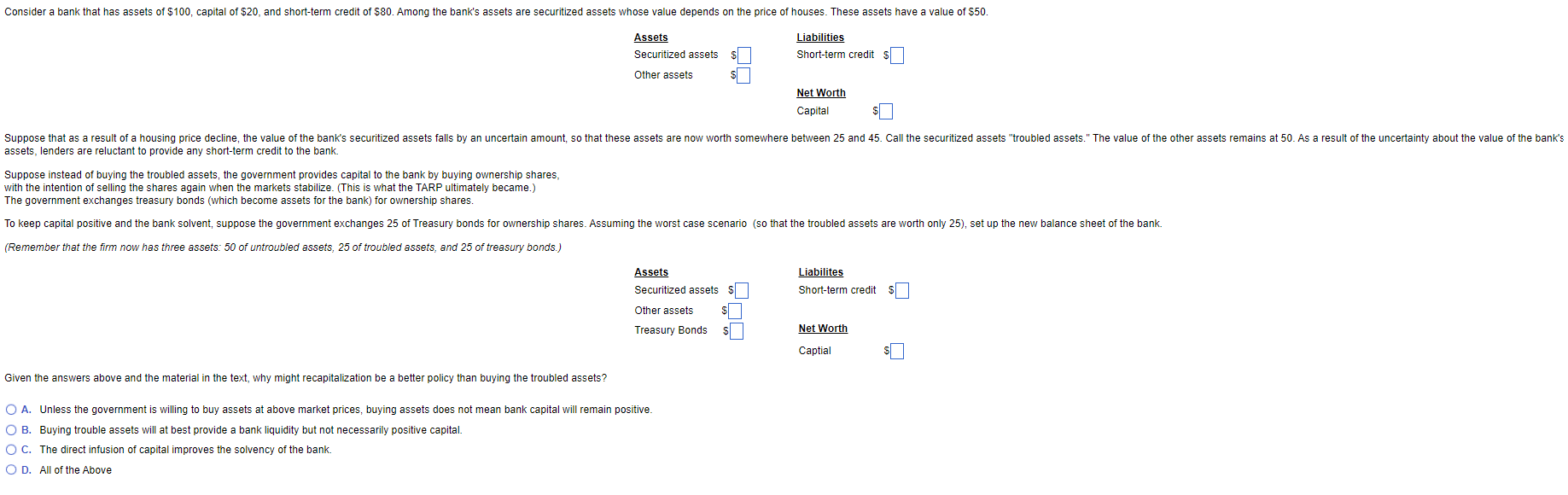
Consider a bank that has assets of $100, capital of $20, and short-term credit of $80. Among the bank's assets are securitized assets whose value depends on the price of houses. These assets have a value of $50. Assets Securitized assets Other assets Liabilities Short-term credit Net Worth Capital S Suppose that as a result of a housing price decline, the value of the bank's securitized assets falls by an uncertain amount, so that these assets are now worth somewhere between 25 and 45. Call the securitized assets "troubled assets." The value of the other assets remains at 50. As a result of the uncertainty about the value of the bank's assets, lenders are reluctant to provide any short-term credit to the bank. Suppose instead of buying the troubled assets, the government provides capital to the bank by buying ownership shares, with the intention of selling the shares again when the markets stabilize. (This is what the TARP ultimately became.) The government exchanges treasury bonds (which become assets for the bank) for ownership shares. To keep capital positive and the bank solvent, suppose the government exchanges 25 of Treasury bonds for ownership shares. Assuming the worst case scenario (so that the troubled assets are worth only 25), set up the new balance sheet of the bank. (Remember that the firm now has three assets: 50 of untroubled assets, 25 of troubled assets, and 25 of treasury bonds.) Liabilites Short-term credit S Assets Securitized assets $ Other assets $ Treasury Bonds $ Net Worth Captial Given the answers above and the material in the text, why might recapitalization be a better policy than buying the troubled assets? O A. Unless the government is willing to buy assets at above market prices, buying assets does not mean bank capital will remain positive. O B. Buying trouble assets will at best provide a bank liquidity but not necessarily positive capital. O C. The direct infusion of capital improves the solvency of the bank. O D. All of the Above Consider a bank that has assets of $100, capital of $20, and short-term credit of $80. Among the bank's assets are securitized assets whose value depends on the price of houses. These assets have a value of $50. Assets Securitized assets Other assets Liabilities Short-term credit Net Worth Capital S Suppose that as a result of a housing price decline, the value of the bank's securitized assets falls by an uncertain amount, so that these assets are now worth somewhere between 25 and 45. Call the securitized assets "troubled assets." The value of the other assets remains at 50. As a result of the uncertainty about the value of the bank's assets, lenders are reluctant to provide any short-term credit to the bank. Suppose instead of buying the troubled assets, the government provides capital to the bank by buying ownership shares, with the intention of selling the shares again when the markets stabilize. (This is what the TARP ultimately became.) The government exchanges treasury bonds (which become assets for the bank) for ownership shares. To keep capital positive and the bank solvent, suppose the government exchanges 25 of Treasury bonds for ownership shares. Assuming the worst case scenario (so that the troubled assets are worth only 25), set up the new balance sheet of the bank. (Remember that the firm now has three assets: 50 of untroubled assets, 25 of troubled assets, and 25 of treasury bonds.) Liabilites Short-term credit S Assets Securitized assets $ Other assets $ Treasury Bonds $ Net Worth Captial Given the answers above and the material in the text, why might recapitalization be a better policy than buying the troubled assets? O A. Unless the government is willing to buy assets at above market prices, buying assets does not mean bank capital will remain positive. O B. Buying trouble assets will at best provide a bank liquidity but not necessarily positive capital. O C. The direct infusion of capital improves the solvency of the bank. O D. All of the Above







