Question
Computing the area of overlapping objects is a common and important task. Examples include detecting collisions of objects in computer games or scientific simulations, computing
Computing the area of overlapping objects is a common and important task. Examples include detecting collisions of objects in computer games or scientific simulations, computing the area of a blueprint floorplan made up of overlapping objects, and displaying the visible parts of overlapping windows on a computer screen.
In this homework you will implement a Rectangle class that stores the coordinates of the upper left corner and the height and width of the rectangle. In addition, your Rectangle class will have methods that compute the area of the union and intersections of up to three rectangles. Below are some useful equations for this assignment. Notice that the positive direction of the y-coordinate is down.
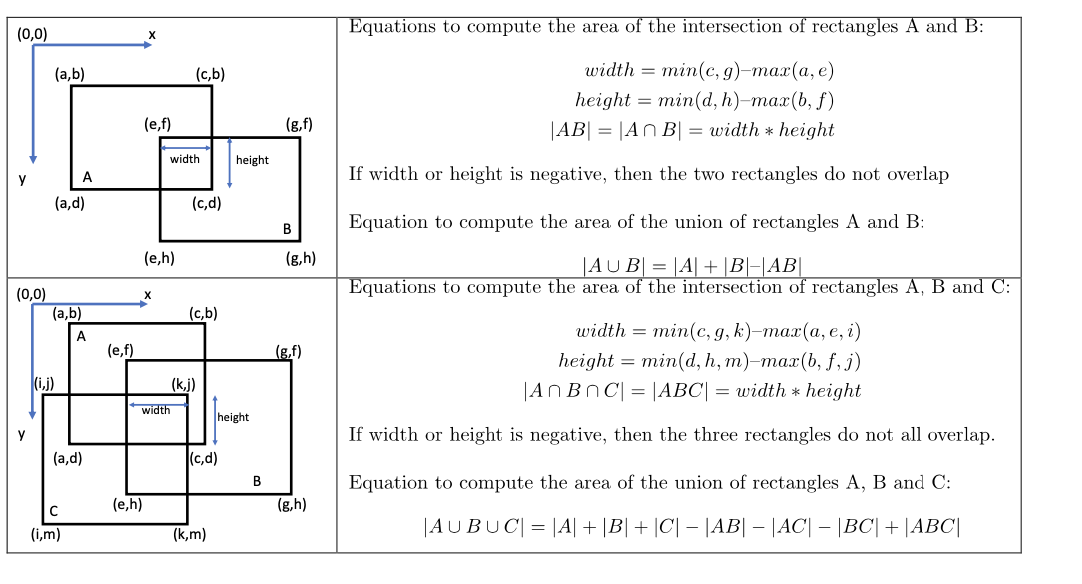
Notes:
-
All your Rectangle methods must have a comment block that describes the inputs, outputs and a
description of the function. This can be in Rectangle.h or Rectangle.cpp.
-
Please remember to pass objects to functions by constant reference.
-
You may need to add #include
to use the min and max commands.
Part 1. (60pts) 1. Define a Rectangle class in the file Rectangle.h and store the implementation of the Rectangle class in
Rectangle.cpp.
-
Define Rectangle class private variables m_x and m_y to store the upper-left coordinates of the Rectangle object. Define m_x and m_y to be doubles.
-
Similarly, define private variables m_h and m_w to store the height and width of the Rectangle object, respectively. These variables should also be doubles.
-
Define and implement public getter and setter Rectangle class methods for m_x, m_y, m_h and m_w. Call these functions getX, setX, etc. Note that the setter functions for your width and height variables should prevent the user from assigning negative values for m_h and m_w.
-
Define and implement a public function print in the Rectangle class that prints the values of m_x, m_y, m_h and m_w. This function should make it clear which values correspond to which variables, i.e., please do not just print four numbers to the screen.
-
Define and implement a constructor for the Rectangle class with four inputs, i.e., one for each member variable. This constructor, Rectangle, should initialize all member variables to valid values, i.e., this constructor should prevent assigning m_h and m_w to negative values. Provide default values for each input. Define this constructor to be explicit.
-
Define and implement a public function called area in the Rectangle class that returns the area of the rectangle.
-
Define and implement a public function called intersectArea in the Rectangle class that takes a rectangle object as input and returns the area of the intersection of the two rectangles.
-
Define and implement a public function called unionArea in the Rectangle class that takes a rectangle object as input and returns the area of the union of the two rectangles.
-
Define and implement a public function called intersectArea in the Rectangle class that takes two rectangle objects as input and returns the area of the intersection of the three rectangles. (Note: This is an example of function overloading.)
-
Define and implement a public function called unionArea in the Rectangle class that takes two rectangle objects as input and returns the area of the union of the three rectangles. (Note: This is an example of function overloading.)
Part 2. (20pts)
-
Write and document a main program to test your Rectangle class. The main program should hard code the creation of Rectangle objects and calls to the Rectangle methods. Remember to print both the expected output and the actual output. See hw2 for reference.
-
Write enough test cases to make sure all your functions work. For example, when testing your constructor make sure that you can properly create an object with no inputs, with 1-4 inputs, and with invalid inputs.
-
Methods you need to test are: the constructor, setH, setW, both intersectArea and both unionArea. There is no need to specifically test the print, area, getters, setX and setY methods since they will be tested implicitly when you test the other methods.
Part 3. (20pts)
Add the following functionality to your main program after the code you write for part 2 above.
-
Create a file that contains the values for multiple rectangles. The format of the file should be as follows. Each line should correspond to a different rectangle. Each line should list the x, y, h and w values for the
rectangle separated by spaces.
-
Write code to read the rectangles from the file and store them in a vector of Rectangles.
-
Write a loop to print out all the rectangles that were read into the program to make sure you correctly read
the data from the file.
-
Compute and print to the screen the area of the union and intersection of rectangles 1, 2, and 3, then
rectangles 2, 3, and 4, etc. until you reach the end of the vector.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


