Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Compute P(X) using the binomial probability formula. Then determine whether the normal distribution can be used to estimate this probability. If so, approximate P(X)
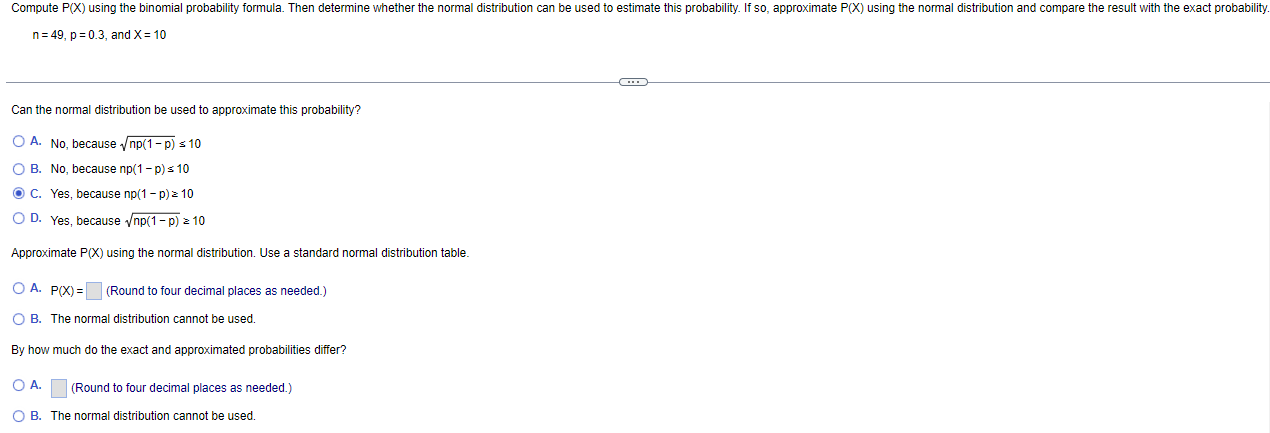
Compute P(X) using the binomial probability formula. Then determine whether the normal distribution can be used to estimate this probability. If so, approximate P(X) using the normal distribution and compare the result with the exact probability. n=49, p=0.3, and X = 10 Can the normal distribution be used to approximate this probability? OA. No, because np(1 - p) = 10 B. No, because np(1 - p) 10 C. Yes, because np(1 - p) 10 OD. Yes, because np(1 - p) 10 Approximate P(X) using the normal distribution. Use a standard normal distribution table. OA. P(X)= (Round to four decimal places as needed.) OB. The normal distribution cannot be used. By how much do the exact and approximated probabilities differ? A. (Round to four decimal places as needed.) B. The normal distribution cannot be used.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


