Question: CompTIA Linux+ Guide to Linux Certification |(4th Edition) Chapter 5, Problem 7P Bookmark Show all steps ON Post Answer homew Problemm Ente These projects should
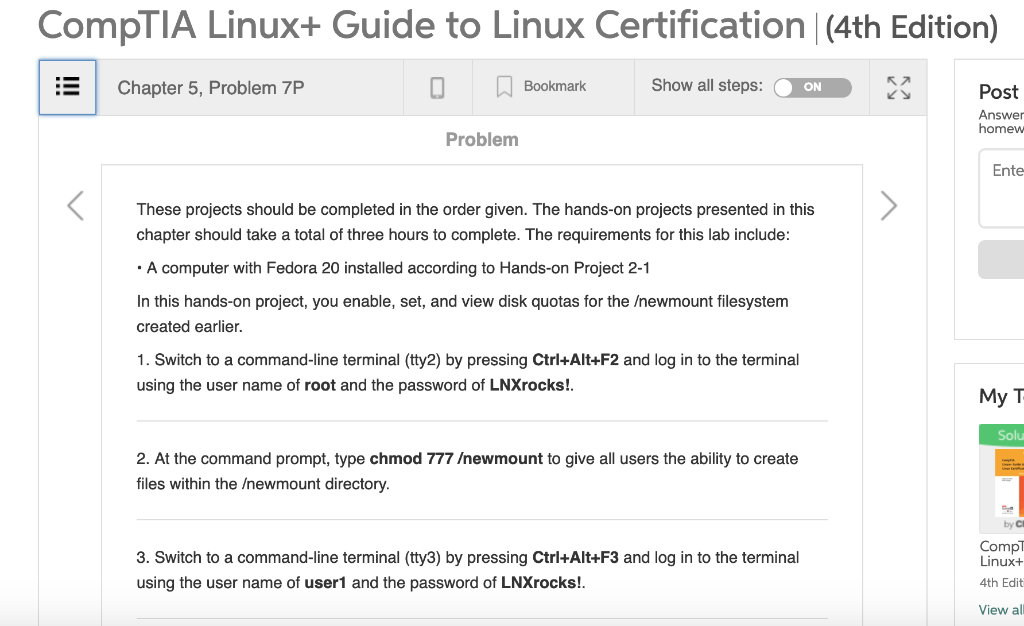
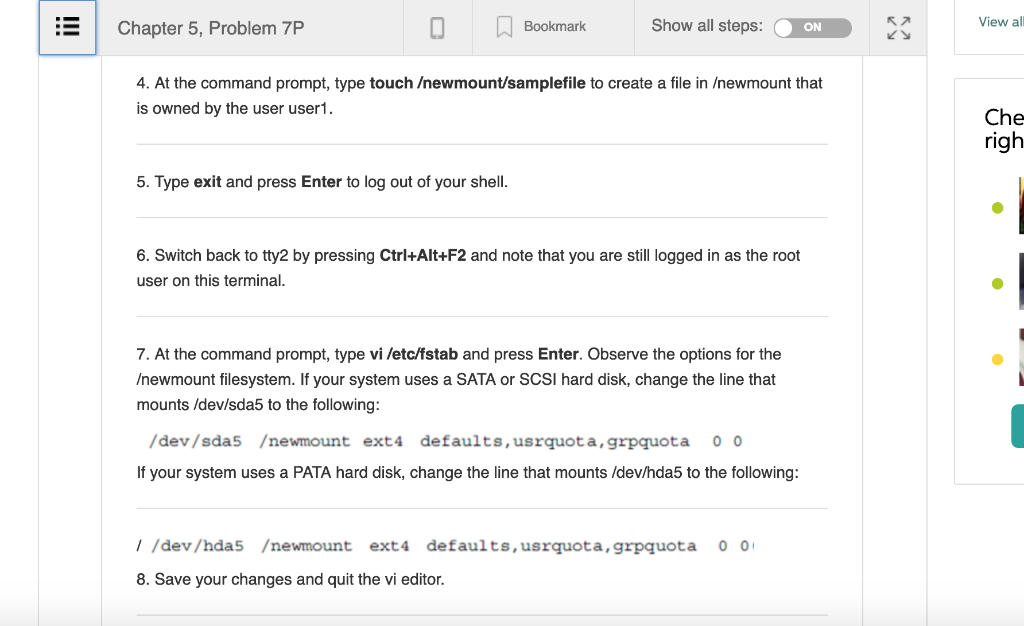
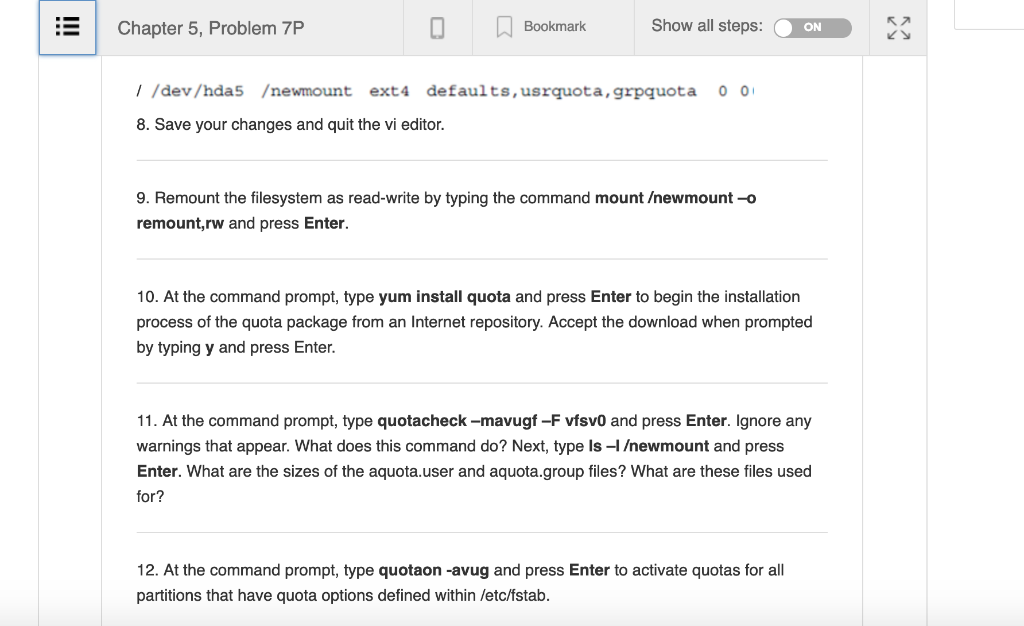
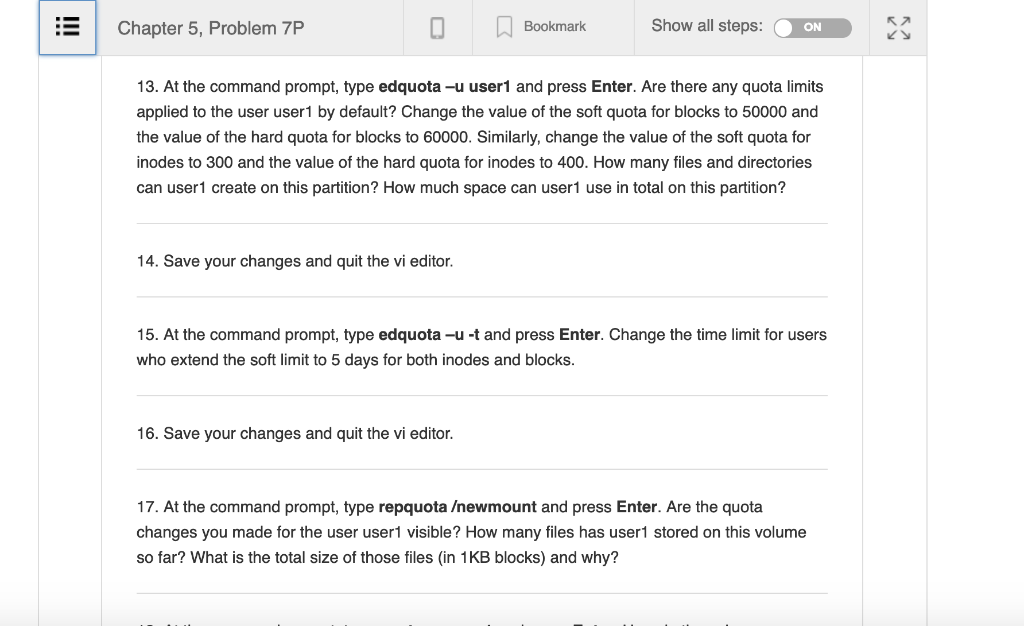
CompTIA Linux+ Guide to Linux Certification |(4th Edition) Chapter 5, Problem 7P Bookmark Show all steps ON Post Answer homew Problemm Ente These projects should be completed in the order given. The hands-on projects presented in this chapter should take a total of three hours to complete. The requirements for this lab include A computer with Fedora 20 installed according to Hands-on Project 2-1 In this hands-on project, you enable, set, and view disk quotas for the ewmount filesystem created earlier 1. Switch to a command-line terminal (tty2) by pressing Ctrl+Alt+F2 and log in to the terminal using the user name of root and the password of LNXrocks! My T Solu 2. At the command prompt, type chmod 777 ewmount to give all users the ability to create files within the ewmount directory. by Cl Compl 3. Switch to a command-line terminal (tty3) by pressing Ctri+Alt+F3 and log in to the terminal using the user name of user1 and the password of LNXrocks! Linux+ 4th Edit View all Chapter 5, Problem 7P K, View al Bookmark Show all steps: N 4. At the command prompt, type touchewmount/samplefile to create a file in ewmount that is owned by the user user Che righ 5. Type exit and press Enter to log out of your shell. 6. Switch back to tty2 by pressing Ctrl+Alt+F2 and note that you are still logged in as the root user on this terminal. 7. At the command prompt, type vi /etc/fstab and press Enter. Observe the options for the ewmount filesystem. If your system uses a SATA or SCSI hard disk, change the line that mounts /dev/sda5 to the following: /dev/sda5 ewmount ext4 defaults, usrquota, grpquota If your system uses a PATA hard disk, change the line that mounts /dev/hda5 to the following: / /dev/hda5 ewmount ext4 defaults,usrquota,grpquota o 0 8. Save your changes and quit the vi editor. Chapter 5, Problem 7P BookmarkShow all steps: ON / /dev/hda5 ewmount ext4 defaults,usrquota, grpquota 8. Save your changes and quit the vi editor. 