Complete Question #5: When calculating the debt ratio, assume debt is equal to the long term liabilities in Table 7.1. Also, when calculating the ratios in Question #5, just use the figures in the far left of Table 7.1, i.e., those figures listed under column "3/31/17.

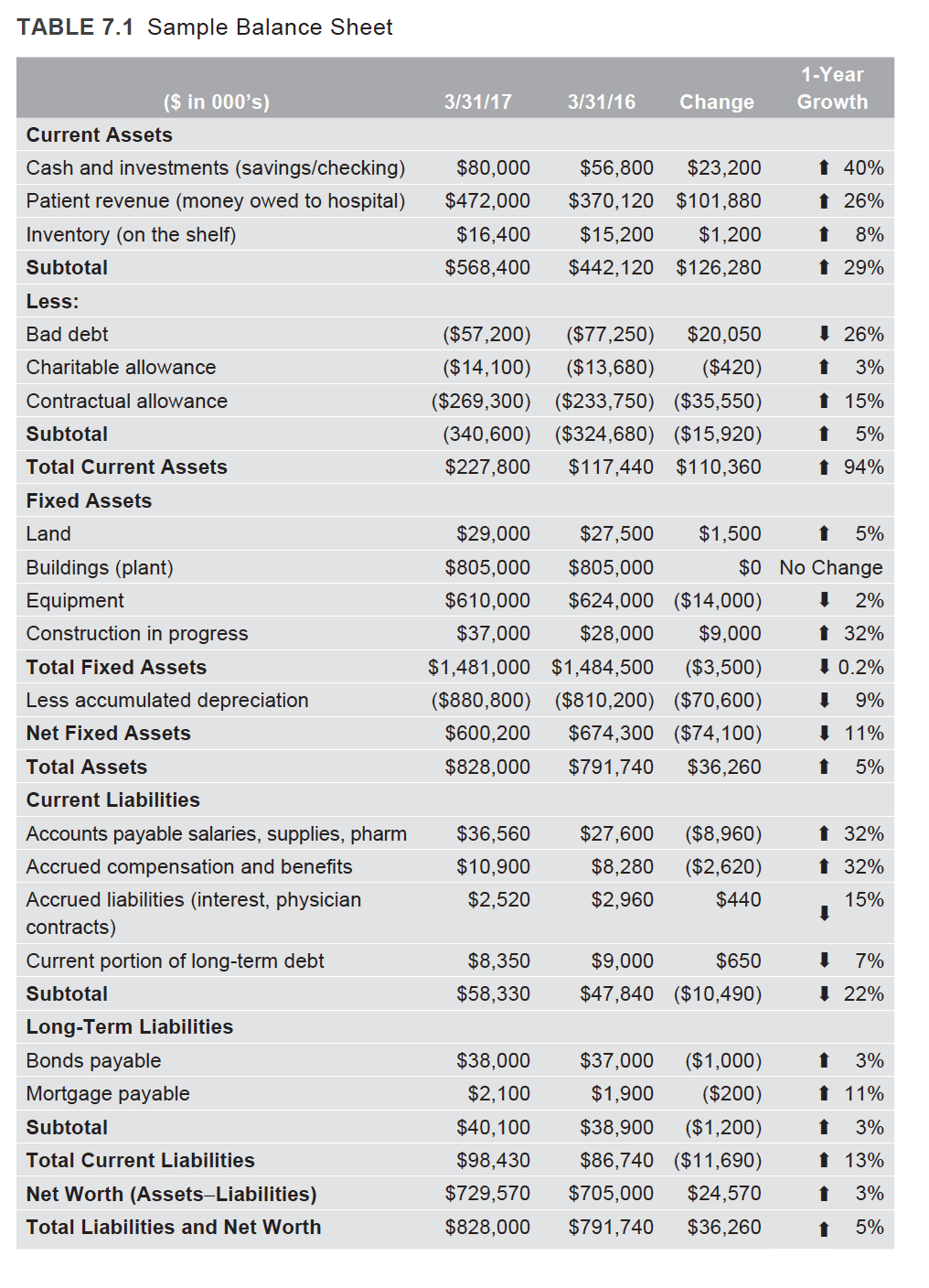
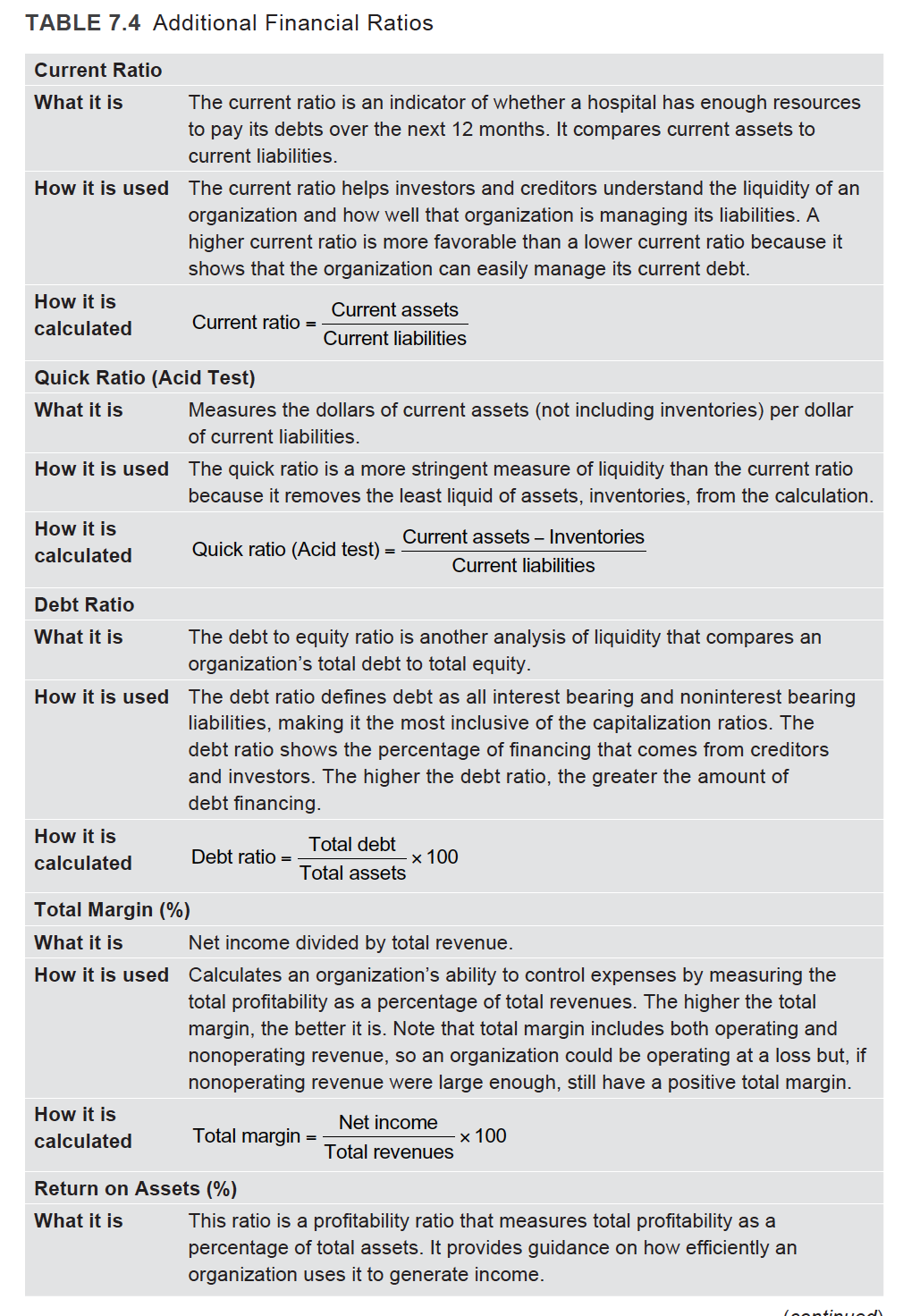
5. Using the data in Table 7.1 and the definitions from Table 7.4, calculate the current ratio, quick ratio, and the debt ratio. a. What information do these ratios provide? b. If you were concerned about the result, what could be done to adjust these ratios? c. In what ways could these ratios be negatively impacted? d. When assessing the results of these ratios, what advice would you have for this organiza- tion if it was considering securing financing for a major capital expense? TABLE 7.1 Sample Balance Sheet 1-Year Growth 3/31/17 3/31/16 Change 1 40% ($ in 000's) Current Assets Cash and investments (savings/checking) Patient revenue (money owed to hospital) Inventory (on the shelf) Subtotal 1 26% $80,000 $472,000 $16,400 $568,400 $56,800 $23,200 $370,120 $101,880 $15,200 $1,200 $442,120 $126,280 1 8% 1 29% Less: Bad debt I 26% Charitable allowance 1 3% Contractual allowance ($57,200) ($77,250) $20,050 ($14,100) ($13,680) ($420) ($269,300) ($233,750) ($35,550) (340,600) ($324,680) ($15,920) $227,800 $117,440 $110,360 1 15% 1 5% Subtotal Total Current Assets 1 94% Fixed Assets Land Buildings (plant) Equipment Construction in progress Total Fixed Assets Less accumulated depreciation Net Fixed Assets $29,000 $27,500 $1,500 t 5% $805,000 $805,000 $0 No Change $610,000 $624,000 ($14,000) 1 2% $37,000 $28,000 $9,000 1 32% $1,481,000 $1,484,500 ($3,500) 1 0.2% ($880,800) ($810,200) ($70,600) ! 