
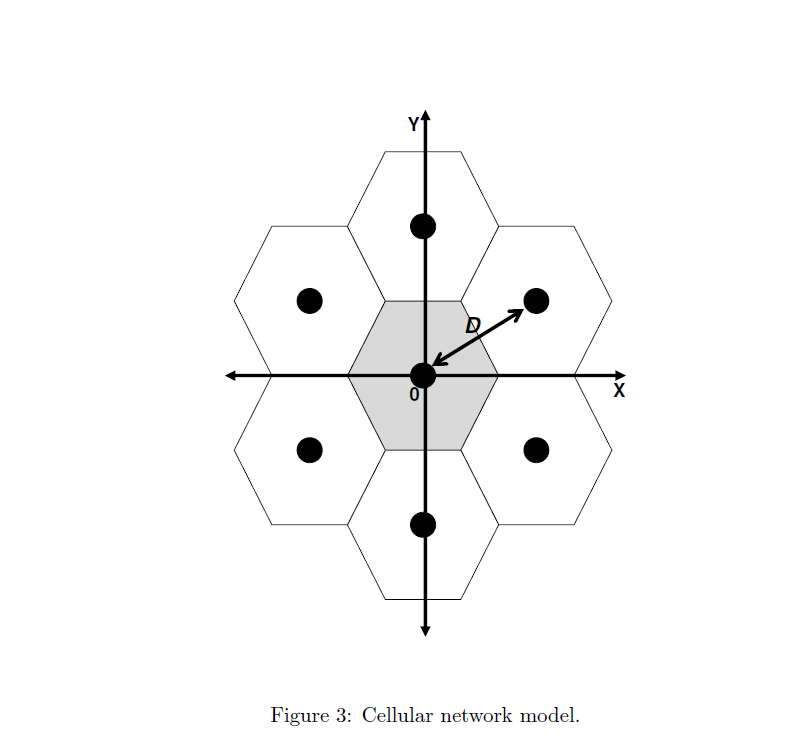
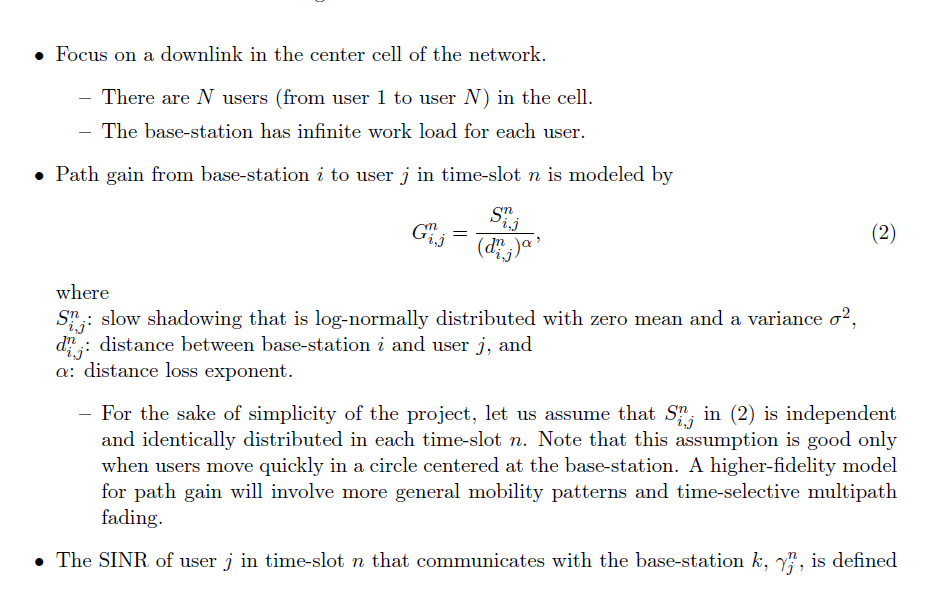
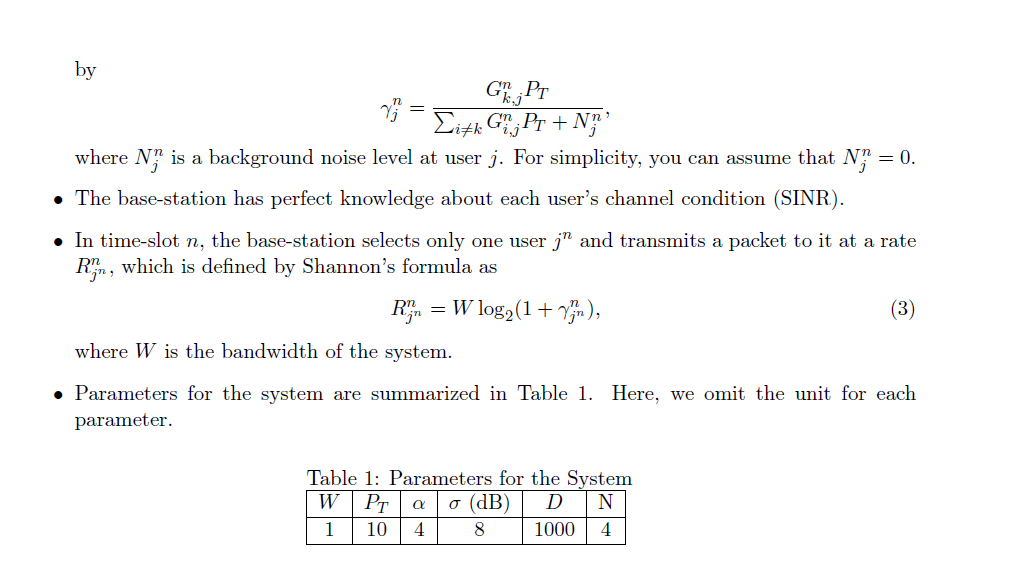
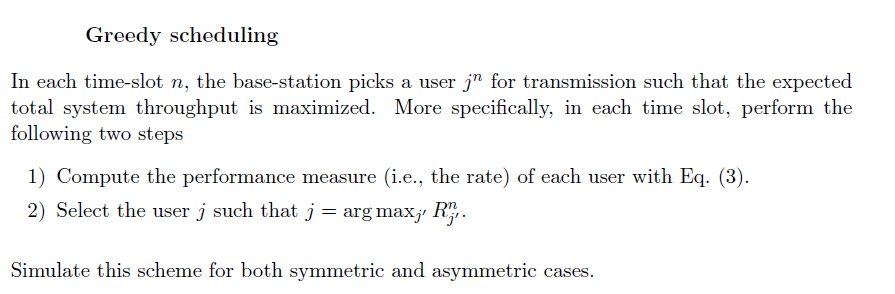
- Consider a cellular network in Figure 3. - A base-station is located at the center of each cell. - Distance between base-stations is D. - We will be interested in the center-cell and take the power from other cells as interference. - The system is time-slotted. - Each base-station transmits at the power level PT. Figure 3: Cellular network model. - Focus on a downlink in the center cell of the network. - There are N users (from user 1 to user N ) in the cell. - The base-station has infinite work load for each user. - Path gain from base-station i to user j in time-slot n is modeled by Gi,jn=(di,jn)Si,jn, where Si,jn : slow shadowing that is log-normally distributed with zero mean and a variance 2, di,jn : distance between base-station i and user j, and : distance loss exponent. - For the sake of simplicity of the project, let us assume that Si,jn in (2) is independent and identically distributed in each time-slot n. Note that this assumption is good only when users move quickly in a circle centered at the base-station. A higher-fidelity model for path gain will involve more general mobility patterns and time-selective multipath fading. - The SINR of user j in time-slot n that communicates with the base-station k,jn, is defined by jn=i=kGi,jnPT+NjnGk,jnPT, where Njn is a background noise level at user j. For simplicity, you can assume that Njn=0. - The base-station has perfect knowledge about each user's channel condition (SINR). - In time-slot n, the base-station selects only one user jn and transmits a packet to it at a rate Rjnn, which is defined by Shannon's formula as Rjnn=Wlog2(1+jnn), where W is the bandwidth of the system. - Parameters for the system are summarized in Table 1. Here, we omit the unit for each parameter. Table 1: Parameters for the Svstem Greedy scheduling In each time-slot n, the base-station picks a user jn for transmission such that the expected total system throughput is maximized. More specifically, in each time slot, perform the following two steps 1) Compute the performance measure (i.e., the rate) of each user with Eq. (3). 2) Select the user j such that j=argmaxjRjn. Simulate this scheme for both symmetric and asymmetric cases