9. Remount the filesystem as read-write by typing the command mount ewmount-o remount,rw and press Enter. 10. At the command prompt, type yum install quota and press Enter to begin the installation process of the quota package from an Internet repository. Accept the download when prompted by typing y and press Enter. 11. At the command prompt, type quotacheck-mavugf -F vfsvO and press Enter. Ignore any warnings that appear. What does this command do? Next, type Is - ewmount and press Enter. What are the sizes of the aquota.user and aquota.group files? What are these files used for? 12. At the command prompt, type quotaon -avug and press Enter to activate quotas for all partitions that have quota options defined within /etc/fstab R7 Chapter 5, Problem 7P Show all steps: Bookmark ON 13. At the command prompt, type edquota-u user1 and press Enter. Are there any quota limits applied to the user user1 by default? Change the value of the soft quota for blocks to 50000 and the value of the hard quota for blocks to 60000. Similarly, change the value of the soft quota for inodes to 300 and the value of the hard quota for inodes to 400. How many files and directories can user1 create on this partition? How much space can user1 use in total on this partition? 14. Save your changes and quit the vi editor. 5. At the command prompt, type edquota -u -t and press Enter. Change the time limit for users who extend the soft limit to 5 days for both inodes and blocks. 16. Save your changes and quit the vi editor. 17. At the command prompt, type repquota ewmount and press Enter. Are the quota changes you made for the user user1 visible? How many files has user1 stored on this volume so far? What is the total size of those files (in 1KB blocks) and why? Chapter 5, Problem 7P BookmarkShow all steps: ON 15. At the command prompt, type edquota-u -t and press Enter. Change the time limit for users who extend the soft limit to 5 days for both inodes and blocks 16. Save your changes and quit the vi editor. 