9% $600,200 $674,300 ($74,100) I 11% $828,000 $791,740 $36,260 t 5% Total Assets 1 32% $36,560 $10,900 $2,520 $27,600 $8,280 $2,960 ($8,960) ($2,620) $440 1 32% 15% I 7% $8,350 $58,330 $9,000 $650 $47,840 ($10,490) I 22% Current Liabilities Accounts payable salaries, supplies, pharm Accrued compensation and benefits Accrued liabilities (interest, physician contracts) Current portion of long-term debt Subtotal Long-Term Liabilities Bonds payable Mortgage payable Subtotal Total Current Liabilities Net Worth (Assets-Liabilities) Total Liabilities and Net Worth 1 3% 1 11% 1 3% $38,000 $2,100 $40,100 $98,430 $729,570 $828,000 $37,000 ($1,000) $1,900 ($200) $38,900 ($1,200) $86,740 ($11,690) $705,000 $24,570 $791,740 $36,260 1 13% t 3% t 5% TABLE 7.4 Additional Financial Ratios Current Ratio What it is The current ratio is an indicator of whether a hospital has enough resources to pay its debts over the next 12 months. It compares current assets to current liabilities. How it is used The current ratio helps investors and creditors understand the liquidity of an organization and how well that organization is managing its liabilities. A higher current ratio is more favorable than a lower current ratio because it shows that the organization can easily manage its current debt. How it is Current assets calculated Current ratio = Current liabilities Quick Ratio (Acid Test) What it is Measures the dollars of current assets (not including inventories) per dollar of current liabilities. How it is used The quick ratio is a more stringent measure of liquidity than the current ratio because it removes the least liquid of assets, inventories, from the calculation. How it is Current assets Inventories calculated Quick ratio (Acid test) Current liabilities Debt Ratio What it is The debt to equity ratio is another analysis of liquidity that compares an organization's total debt to total equity. How it is used the debt ratio defines debt as all interest bearing and noninterest bearing liabilities, making it