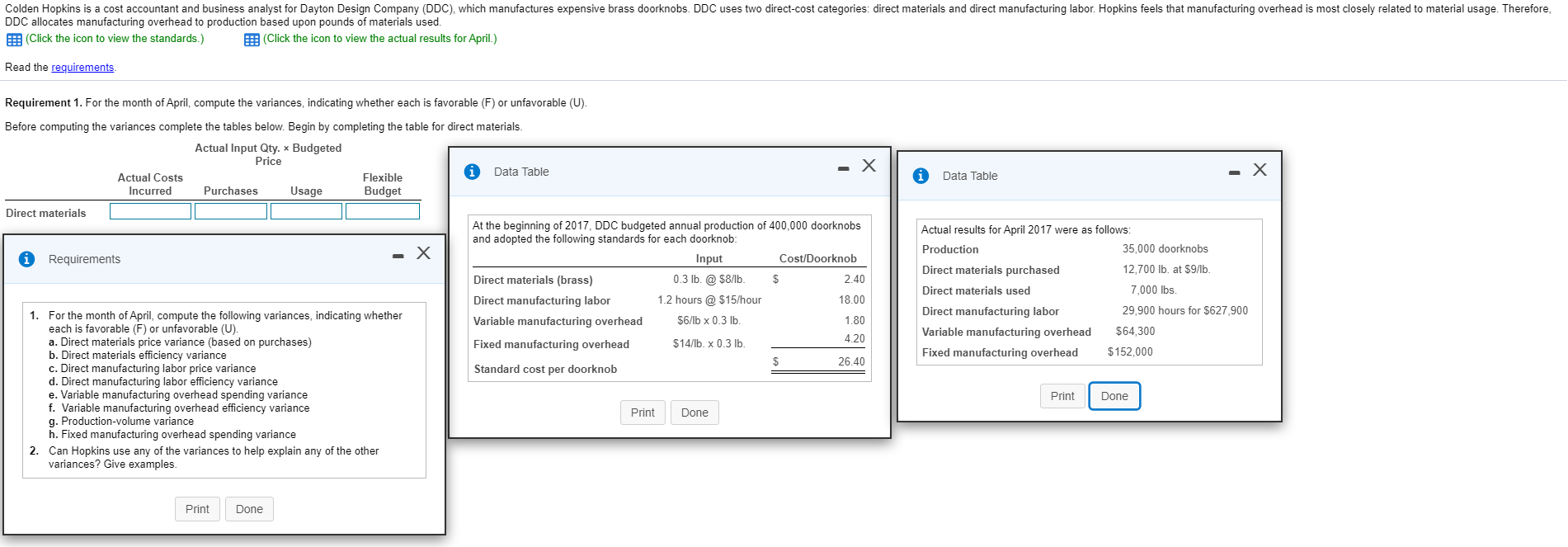
Colden Hopkins is a cost accountant and business analyst for Dayton Design Company (DDC), which manufactures expensive brass doorknobs. DDC uses two direct-cost categories: direct materials and direct manufacturing labor. Hopkins feels that manufacturing overhead is most closely related to material usage. Therefore, DDC allocates manufacturing overhead to production based upon pounds of materials used. BE: (Click the icon to view the standards.) P: (Click the icon to view the actual results for April.) Read the requirements. Requirement 1. For the month of April, compute the variances, indicating whether each is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). Before computing the variances complete the tables below. Begin by completing the table for direct materials. Actual Input Qty. ~ Budgeted Price Data Table Actual Costs Flexible Incurred Purchases Usage Budget - X X i - Data Table Direct materials 0 Requirements - X At the beginning of 2017, DDC budgeted annual production of 400,000 doorknobs and adopted the following standards for each doorknob: Input Cost/Doorknob Direct materials (brass) 0.3 lb. @ $8/1b. $ 2.40 Direct manufacturing labor 1.2 hours @ $15/hour 18.00 Variable manufacturing overhead $6/b x 0.3 lb. 1.80 4.20 Fixed manufacturing overhead $14/lb. x 0.3 lb. 26.40 Standard cost per doorknob Actual results for April 2017 were as follows: Production 35,000 doorknobs Direct materials purchased 12,700 lb. at $9/1b. Direct materials used 7,000 lbs. Direct manufacturing labor 29,900 hours for $627,900 Variable manufacturing overhead $64,300 Fixed manufacturing overhead $152,000 1. For the month of April, compute the following variances, indicating whether each is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). a. Direct materials price variance (based on purchases) b. Direct materials efficiency variance c. Direct manufacturing labor price variance d. Direct manufacturing labor efficiency variance e. Variable manufacturing overhead spending variance f. Variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance g. Production-volume variance h. Fixed manufacturing overhead spending variance 2. Can Hopkins use any of the variances to help explain any of the other variances? Give examples. | Print Done] Print Done Print Done Colden Hopkins is a cost accountant and business analyst for Dayton Design Company (DDC), which manufactures expensive brass doorknobs. DDC uses two direct-cost categories: direct materials and direct manufacturing labor. Hopkins feels that manufacturing overhead is most closely related to material usage. Therefore, DDC allocates manufacturing overhead to production based upon pounds of materials used. BE: (Click the icon to view the standards.) P: (Click the icon to view the actual results for April.) Read the requirements. Requirement 1. For the month of April, compute the variances, indicating whether each is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). Before computing the variances complete the tables below. Begin by completing the table for direct materials. Actual Input Qty. ~ Budgeted Price Data Table Actual Costs Flexible Incurred Purchases Usage Budget - X X i - Data Table Direct materials 0 Requirements - X At the beginning of 2017, DDC budgeted annual production of 400,000 doorknobs and adopted the following standards for each doorknob: Input Cost/Doorknob Direct materials (brass) 0.3 lb. @ $8/1b. $ 2.40 Direct manufacturing labor 1.2 hours @ $15/hour 18.00 Variable manufacturing overhead $6/b x 0.3 lb. 1.80 4.20 Fixed manufacturing overhead $14/lb. x 0.3 lb. 26.40 Standard cost per doorknob Actual results for April 2017 were as follows: Production 35,000 doorknobs Direct materials purchased 12,700 lb. at $9/1b. Direct materials used 7,000 lbs. Direct manufacturing labor 29,900 hours for $627,900 Variable manufacturing overhead $64,300 Fixed manufacturing overhead $152,000 1. For the month of April, compute the following variances, indicating whether each is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). a. Direct materials price variance (based on purchases) b. Direct materials efficiency variance c. Direct manufacturing labor price variance d. Direct manufacturing labor efficiency variance e. Variable manufacturing overhead spending variance f. Variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance g. Production-volume variance h. Fixed manufacturing overhead spending variance 2. Can Hopkins use any of the variances to help explain any of the other variances? Give examples. | Print Done] Print Done Print Done







