Question
Comprehensive Problem 1 Part 2 and Part 3: The following is a comprehensive problem which encompasses all of the elements learned in previous chapters. You

Comprehensive Problem 1 Part 2 and Part 3:
The following is a comprehensive problem which encompasses all of the elements learned in previous chapters. You can refer to the objectives for each chapter covered as a review of the concepts. Note: You must complete part 1 before completing parts 2 and 3.
Part 2: Using the attached spreadsheet, post the journal entries from part 1 to a ledger of four-column accounts.
Part 3: Prepare an unadjusted trial balance. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank.
Comprehensive Problem 1 Part 4 and Part 6:
The following is a comprehensive problem which encompasses all of the elements learned in previous chapters. You can refer to the objectives for each chapter covered as a review of the concepts. Note: You must complete parts 1, 2 and 3 before completing parts 4 and 6. Please note that part 5 is optional.
Part 4: At the end of May, the following adjustment data were assembled. Analyze and use these data to complete parts (5) and (6).
a. Insurance expired during May is $275. b. Supplies on hand on May 31 are $715. c. Depreciation of office equipment for May is $330. d. Accrued receptionist salary on May 31 is $325. e. Rent expired during May is $1,600. f. Unearned fees on May 31 are $3,210.
Part 6: Journalize the adjusting entries. Then, post the entries to the attached spreadsheet from part 2.
Comprehensive Problem 1 Part 7:
The following is a comprehensive problem which encompasses all of the elements learned in previous chapters. You can refer to the objectives for each chapter covered as a review of the concepts. Note: You must complete parts 1, 2, 3, 4, and 6 before completing part 7. Part 5 is optional.
Prepare an adjusted trial balance. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank.
Comprehensive Problem 1 Part 8:
The following is a comprehensive problem which encompasses all of the elements learned in previous chapters. You can refer to the objectives for each chapter covered as a review of the concepts.
NOTE: You must complete parts 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 and 7 before completing part 8. Part 5 is optional.
Prepare an income statement, Prepare a retained earnings statement, Prepare a retained earnings statement.
Comprehensive Problem 1 Part 9:
The following is a comprehensive problem which encompasses all of the elements learned in previous chapters. You can refer to the objectives for each chapter covered as a review of the concepts.
Note: You must complete parts 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7 and 8 before completing part 9. Part 5 is optional.
Part 9: Prepare the closing entries below. Then, using the attached spreadsheet from part 2, post the entries to your general ledger. (Income Summary is account #34 in the chart of accounts.) If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank.
Comprehensive Problem 1 Part 10:
The following is a comprehensive problem which encompasses all of the elements learned in previous chapters. You can refer to the objectives for each chapter covered as a review of the concepts.
Note: You must complete parts 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 and 9 before completing part 10. Part 5 is optional.
Prepare a post-closing trial balance. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank.
