Question
COMPLIANCE MANAGEMENT ASSIGNMNET: Module 5 requires you to submit Part 1 of the three-part ongoing project for this course. In this submission, you will apply
COMPLIANCE MANAGEMENT ASSIGNMNET:
Module 5 requires you to submit Part 1 of the three-part ongoing project for this course. In this submission, you will apply all of the skills you have learnt related to identifying risks to create a risk matrix for a compliance risk management plan.
For this submission, download the Excel spreadsheet from the Online Campus. This spreadsheet provides you with a format for the compliance risk management plan, which you can either create for your own organisation, or you may use the fictional case study provided on the Online Campus. Remember to only use the fictional case study provided if you have chosen not to use your own organisation (or another organisation you are familiar with).
VERY IMPORTANT: Part 1 of the ongoing project requires you to create a risk matrix for your risk management plan, for which you will need to complete columns A, B, C, D, E, F, and G of the Compliance risk management plan tab. You will need to use the Risk matrix and Risk rating scales tabs in order to do this. Follow these steps to complete the relevant sections:
Consider the context of the organisation: Before completing the spreadsheet consider the context of the organisation; for example, where the organisation is based, the industry it is in, the size, products and services, frameworks, culture, and regulations that would impact the operations of the organisation.
Identify relevant legislative acts: Conduct your own research and identify one or two acts or regulations that are relevant to the industry and nature of services of the organisation. For example, if you were creating a compliance risk management plan for a mining company, the National Environmental Management Act (NEMA) or the Mineral and Petroleum Resources Development Act (MPRDA) would apply to the organisation.
Decide on relevant chapters or extracts from the chosen legislation: Legislation is separated into chapters, and each chapter is often divided according to the theme it attempts to address. Read the contents page of the legislation carefully to determine which chapter would be relevant to your organisation or the case study. For this ongoing project, you are required to identify at least 12 extracts from the chosen legislation, but you may include more. Each extract should be considered a compliance obligation and included in its own row in the spreadsheet. Add the extracts or chapters from these acts to the tab called Compliance risk management plan under the heading Regulatory provision (Column A).
Highlight areas of concern or compliance obligations: Provide an interpretation of each extract in the Interpretation of section column (Column B). To do this, find phrases or statements that you think could be classified as compliance obligations. Remember that all stakeholders will have an understanding of law text. Therefore, you should provide a simple interpretation of the text you have highlighted, and this interpretation can also be seen as the compliance obligation that needs to be fulfilled. You should be aware of any phrases that are ambiguous or unclear, or phrases that are prescriptive. You may choose to add the legislative shorthand, such as Article 33 of the GDPR; however, inserting the actual extract will make it easier for you to analyse.
Identify the risk drivers: Remember that risks and risk drivers are a pivotal part of your risk management plan, as they will inform the nature of your risk rating scales. Therefore, it is advised that you populate this section of your compliance risk management plan with as much detail as possible. This section is split into two columns called Risk drivers (Column C) and Consequences (Column D).
Create impact and likelihood scales: Navigate to the second tab in the spreadsheet, the Risk rating scales tab. This sheet contains generic risk impact and risk likelihood scales. Alter the scales in the sheet to better suit the context of your chosen organisation. There is a generic risk matrix in the third sheet called Risk matrix that you should use when editing the scales.
Assign risk ratings: Navigate back to the first tab, the Compliance risk management plan, and assign an impact (Column E) and likelihood (Column F) rating for each extract. If you click on the cell a little arrow will appear and you can choose a risk number and a likelihood letter. The combination you choose will automatically reflect in Column G. You will notice that this automation is linked to the risk matrix.
Note:
Check that you have populated the columns up until, and including, Column G for at least 12 rows. Do not fill in the blue section called Compliance monitoring plan yet (Columns L to T).
For this part of the ongoing project, you do not need to look at the Control environment and Control design details tabs (Columns H to K of the Compliance risk management plan tab). You also are not yet required to use the Control design considerations tab,
Module 5 requires you to submit Part 1 of the three-part ongoing project for this course. In this submission, you will apply all of the skills you have learnt related to identifying risks to create a risk matrix for a compliance risk management plan.