the most inclusive of the capitalization ratios. The debt ratio shows the percentage of financing that comes from creditors and investors. The higher the debt ratio, the greater the amount of debt financing. How it is calculated Total debt Debt ratio = Total assets x 100 Total Margin (%) What it is Net income divided by total revenue. How it is used Calculates an organization's ability to control expenses by measuring the total profitability as a percentage of total revenues. The higher the total margin, the better it is. Note that total margin includes both operating and nonoperating revenue, so an organization could be operating at a loss but, if nonoperating revenue were large enough, still have a positive total margin. How it is Net income calculated Total margin x 100 Total revenues Return on Assets (%) What it is This ratio is a profitability ratio that measures total profitability as a percentage of total assets. It provides guidance on how efficiently an organization uses it to generate income. (nontinued TABLE 7.4 Additional Financial Ratios (continued) Average Daily Census How it is calculated Average daily census Total number of inpatient services for a given period Total number of days in the same period Inpatient Bed Occupancy Rate/Bed Utilization Rate What it is The occupancy rate is the actual number of inpatient beds occupied by patients over a given time. It is expressed as a percentage of the total number of available beds. How it is used This ratio is used to gauge the appropriate balance between the demand for inpatient care and the number of beds available to provide inpatient care. The occupancy rate is a calculation used to show the actual utilization of an inpatient health facility for a given time period. How it is Total number of inpatient beds occupied calculated Occupancy rate = Total number of inpatient beds available x 100










