Question: Consider a version of a binary search tree (BST) for sorted maps that stores additional information as data members of each node w of

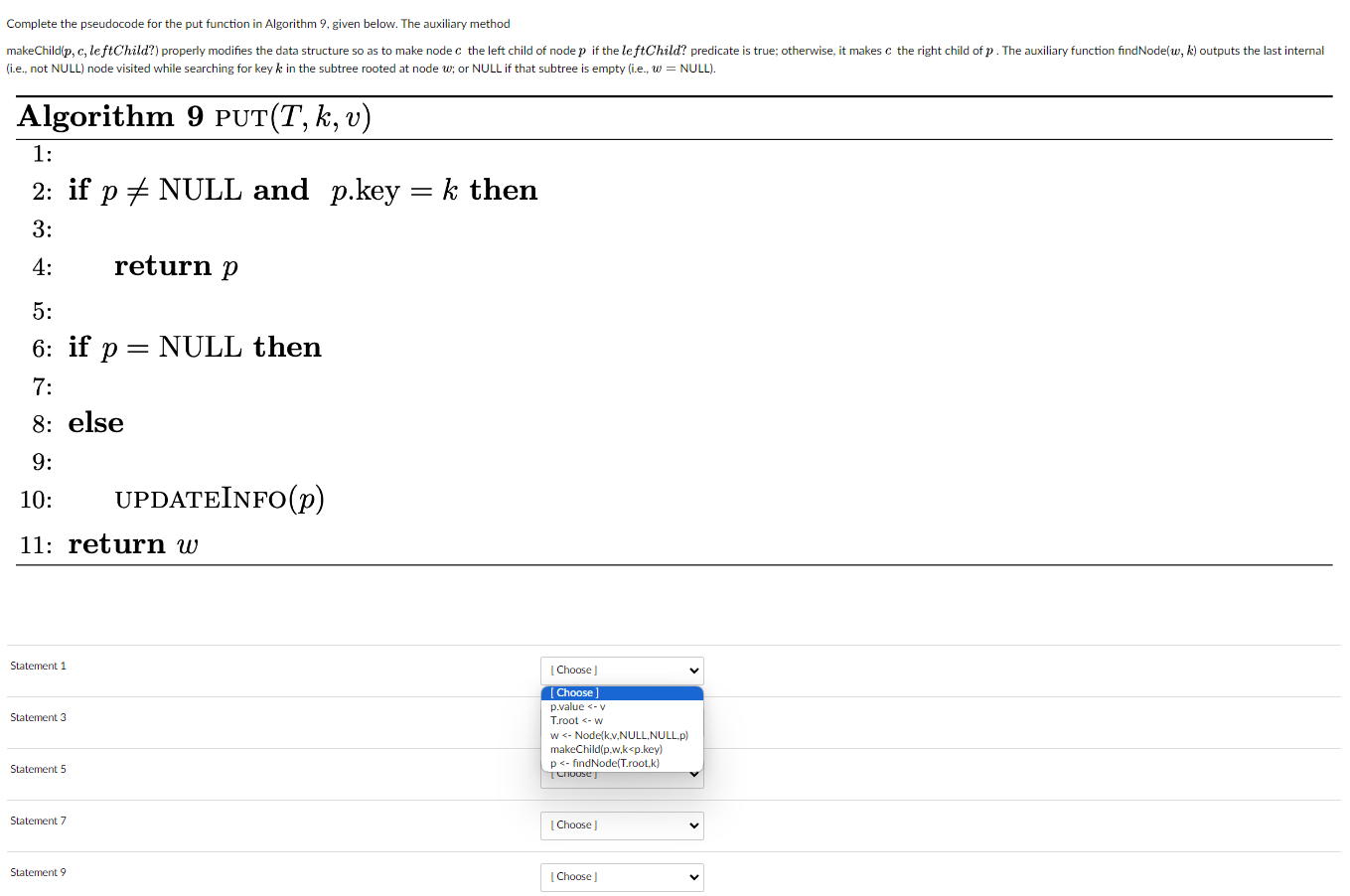
Consider a version of a binary search tree (BST) for sorted maps that stores additional information as data members of each node w of the tree to account for the smallest and largest keys in the subtree rooted at w. Suppose that we can access this information using w. min, for the smallest integer key, and w. max, for the largest. Algorithm 6 (Node), given below, provides the pseudocode for the constructor of a node in a binary tree with the additional information. Algorithm 6 NODE(k, v, left, right, parent) 1: w new node 2: w.key k 3: w.value v 4: w.left left 5: w.right right 6: w.parent parent 7: w.min k 8: w.max k 9: return w Complete the pseudocode for the put function in Algorithm 9, given below. The auxiliary method makeChild(p, c, leftChild?) properly modifies the data structure so as to make node c the left child of node p if the leftChild? predicate is true; otherwise, it makes c the right child of p. The auxiliary function findNode(w, k) outputs the last internal (i.e., not NULL) node visited while searching for keyk in the subtree rooted at node w; or NULL if that subtree is empty (i.e., w = NULL). Algorithm 9 PUT(T, k, v) 1: 2: if p = NULL and p.key 3: 4: 5: 6: if p = p = NULL then 7: 8: else 9: 10: UPDATEINFO(p) 11: return w Statement 1 Statement 3 Statement 5 Statement 7 return p Statement 9 = k then [Choose ] [Choose] p.value
Step by Step Solution
3.31 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