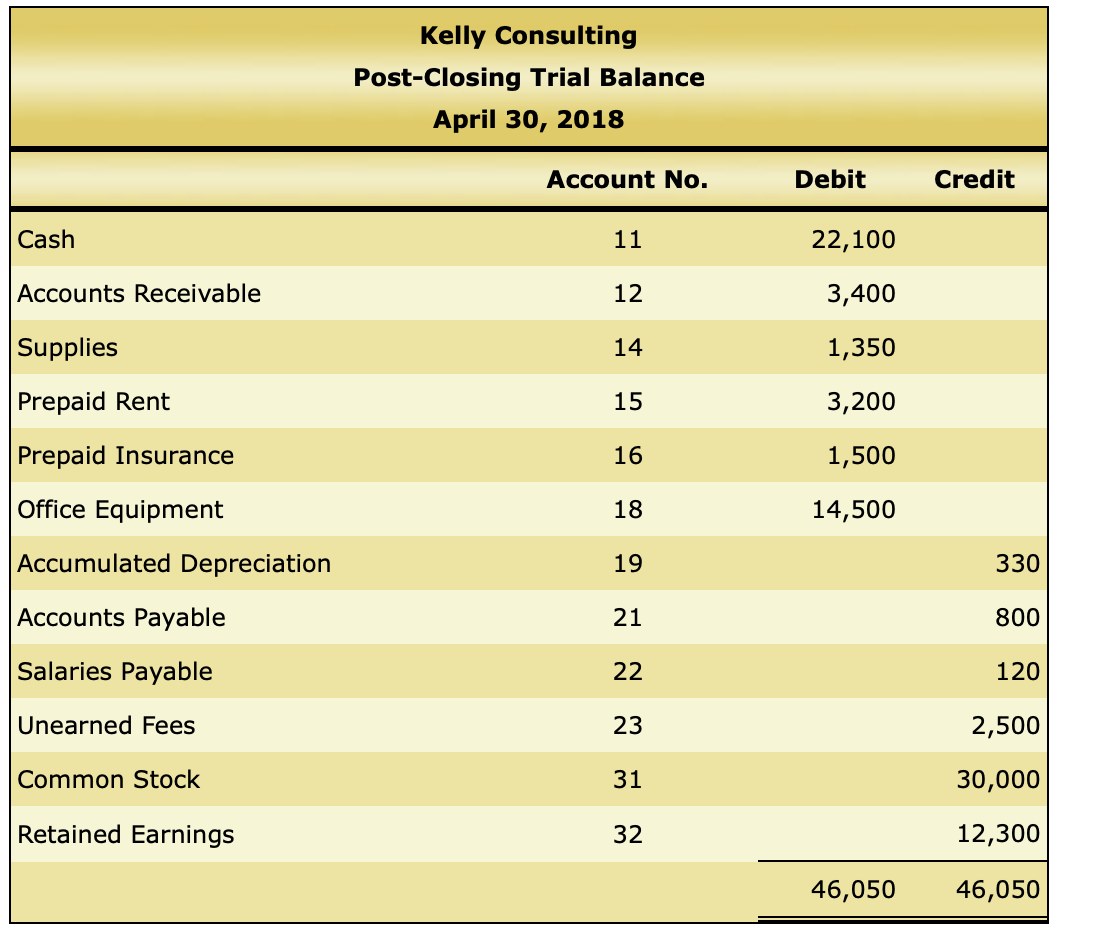
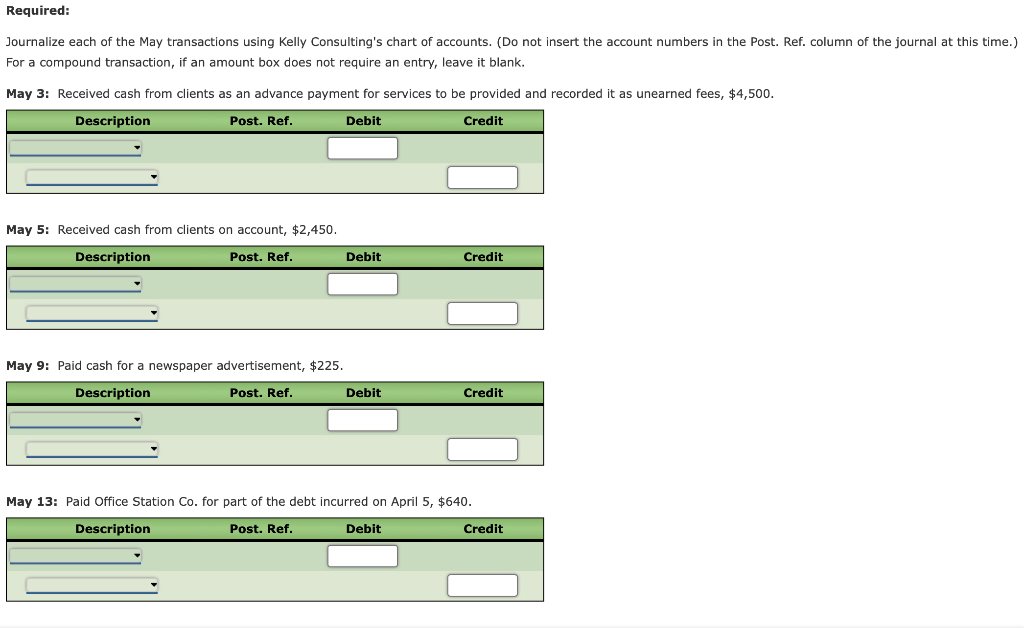
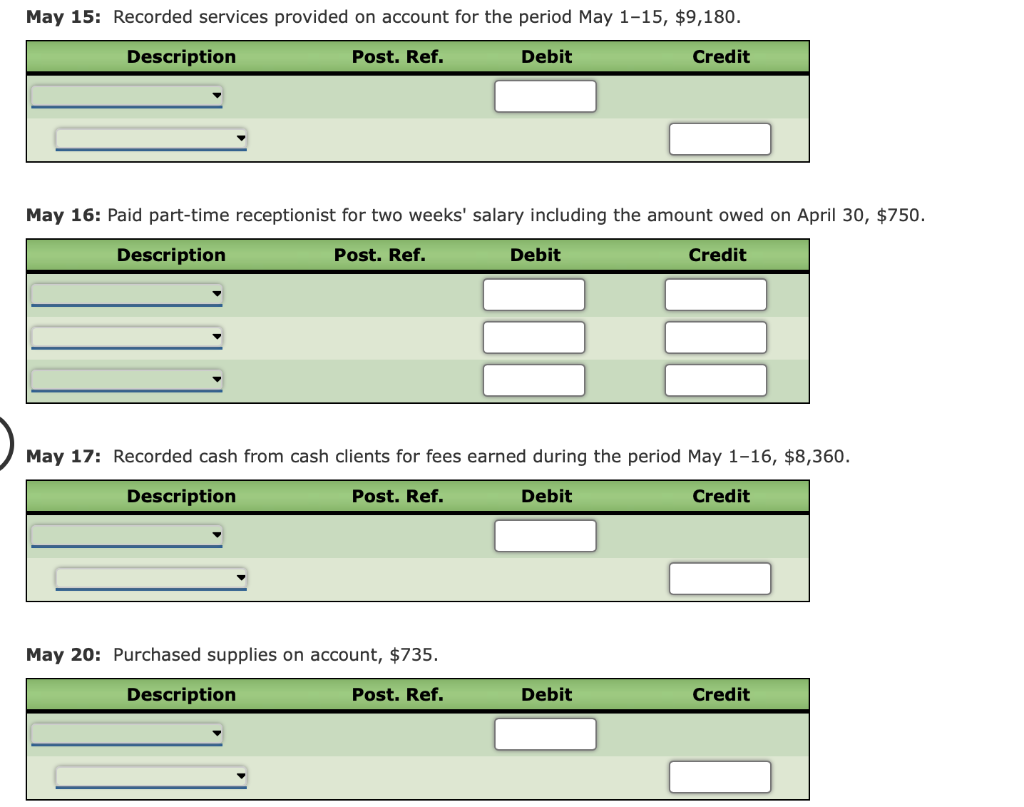
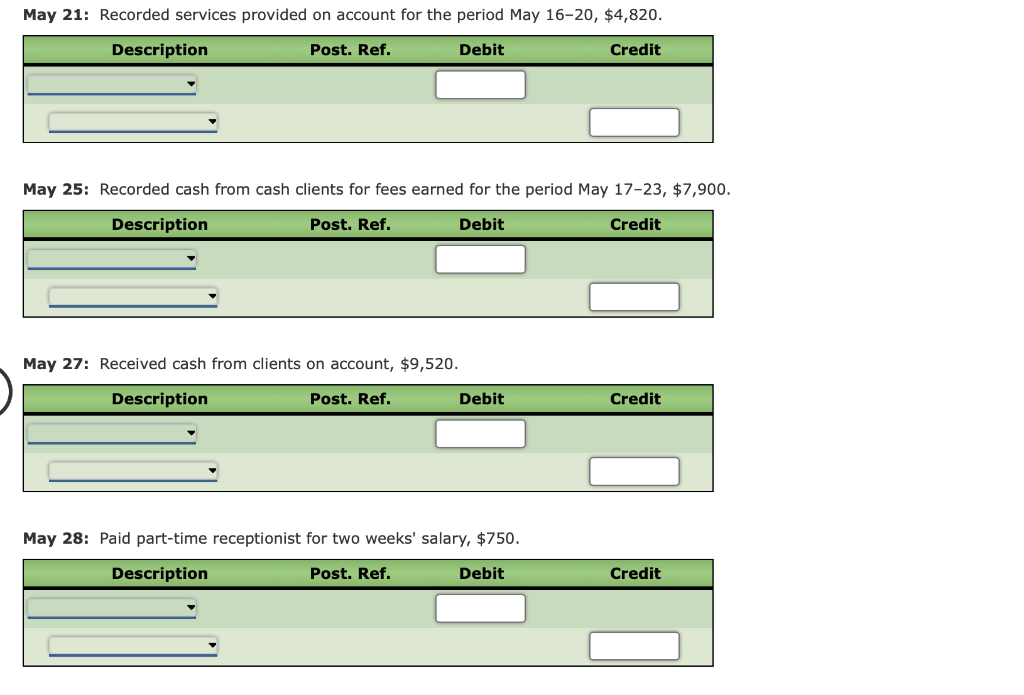
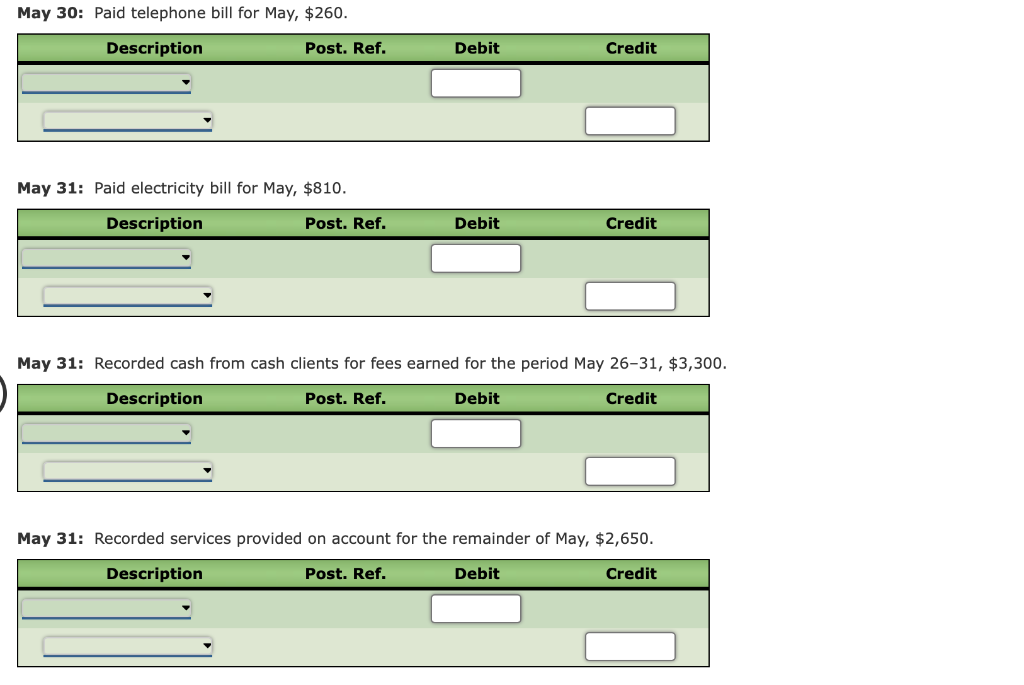
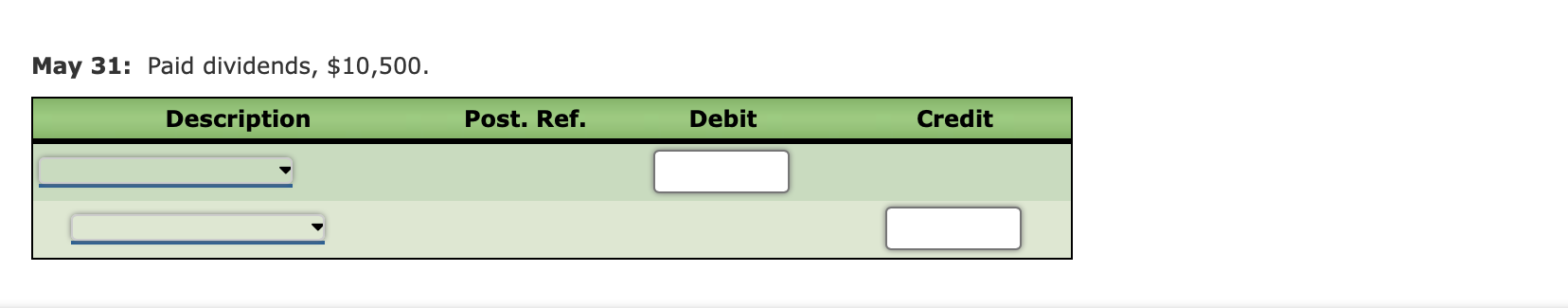
The following is a comprehensive problem which encompasses all of the elements learned in previous chapters. You can refer to the objectives for each covere a review of the concepts. Kelly Pitney began her consulting business, Kelly Consulting, on April 1, 2018. The chart of accounts for Kelly Consulting is shown below: 11 Cash 32 Retained Earnings 