Question
(a) Consider a plaintext space M = {M1,M2,M3,M4}, with corresponding ciphertext space C = {C1,C2,C3,C4}. Suppose that each plaintext and each ciphertext is equally likely,
(a) Consider a plaintext space M = {M1,M2,M3,M4}, with corresponding ciphertext space C = {C1,C2,C3,C4}. Suppose that each plaintext and each ciphertext is equally likely, i.e. p(Mi) = p(Cj) = 1/4 for 1 ≤ i,j ≤ 4. Now suppose that each ciphertext Cj narrows down the choice of corresponding plaintext Mi to two of the four possibilities as follows: C1: M1 or M2 C2: M3 or M4 C3: M2 or M3 C4: M1 or M4 3 Compute H(M|C).
(b) Suppose a cryptosystem provides perfect secrecy, and p(M) > 0 for all M ∈ M. Prove that H(M|C) = H(M).
(c) Does the example of part (a) provide perfect secrecy? Explain your answer?
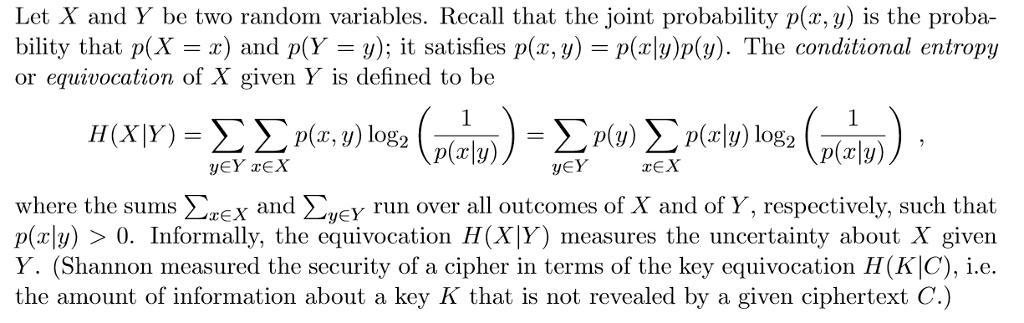
Let X and Y be two random variables. Recall that the joint probability p(x, y) is the proba- bility that p(X = x) and p(Y = y); it satisfies p(x, y) = p(r|y)p(y). The conditional entropy or equivocation of X given Y is defined to be (X ) - (, ) log YY xEX yY xEX where the sums ErEx and uey run over all outcomes of X and of Y, respectively, such that p(x|y) > 0. Informally, the equivocation H(X|Y) measures the uncertainty about X given Y. (Shannon measured the security of a cipher in terms of the key equivocation H(K|C), i.e. the amount of information about a key K that is not revealed by a given ciphertext C.)
Step by Step Solution
3.37 Rating (172 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
first calculate pM1C1 pM2C1 pM3C2 and pM4C2 We know that pM1C1 pM2C1 12 ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Document Format ( 2 attachments)
635e4022c826b_183271.pdf
180 KBs PDF File
635e4022c826b_183271.docx
120 KBs Word File
Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


