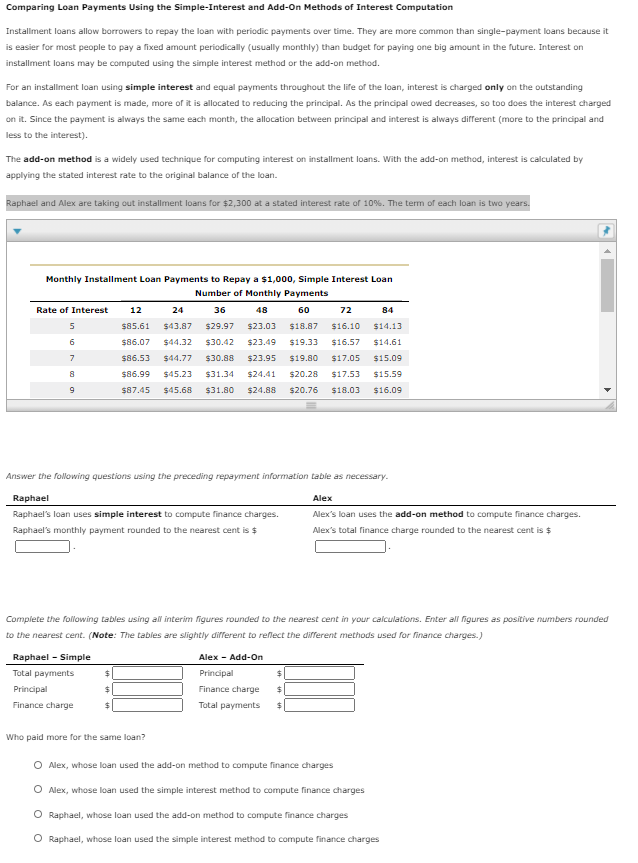
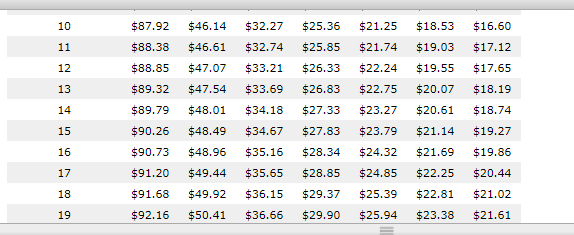
Comparing Loan Payments Using the Simple-Interest and Add-On Methods of Interest Computation Installment loans allow borrowers to repay the loan with periodic payments over time. They are more common than single-payment loans because it is easier for most people to pay a fixed amount periodically (usually monthly) than budget for paying one big amount in the future. Interest on installment loans may be computed using the simple interest method or the add-on method. For an installment loan using simple interest and equal payments throughout the life of the loan, interest is charged only on the outstanding balance. As each payment is made, more of it is allocated to reducing the principal. As the principal owed decreases, so too does the interest charged on it. Since the payment is always the same each month, the allocation between principal and interest is always different (more to the principal and less to the interest). The add-on method is a widely used technique for computing interest on installment loans. With the add-on method, interest is calculated by applying the stated interest rate to the original balance of the loan. Raphael and Alex are taking out installment loans for $2,300 at a stated interest rate of 10%. The term of each loan is two years. Monthly Installment Loan Payments to Repay a $1,000, Simple Interest Loan Number of Monthly Payments Rate of Interest 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 5 $85.61 $43.87 $29.97 $23.03 $18.87 $16.10 $14.13 6 $86.07 $44.32 $30.42 $23.49 $19.33 $16.57 $14.61 7 $86.53 $44.77 $30.88 $23.95 $19.80 $17.05 $15.09 8 $86.99 $45.23 $31.34 $24.41 $20.28 $17.53 $15.59 9 $87.45 $45.68 $31.80 $24.88 $20.76 $18.03 $16.09 Answer the following questions using the preceding repayment information table as necessary Raphael Alex Raphael's loan uses simple interest to compute finance charges. Alex's loan uses the add-on method to compute finance charges. Raphael's monthly payment rounded to the nearest cent is $ Alex's total finance charge rounded to the nearest cent is $ Complete the following tables using all interim figures rounded to the nearest cent in your calculations. Enter all figures as positive numbers rounded to the nearest cent. (Note: The tables are slightly different to reflect the different methods used for finance charges.) Raphael - Simple Alex - Add-On Total payments Principal Principal Finance charge Finance charge Total payments $ $ $ $ $ Who paid more for the same loan? Alex, whose loan used the add-on method to compute finance charges Alex, whose loan used the simple interest method to compute finance charges O Raphael, whose loan used the add-on method to compute finance charges Raphael, whose loan used the simple interest method to compute finance charges 10 $872 46.14 $32.27 $25,36 21.25 18.53 $16.60 11 588.33 $46.61 $32,74 25.85 21.74 $19.03 17.12 12 $88.85 $47.07 33.21 $22.24 19.55 $17.65 13 589.32 $47.54 $33.69 26.33 26.83 $27,33 522.75 520.07 $18.19 14 $89,79 $48.01 20,61 $18.74 $34.13 534.57 23.27 23.79 15 $21.14 $19,27 90.25 $90.3 $48.49 $48.96 $27.83 28.34 16 35.16 $24.32 $21.59 19.86 17 591.20 $49.44 $35.65 528.85 24.85 22.25 520.44 18 91.63 49.92 $29.37 $25.39 22.81 $21.02 36.15 $36.66 19 $92.16 $50.41 $29.90 $25.94 $23.33 21.51