For this submission, download the Excel spreadsheet from the Online Campus. This spreadsheet provides you with a format for the compliance risk management plan, which you can either create for your own organisation, or you may use the fictional case study provided on the Online Campus. Remember to only use the fictional case study provided if you have chosen not to use your own organisation (or another organisation you are familiar with).
Part 1 of the ongoing project requires you to create a risk matrix for your risk management plan, for which you will need to complete columns A, B, C, D, E, F, and G of the Compliance risk management plan tab. You will need to use the Risk matrix and Risk rating scales tabs in order to do this. Follow these steps to complete the relevant sections:
Consider the context of the organisation: Before completing the spreadsheet consider the context of the organisation; for example, where the organisation is based, the industry it is in, the size, products and services, frameworks, culture, and regulations that would impact the operations of the organisation.
Identify relevant legislative acts: Conduct your own research and identify one or two acts or regulations that are relevant to the industry and nature of services of the organisation. For example, if you were creating a compliance risk management plan for a mining company, the National Environmental Management Act (NEMA) or the Mineral and Petroleum Resources Development Act (MPRDA) would apply to the organisation.
Decide on relevant chapters or extracts from the chosen legislation: Legislation is separated into chapters, and each chapter is often divided according to the theme it attempts to address. Read the contents page of the legislation carefully to determine which chapter would be relevant to your organisation or the case study. For this ongoing project, you are required to identify at least 12 extracts from the chosen legislation, but you may include more. Each extract should be considered a compliance obligation and included in its own row in the spreadsheet. Add the extracts or chapters from these acts to the tab called Compliance risk management plan under the heading Regulatory provision (Column A).
Highlight areas of concern or compliance obligations: Provide an interpretation of each extract in the Interpretation of section column (Column B). To do this, find phrases or statements that you think could be classified as compliance obligations. Remember that all stakeholders will have an understanding of law text. Therefore, you should provide a simple interpretation of the text you have highlighted, and this interpretation can also be seen as the compliance obligation that needs to be fulfilled. You should be aware of any phrases that are ambiguous or unclear, or phrases that are prescriptive. You may choose to add the legislative shorthand, such as Article 33 of the GDPR; however, inserting the actual extract will make it easier for you to analyse.
Identify the risk drivers: Remember that risks and risk drivers are a pivotal part of your risk management plan, as they will inform the nature of your risk rating scales. Therefore, it is advised that you populate this section of your compliance risk management plan with as much detail as possible. This section is split into two columns called Risk drivers (Column C) and Consequences (Column D).
Create impact and likelihood scales: Navigate to the second tab in the spreadsheet, the Risk rating scales tab. This sheet contains generic risk impact and risk likelihood scales. Alter the scales in the sheet to better suit the context of your chosen organisation. There is a generic risk matrix in the third sheet called Risk matrix that you should use when editing the scales.
Assign risk ratings: Navigate back to the first tab, the Compliance risk management plan, and assign an impact (Column E) and likelihood (Column F) rating for each extract. If you click on the cell a little arrow will appear and you can choose a risk number and a likelihood letter. The combination you choose will automatically reflect in Column G. You will notice that this automation is linked to the risk matrix.
Note:
Check that you have populated the columns up until, and including, Column G for at least 12 rows. Do not fill in the blue section called Compliance monitoring plan yet (Columns L to T).
For this part of the ongoing project, you do not need to look at the Control environment and Control design details tabs (Columns H to K of the Compliance risk management plan tab). You also are not yet required to use the Control design considerations tab,
CASE STUDY
Case study: Lightning Communications and GS Bank initiative
Lightning Communications is a large telecommunications service provider listed on the Johannesburg Stock Exchange. It has many stakeholders across South Africa and caters for both private and corporate services. The total client base consists of approximately 40 million customers, the bulk of which are private persons.