17. At the command prompt, type repquota ewmount and press Enter. Are the quota changes you made for the user user1 visible? How many files has user1 stored on this volume so far? What is the total size of those files (in 1KB blocks) and why? 18. At the command prompt, type quota -u userl and press Enter. How do the values compare with those from the previous step? 19. Type exit and press Enter to log out of your shell. Step-by-step solution CompTIA Linux+ Guide to Linux Certification |(4th Edition) Chapter 5, Problem 7P Bookmark Show all steps ON Post Answer homew Problemm Ente These projects should be completed in the order given. The hands-on projects presented in this chapter should take a total of three hours to complete. The requirements for this lab include A computer with Fedora 20 installed according to Hands-on Project 2-1 In this hands-on project, you enable, set, and view disk quotas for the ewmount filesystem created earlier 1. Switch to a command-line terminal (tty2) by pressing Ctrl+Alt+F2 and log in to the terminal using the user name of root and the password of LNXrocks! My T Solu 2. At the command prompt, type chmod 777 ewmount to give all users the ability to create files within the ewmount directory. by Cl Compl 3. Switch to a command-line terminal (tty3) by pressing Ctri+Alt+F3 and log in to the terminal using the user name of user1 and the password of LNXrocks! Linux+ 4th Edit View all Chapter 5, Problem 7P K, View al Bookmark Show all steps: N 4. At the command prompt, type touchewmount/samplefile to create a file in ewmount that is owned by the user user Che righ 5. Type exit and press Enter to log out of your shell. 6. Switch back to tty2 by pressing Ctrl+Alt+F2 and note that you are still logged in as the root user on this terminal. 7. At the command prompt, type vi /etc/fstab and press Enter. Observe the options for the ewmount filesystem. If your system uses a SATA or SCSI hard disk, change the line that mounts /dev/sda5 to the following: /dev/sda5 ewmount ext4 defaults, usrquota, grpquota If your system uses a PATA hard disk, change the line that mounts /dev/hda5 to the following: / /dev/hda5 ewmount ext4 defaults,usrquota,grpquota o 0 8. Save your changes and quit the vi editor. Chapter 5, Problem 7P BookmarkShow all steps: ON / /dev/hda5 ewmount ext4 defaults,usrquota, grpquota 8. Save your changes and quit the vi editor. 9. Remount the filesystem as read-write by typing the command mount ewmount-o remount,rw and press Enter. 10. At the command prompt, type yum install quota and press Enter to begin the installation process of the quota package from an Internet repository. Accept the download when prompted by typing y and press Enter. 