12 Accounts Receivable 33 Dividends 14 Supplies 34 Income Summary 15 Prepaid Rent 41 Fees Earned 16 Prepaid Insurance 51 Salary Expense 18 Office Equipment 52 Rent Expense 19 Accumulated Depreciation 53 Supplies Expense 21 Accounts Payable 54 Depreciation Expense 22 Salaries Payable 55 Insurance Expense 23 Unearned Fees 59 Miscellaneous Expense 31 Common Stock Journalize each of the May transactions using Kelly Consulting's chart of accounts. (Do not insert the account numbers in the Post. Ref. column of the journal at this time. For a compound transaction, if an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. May 3: Received cash from clients as an advance payment for services to be provided and recorded it as unearned fees, $4,500. May 5: Received cash from clients on account, $2,450. May 9: Paid cash for a newspaper advertisement, $225. May 13: Paid Office Station Co. for part of the debt incurred on April 5, $640. May 16: Paid part-time receptionist for two weeks' salary including the amount owed on Apr May 17: Recorded cash from cash clients for fees earned during the period May 1-16, $8,3 May 20: Purchased supplies on account, $735. May 21: Recorded services provided on account for the period May 1620,$4,820. May 25: Recorded cash from cash clients for fees earned for the period May 17-23, $7,900. May 27: Received cash from clients on account, $9,520. May 28: Paid part-time receptionist for two weeks' salary, $750. May 30: Paid telephone bill for May, $260. May 31: Paid electricity bill for May, $810. May 31: Recorded cash from cash clients for fees earned for the period May 26-31, $3,300. May 31: Recorded services provided on account for the remainder of May, $2,650. May 31: Paid dividends, $10,500
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