The board and executive committee of Lightning Communications have recently engaged in discussions with one of the large retail banks in the country, GS Bank. GS Bank also has a large client and stakeholder base across the country. GS Bank is one of the Southern African Development Community (SADC) regions largest retail banks, and one of the largest three in South Africa. It has a total client base of approximately 16.5 million clients, with 28 million cards in issue (including debit, credit, and petrol cards).
Discussions between the two organisations have focused on the alignment of several mutual interests. There are three critical points of alignment that the GS Bank executive committee has proposed to implement operationally within the next 12 to 18 months:
Lightning Communications will provide location tracking and GPS data of private persons to GS Bank. The idea is that by using this data set, GS Bank can better track the movement of its customers to offer them a better, more personalised service linked with their accounts. This would include retail specials and petrol discounts at specific filling stations, among other incentives.
GS Bank can use this same data for know your customer purposes. The argument is that the GPS and location data provide a far more accurate, real-time picture of the actual place of residence of their clients.
Lightning Communications can incorporate a secure payment method for accounts and a scan-to-pay function through its app. Both functions would rely on a pay-gate service using the GS Bank's current
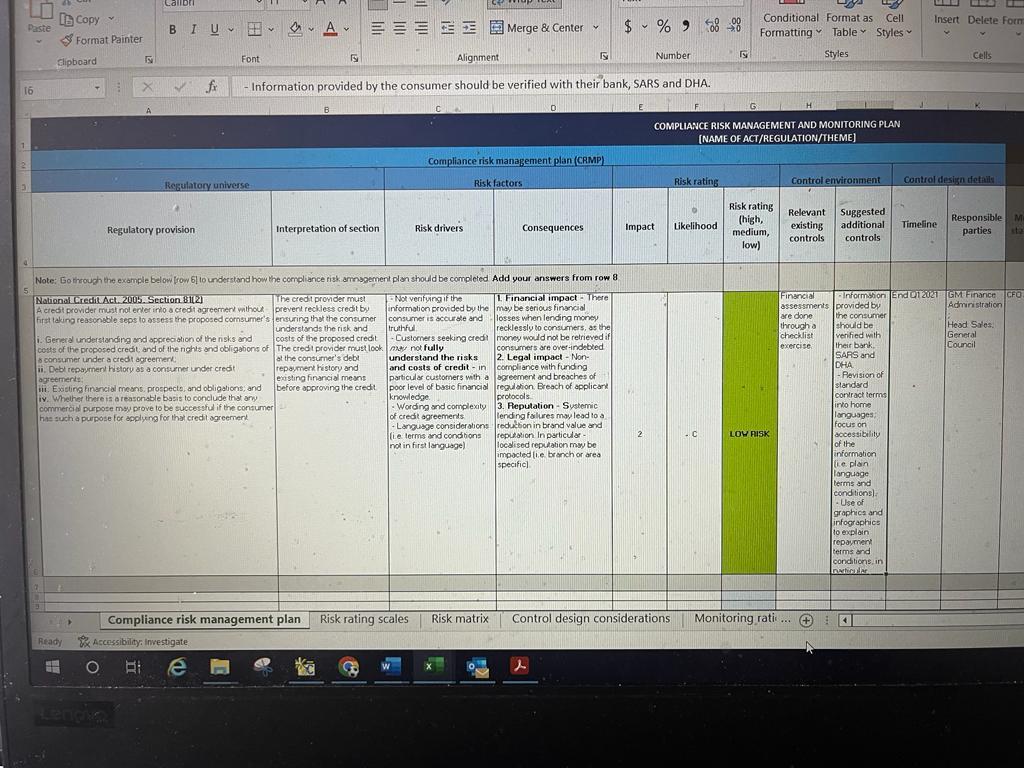
ABOVE IS THE COMPLIANCE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN
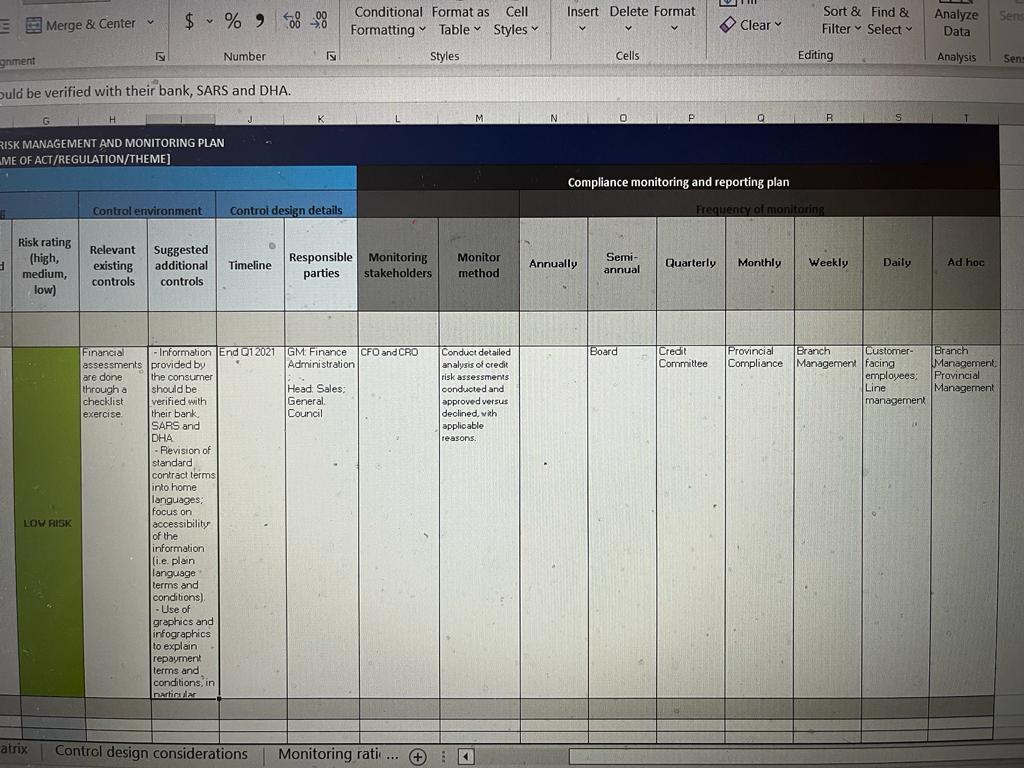
ABOVE IS THE LAST PART OF THE COMPLIANCE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN
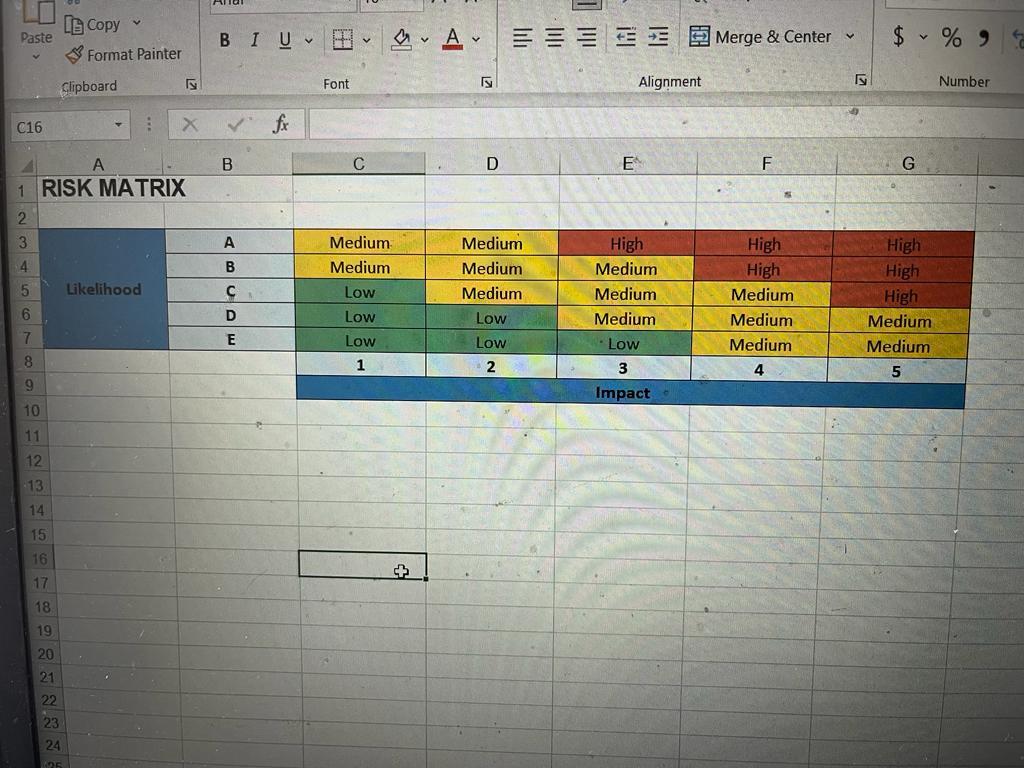
ABOVE IS THE RISK MATRIX PLAN
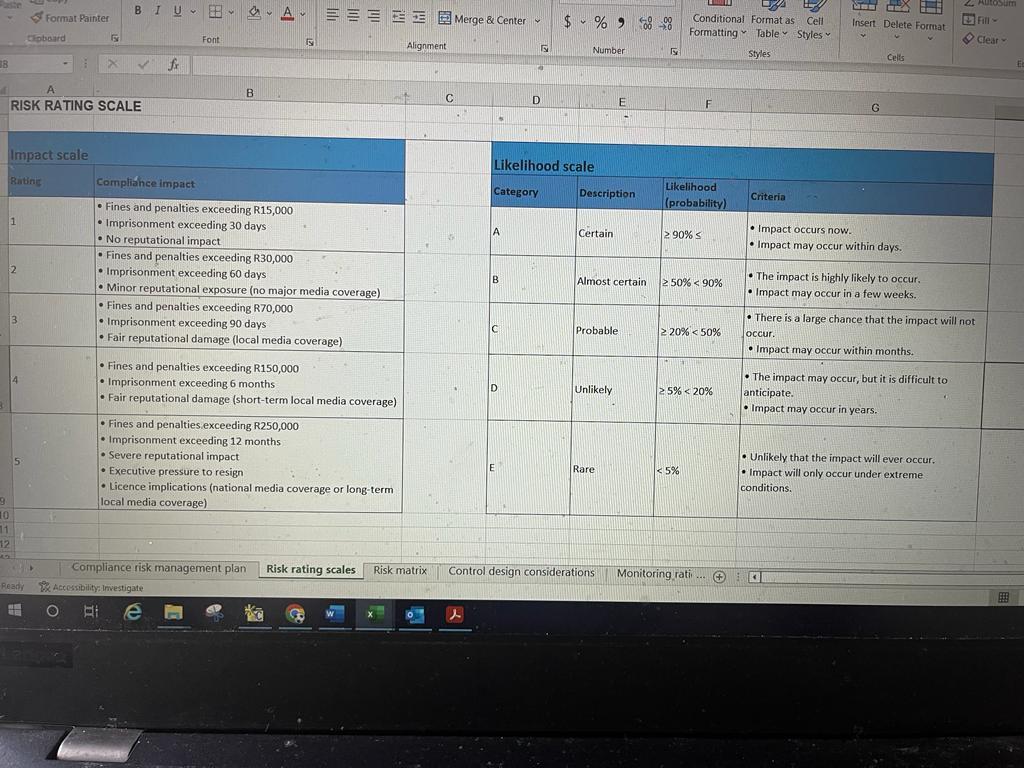
ABOVE IS THE RISK RATING SCALES
suld be verified with their bank, SARS and DHA. RISK MANAGEMENT AND MONITORING PLAN ME OF ACT/REGULATION/THEME]Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