11. At the command prompt, type quotacheck-mavugf -F vfsvO and press Enter. Ignore any warnings that appear. What does this command do? Next, type Is - ewmount and press Enter. What are the sizes of the aquota.user and aquota.group files? What are these files used for? 12. At the command prompt, type quotaon -avug and press Enter to activate quotas for all partitions that have quota options defined within /etc/fstab R7 Chapter 5, Problem 7P Show all steps: Bookmark ON 13. At the command prompt, type edquota-u user1 and press Enter. Are there any quota limits applied to the user user1 by default? Change the value of the soft quota for blocks to 50000 and the value of the hard quota for blocks to 60000. Similarly, change the value of the soft quota for inodes to 300 and the value of the hard quota for inodes to 400. How many files and directories can user1 create on this partition? How much space can user1 use in total on this partition? 14. Save your changes and quit the vi editor. 5. At the command prompt, type edquota -u -t and press Enter. Change the time limit for users who extend the soft limit to 5 days for both inodes and blocks. 16. Save your changes and quit the vi editor. 17. At the command prompt, type repquota ewmount and press Enter. Are the quota changes you made for the user user1 visible? How many files has user1 stored on this volume so far? What is the total size of those files (in 1KB blocks) and why? Chapter 5, Problem 7P BookmarkShow all steps: ON 15. At the command prompt, type edquota-u -t and press Enter. Change the time limit for users who extend the soft limit to 5 days for both inodes and blocks 16. Save your changes and quit the vi editor. 17. At the command prompt, type repquota ewmount and press Enter. Are the quota changes you made for the user user1 visible? How many files has user1 stored on this volume so far? What is the total size of those files (in 1KB blocks) and why? 18. At the command prompt, type quota -u userl and press Enter. How do the values compare with those from the previous step? 19. Type exit and press Enter to log out of your shell. Step-by-step solution
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


