Colin Kreevy, a student of economics, has only $20 of his monthly budget left. He wants to spend this amount on movies and burgers
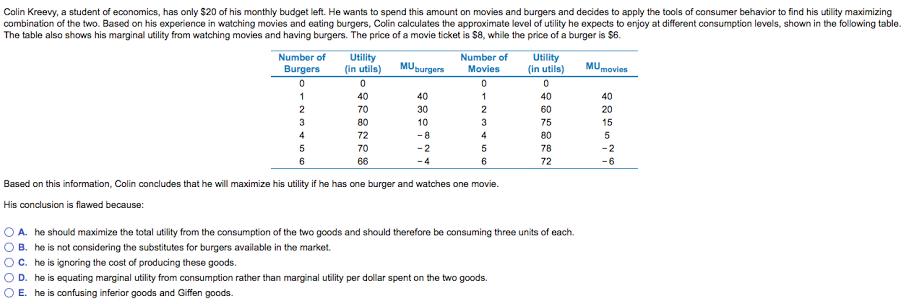
Colin Kreevy, a student of economics, has only $20 of his monthly budget left. He wants to spend this amount on movies and burgers and decides to apply the tools of consumer behavior to find his utility maximizing combination of the two. Based on his experience in watching movies and eating burgers, Colin calculates the approximate level of utility he expects to enjoy at different consumption levels, shown in the following table. The table also shows his marginal utility from watching movies and having burgers. The price of a movie ticket is $8, while the price of a burger is $6. Utility (in utils) Number of Utility (in utils) Number of Burgers MUpurgers MUmovies Movies 40 40 40 40 2 70 30 60 20 3 80 10 3 75 15 4 72 -8 4 80 5 70 -2 5 78 -2 6 66 -4 6 72 -6 Based on this information, Colin concludes that he will maximize his utility if he has one burger and watches one movie. His conclusion is flawed because: A. he should maximize the total utility from the consumption of the two goods and should therefore be consuming three units of each. B. he is not considering the substitutes for burgers available in the market. C. he is ignoring the cost of producing these goods. D. he is equating marginal utility from consumption rather than marginal utility per dollar spent on the two goods. E. he is confusing inferior goods and Giffen goods.
Step by Step Solution
3.30 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The correct option ...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


